Pain in an inguinal hernia
introduction

As an inguinal hernia (also inguinal hernia or Inguinal hernia) refers to the displacement of parts of the so-called inguinal canal through the abdominal wall to the outside. A so-called hernial sac forms, which is filled with the contents of the hernia and the wall of which is covered with peritoneum.
Inguinal hernias are the most common form of hernia in both women and men. However, the majority of inguinal hernias occur in men.
Swelling and pain in the groin area can be a major symptom of an inguinal hernia, but there can be other causes as well. Often an existing hernia is accompanied by no or only very little pain in the groin region. In the event of severe, persistent or recurring pain in the groin region, a doctor should be consulted to rule out a hernia or other important causes of the pain.
Symptoms
For the layman is a Inguinal hernia not always recognizable as such. Often one occurs swelling in the area of the bar. This can also be done in the male Scrotum, with the woman in the Labiato emerge. A swelling can, however, be completely absent or in the Idle state not be recognizable. Pain in the groin can occur, but is not always present, so a hernia cannot be ruled out in the absence of pain.
However, recurring, pulling pain in the groin area may indicate an inguinal hernia, even if one There is no swelling, or is not recognized by the layman.
The pain from an inguinal hernia does not necessarily have to be in the area of the groin itself. So is one too Radiation of pain in the area around the groin is possible. Pain can therefore also develop in the area of the thigh, the lower abdomen, the Testicle, or the female reproductive organs. In some cases, the local assignment of the pain is not straightforward. If there is pain, it is usually called pulling felt.
Even a small hernia can lead to severe pain lead, but these can be completely absent even with a large hernia. If there is pain, it is particularly noticeable when standing and during activities that increase the pressure in the abdomen. Thus, pain in the groin area, for example when defecating, when to cough, or at Lifting loads represent an indication of an inguinal hernia.
It is important to take pain seriously and its Have a doctor identify the cause. A painless swelling in the groin region, in the area of the scrotum or the labia, should also be promptly assessed by a doctor.
Particular attention should be given to severe and sudden pain in the groin area or its Surroundings (also belly) are given as this reference to a Entrapment (Incarceration) of the contents of the fracture. If this is the case, it is imperative that you hurry, since it is one emergency that requires immediate surgery. Otherwise, tissue may die.
Inguinal hernia and pain when walking
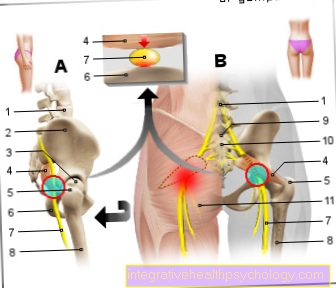
In the case of a hernia, part of the abdominal organs in a hernial sac turns inside out through a muscular weak point in the groin area (Transition from belly to Thigh) outward.
However, this does not have to be accompanied by pain. In many of the mainly male patients, an inguinal hernia remains unnoticed for a longer period of time, because the hernial sac can often shift itself back into the abdomen.
However, if there is an increase in pressure in the abdomen (e.g. by pressing while bowel movement, to cough, Sneeze or at Lifting heavy objects), it is possible that a small, plum-sized bulge appears in the area of the groin. Some patients then describe a pulling pain up to the scrotum or the labia majora.
Running is usually not restricted by an inguinal hernia. With this type of movement, there is usually no particularly strong pressure in the abdomen and therefore not on the hernial sac. However, if a relaxed walk is already causing severe pain, it is advisable to consult a doctor, as there is a risk that part of the hernial sac has become trapped. This is one of the worst complications of an inguinal hernia, because a sustained reduced blood supply can lead to the death of the stuck intestine and must be operated on immediately (see also: Inguinal hernia surgery) become. Often times, the pain goes with an entrapment nausea and Vomit as well as with fever.
Pain when sitting
An inguinal hernia does not necessarily have to cause pain while sitting.
Many patients describe a completely normal, unimpaired everyday life despite a diagnosed hernia. However, it can also be different. When sitting, bend your hips and bring your thighs a little closer to your stomach. This reduction in the angle between the abdomen and thighs leads to a kind of folding of the groin area.
In the case of hernias, which can be pushed back into the abdomen without any problems, sitting doesn't cause any problems either. In this case, the hernial sac usually moves back into the abdomen while sitting. However, if the hernial sac is permanently outside the abdominal cavity, the folding of the groin area when sitting can cause a kind of entrapment. This can feel like a foreign body sensation, but it can also cause ischemic pain. An extension of the hip (e.g. by getting up or lying down) should in any case bring relief from the symptoms.
Pain after the operation
In most cases, an inguinal hernia is successfully treated with an operative mesh insert to reinforce the abdominal wall. This can be done by a Laparoscopy (laparoscopy) as well as open surgery.
Depending on the surgical procedure, the size of the surgical scar and thus the pain that may be associated with it vary. There is constant movement in the abdominal wall area. With almost every movement there is tension or stretching of the abdominal skin and thus irritation of the surgical scars, which some patients after a Inguinal hernia surgery complain of pain.
To alleviate this pain, it is important to keep bed rest as much as possible and thus give the tissue the opportunity to heal optimally. Another possible cause of pain after inguinal hernia surgery can be injury to vascular or nerve cords.
In most inguinal hernias, the hernial sac with intestinal parts migrates through the inguinal canal and only bulges behind it through the abdominal wall. This is called an indirect hernia. The inguinal canal contains the spermatic cord in the male and the cervical ligament in the female uterus and multiple blood vessels and nerve cords. If these structures are injured during the surgical repositioning of the hernial sac, severe pain can develop after the operation. An injury to the peritoneum by the surgeon could cause similar symptoms. However, these are rather rare complications.
diagnosis
In the event of pain in the groin region that makes the doctor think of an inguinal hernia, this is initially treated in medical interview after possible Trigger factors ask. As such, for example, are violent to cough or that Lifting heavy loads to call. However, patients cannot always remember such specific events.
The patient is also asked about his or her pain. Drawing pains In the area of the groin and its surroundings, the doctor can give an indication of a possibly existing Inguinal hernia give. However, the information on whether there is pain can only be used as a supplement to the diagnosis.
Above all, a detailed physical examination be performed. This includes the assessment of a possibly visible swelling, just like that Scan the groin region, as well as in the male Scrotum and with the wife of Labia. The examination is usually carried out while standing, as it is easier to feel an existing hernia. In addition, an examination lying down can also provide further information.
The doctor may also refer to the patient to cough or Press ask because by the Pressure increase In the abdomen, an inguinal hernia that cannot initially be felt often emerges and can be recognized. If there is a visible or palpable swelling, the doctor will try the Push back the fraction content (so-called reduction). This measure is used Relocation and evaluation of the fracture and should only be performed by a doctor in order to avoid entrapment of the fracture by the layperson.
As a rule, the diagnosis or the exclusion of an inguinal hernia is possible through the physical examination alone. In unclear cases or for more precise determination of the fraction content, the Ultrasound examination the groin region.
Where does the pain occur
When a Inguinal hernia pain causes, these are mostly pulling pains.
The pain can be transmitted from the affected groin side to the labia majora in women or into the scrotum in men. A transmission of pain to other parts of the body has not yet been described. In the event of an entrapment, so-called ischemic pain can occur. An organ that becomes ischemic means an interruption of the blood supply and thus a lack of oxygen, which can ultimately lead to the death of the tissue. Ischemia pain is very uncomfortable and can spread over a large area around the underserved area.
Causes of an inguinal hernia
An inguinal hernia can basically innate be, or only in the course of life arise (so-called acquired hernia). The acquired inguinal hernia is caused by a Connective tissue weakness the abdominal wall in the area of the groin. Increased pressure in the abdominal cavity has a positive effect on the development. One leading to an inguinal hernia Pressure increase can for example by to cough, Lifting heavy loads, or defecating (especially with constipation with strong pressing). The groin region is a very sensitive region. This fact is due to a multitude of annoy justified in this area. If pain occurs with the hernia, it is due to local irritation of these nerves.
therapy
Becomes a Inguinal hernia found the only way of healing is in the surgery. The aim of this is to either pass through the corresponding weak point of the abdominal wall Seams, or by introducing an alien Networkto stabilize. Hernia ligaments are no longer used today because they pose the risk of entrapment of the break.
The operation can be performed at not pinched hernia planned by appointment. But should be a Entrapment that cannot be corrected by the doctor is one emergency surgery necessary to prevent tissue death.
Depending on the extent of the Pain can do this with light pain relievers be treated. Severe and sudden pain must necessarily lead to a doctor's visit, as this can indicate an entrapment of the hernia.
Depending on how long the Entrapment has already passed, the doctor will either try to fix it with their hands or decide to have surgery as soon as possible. If there is severe pain in this situation, it can be treated with painkillers.
forecast
The forecast of Inguinal hernia is generally good.
Of course, a distinction must be made here whether it is a uncomplicated hernia that is planned to be operated on, or one Emergency operation if the break is trapped. It is therefore all the more important to seek medical advice immediately if you suspect an entrapment, as this can significantly improve the prognosis.
Even after being successful surgery there is one, however Risk of recurrence of an inguinal hernia. Depending on the surgical method, this is stated as one to ten percent. Passed Pain, these usually regress after a successful operation. Unfortunately, pain persists in a small proportion of patients. Then the next steps and, if necessary, the sensible use of painkillers must be discussed with the doctor.
prophylaxis
Avoiding the pain that can occur with an inguinal hernia is basically only through the Avoiding the inguinal hernia even possible. Care should be taken not to take any action that would cause a increased pressure in the abdomen cause. This may prevent the occurrence of an inguinal hernia. No heavy loads should be lifted.
In addition, it can be useful at constipation with the doctor about suitable Laxative measures to speak to prevent excessive pressing. Nevertheless, these measures can unfortunately also result in an inguinal hernia not sure prevent it, since the nature of the Connective tissue the individual is responsible. Nevertheless, the measures mentioned should be observed as important support.