Attack of gout
introduction
The gout is a illness which on a Malfunction of the purine metabolism is due and in Spurts runs.
Patients who suffer from gout should consult a doctor promptly and initiate appropriate treatment, as this disease can lead to deposits of gout if the therapy is inadequate Uric acid crystals (so-called Urate) can result in various joints and tissues. It is precisely this urate storage that induces one over time resorption near the joint from Bone substance and various Cartilage changes.

In the long run, the function of the kidney as an excretory organ can also be significantly impaired. The consequence is often the development of renal insufficiency, which in the further course can lead to chronic renal insufficiency. While the damage to the kidneys progresses painlessly over a long period of time, the affected patients suffer from severe pain in the joints at an early stage. In general, a distinction is made between acute gout and the chronic form that develops after several attacks have occurred.
Gout attack - general
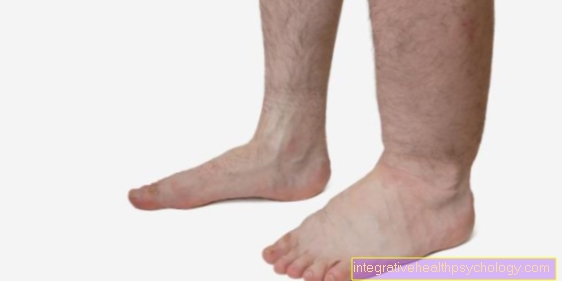
At a Attack of gout (acute gout) usually occurs acute occurrence severe pain in the affected joints. These joints react to contact stimuli with an intensification of pain. Visually, the areas affected by the poisoning attack are due to the appearance of severe redness and Swelling to recognize. In addition, a significant overheating determine. In addition to these locally limited symptoms, during an acute gout attack can also general disease symptomsthat is draining on the within the affected joints inflammatory processes are due.
The typical abnormalities of an acute gout attack include Inflammation symptoms how
- fever
- an increase in the concentration of white blood cells in serum (Leukocytosis)
In addition, most affected patients have one excessively elevated Uric acid level in the blood. However, since the increase in the uric acid concentration in the blood does not necessarily occur with every acute gout attack, a normal value is not an exclusion criterion for the presence of this disease. At appropriate treatment a gout attack can be quickly brought under control, but if therapy is neglected it can last for several days and severely restrict the patient concerned. During the gout attack you can numerous attacks occur both in their Duration, as well as in theirs intensity can increase.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a acute gout attack can be from patient to patient both in their intensity, as well as in theirs Duration differ.
Pain on the affected joints and in the area of the surrounding tissue, however, are typical symptoms of an acute gout attack. In addition, all of them can be found in the joints classic signs of inflammation prove. A joint affected by a gout attack increases in size swelling (tumor), has a characteristic Redness on (Rubor) and is in comparison to the neighboring, unaffected tissue overheated (Calor). Furthermore, the affected joints are in their natural function strong limited (Functio read) and send strong pain stimuli whose intensity increases when touched (Dolor). In addition, this results in the activation of the immune system triggered by the gout attack rise of the White blood cell count (white blood cells) in the serum.
Involvement of the joints
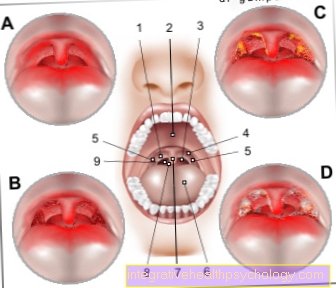
In principle, an acute attack of gout can manifest itself in almost any joint in the body. In addition, it should be noted that not all joints are affected during a gout attack.
The typical symptoms are usually limited to a few joints. Nevertheless, it can be observed that different joint regions are affected more frequently, whereas gout symptoms in other joints almost never occur.
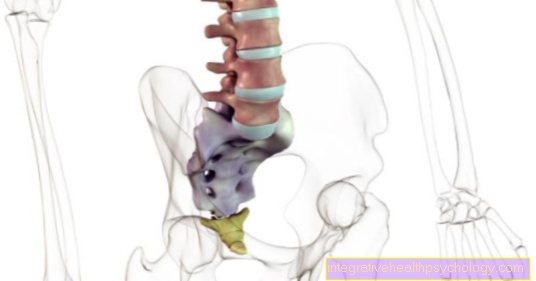
The hocks and joints of the toes are most commonly affected by gout attacks. There is a separate name for the occurrence of a gout attack on the big toe joint, the so-called podagra or foot gout.
Furthermore, many sufferers have gout symptoms in the knee joints. In the area of the upper extremities, the finger joints and wrists (chiragra) are most frequently affected.
For more information on this topic, the editors recommend the following article: Pain in the thumb joint and burning sensation in the knee
Gout attack diagnosis
Of the diagnostic evidence one Attack of gout is divided into different sections. Usually the extensive one already delivers Doctor-patient discussion, in which the patient explains the problems at hand, provides an initial indication of the presence of gout.
This is usually followed by one physical examination, during which the attending physician examines the affected joints and pays attention to swelling, redness and any possible overheating.
Furthermore, the Blood test plays a critical role in gout attack diagnosis. One of the most indicative indicators of the presence of a gout attack is what is known as the one Uric acid level. However, caution should be exercised with this laboratory value. At a increase the uric acid concentration in conjunction with the typical symptoms can be assumed to be a gout attack, a uric acid value in Normal range shoots the presence of this illness however not from. The reason for this is that the concentration of uric acid that can be detected in the blood depends on what the patient has eaten and drunk. For this reason, a normal uric acid concentration does not necessarily mean that a gout attack is excluded. In addition to the uric acid level, the number of white blood cells and the Sedimentation rate (ESR) determined in the blood. Both values are classically elevated in a gout attack.
Making a X-ray for the purpose of diagnosing an acute gout attack is questionable. Visible changes in the bones are mostly visible in the X-ray just at chronic trending gout- Observe shapes. Alternatively, a so-called Urography be carried out, which in contrast to the X-ray image also the detection of individual Urate stones enables. If anything is unclear, a Joint puncture with subsequent proof of Urate crystals secure the diagnosis in the synovial fluid (joint fluid).
therapy
The main goal of the therapy of a gout attack is the rapid relief of pain symptoms as well as the inhibition of the spread of inflammatory processes in the area of the affected joints. An acute gout attack is generally treated by giving various drugs. Drugs that belong to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs for short) are particularly suitable for relieving pain and reducing inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit an important enzyme (so-called cyclooxygenase), which is required for the synthesis of various pain and inflammation mediators.
The drugs most commonly used to treat acute gout attacks are:
- Ibuprofen and
- Diclofenac
Indomethacin promises a good effectiveness in patients who suffer from a gout attack, but due to the frequent side effects, the above mentioned preparations are preferable. Arcoxia® 90mg from the group of coxibs can also be given in the event of an acute episode of gulp.
It is not advisable to take aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) during an attack of gout, as this drug has an inhibitory effect on uric acid excretion.
Many affected patients also respond very well to therapy with the help of colchicine. Colchicine inhibits the uptake of urate crystals in the body's own phagocytes (macrophages) through various mechanisms. In this way, it also reduces the release of inflammatory mediators (cytokines) induced by the macrophages and thus has an anti-inflammatory effect. Colchicine is the poison of the autumn crocus that has been used in medicine for many decades. When giving colchicine, however, it should be noted that it is a poison with high toxicity and therefore a low dosage must always be adhered to. The poison of the autumn crocus should not be used in patients who suffer from renal insufficiency.
In addition to drug treatment of the gout attack, a targeted change in diet can also be useful. Above all, this measure reduces the likelihood of further illnesses. Patients suffering from a gout attack should switch to a low-purine diet in the future. The reduction of the purine (an organic base) ingested with food ensures that less uric acid can be formed in the course of the metabolism. In addition, a general diet for weight loss and the avoidance of obesity should be aimed for. Avoiding certain foods can be effective in preventing another attack of gout.
The main problematic foods are:
- animal proteins
- liver
- herring
- Anchovies and
- Red meat
For this reason, patients suffering from gout should pay attention to the purine content of various foods (see also: Diet for gout - you have to pay attention to this).
In contrast, the consumption of vegetable proteins is completely unproblematic. The consumption of alcoholic beverages should also be greatly reduced in order to prevent another attack of gout. According to extensive studies, the best long-term treatment results can be achieved in those patients who are undergoing both drug therapy and extensive and efficient dietary changes.
Read more on the topic: Diet for gout