Ovulation despite the pill
introduction
Ovulation in spite of the pill is common classic combination pill as good as impossible. Ovulation occurs only if there is a mistake in taking it. Both estrogen free pills, especially with the Mini pill on the other hand, ovulation can occur in a certain percentage. The main job of the progestin in the pill is to thicken the mucus around the cervix.
However, the further development of the preparations has also improved the inhibiting effect on ovulation.

Can ovulation occur despite the pill?
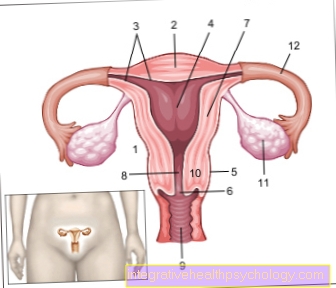
The classic pill contains both estrogen, as well Progestin.
- There is the so-called combination method, in which a constant dose of estrogen and progestin are usually taken over a period of 21 days.
- Then there is the sequence method. Here, the concentrations of the two hormones change over the time they are taken.
With these preparations, if taken properly, ovulation cannot occur. By giving additional hormones, the hormone GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone) inhibited. GnRH is in turn important for the release of hormones LH (Lutenizing hormone) and FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone). Due to the lower concentration of GnRH, LH and FSH are also released less. Since LH is largely responsible for ovulation and this requires a high concentration of LH, ovulation cannot occur.
This mechanism of contraception also applies to those Micropill too, which means that ovulation cannot occur, despite the low dose of hormones.
This is different with the estrogen-free pills, e.g. also the Mini pill. Ovulation can also occur with these preparations. Previously, the rate was 43% of women who ovulated despite taking the pill. However, this rate could be reduced through the further development of the preparations. The preventive effect of the estrogen-free pill is that it thickens the mucus around the entrance of the uterus so that the sperm cannot enter the uterus.
Find out more at: The pill doesn't work
What causes ovulation despite taking pills?
The most common reason why ovulation occurs despite taking pills is incorrect intake. Either the pill is taken too late or completely forgotten. Then ovulation can be triggered by the fluctuating hormone levels.
Therefore it is important use additional contraception after a forgotten pill. This also applies if vomiting or severe diarrhea occurs within 3 to 4 hours of taking the pill. The hormones in the pill could not be adequately absorbed by the body during this period and the prevention of ovulation cannot be guaranteed.
You might also be interested in: Which drugs affect the way the pill works?
With the estrogen-free pills, so with the Mini pill and the progestin-only pills (They contain a higher dose of progestins and are not counted among the mini pills), ovulation is not suppressed as reliably as with the classic pill. Ovulation is not atypical, especially with the minipill. The progestin pills normally have a sufficiently high concentration of active ingredients to prevent the egg cell from maturing and ovulation. However, this is not as safe as the classic pill.
More information can be found here: Forgot the pill - what should be considered?
How can you tell if you are ovulating?
Ovulation is triggered by the rise in the LH hormone. LH can be determined using urinary ovulation tests. Thus, based on the change in the LH concentration in the urine, it is possible to determine whether and when ovulation took place.
In addition, the so-called cervical mucus changes after ovulation. The observation of the cervical mucus as a method of contraception is also called the Billings method. The method is based on the fact that the cervical mucus is most fluid on the day of ovulation and has the greatest spinnability. With a certain level of experience, one can estimate the different phases of the cervical mucus and also the ovulation with this method relatively well.
In addition to observing the cervical mucus, it is useful to determine the basal temperature. The temperature is measured in the mouth or rectally in the morning after getting up. Temperature measurements in the armpit or on the forehead are usually too imprecise. Before ovulation, the body temperature drops a little and then increases by up to half a degree on the day of ovulation.
Read more on the subject at: Ovulation and temperature - what is the relationship?
Both the Billings method and the measurement of the basal temperature are optimized for the normal cycle without taking the pill. If it is to be determined whether ovulation has occurred despite taking the pill, the methods may not work so reliably. Then the concentration of LH in the urine should be measured to be sure.
These symptoms can indicate ovulation despite taking the pill
The symptoms that can occur during ovulation are all rather unspecific and not every woman perceives them to the same extent. Chest pain or a middle pain at the time of ovulation may be felt. Furthermore, ovulatory bleeding occurs in a small proportion of all women. This is triggered by the sudden drop in the hormone estrogen. The bleeding is usually very light. There may also be just a discolored discharge. It is important that this ovulatory bleeding can be confused with a menstrual period, but should still be prevented if you do not wish to have children.
A well-known symptom that can occur 10 to 14 days before menstruation, i.e. also at ovulation, is premenstrual syndrome (PMS). This syndrome is associated with a wide variety of possible symptoms. Underneath can Fatigue, irritability, depressed mood or edema be. The severity of the premenstrual syndrome can vary. Some women do not notice any changes, while it can also lead to temporary incapacity for work.
Can you feel ovulation?
There are no body signals that reliably indicate ovulation. Sometimes women feel unspecific symptoms that can be associated with ovulation. First of all, the so-called middle pain can be noticed. This is perceived as spasmodic or pulling in the right or left lower abdomen. The pain is caused by the rupture of the egg follicle.
Only about a third of all women even notice this pain. It is similar with chest pain. These typically occur more in the second half of a woman's cycle, but can also occur near ovulation. Chest pain varies in women and can only be perceived as swelling of the breast. In the fertile phase at ovulation and in the days afterwards, some women have an increased libido, which then flattens out again over the course of the second half of the cycle.
More information can be found here: Fertile days
The pain of implantation
Implantation pain is described as mild pain during the course of implantation of the blastocyst. In fact, the intensity of the pain is usually so low that it can hardly be perceived. However, there have been reports of implantation pain in women who are particularly sensitive to symptoms of their body. There is no scientific proof of implantation pain either. Therefore, it is not counted among the uncertain signs of pregnancy. A possible mix-up can be the normal pelvic pain, which can occur as part of the normal female cycle.
Read more on the subject at: Implantation pain
Recommendations from our editorial team
- Pill and alcohol - are they compatible?
- Side effects of the pill
- Thrombosis while taking the pill
- What happens if you stop taking the pill?
- Mechanical contraceptives and hormonal contraceptives