Bruise in the eye
introduction
The eye is supplied by numerous blood vessels. They ensure that vital and oxygen-rich blood is delivered to all parts of the eye, e.g. the lens and retina. The muscles that control the eye are also well supplied with blood vessels. You can find out what a bruise on the eye means and what treatment options are available here. See also: How do you treat a bruise?

What are the symptoms of a bruise in the eye?
With a harmless bruise in the eye, which is caused by broken veins, there are usually no further symptoms. However, accompanying pain around the eye and severe headaches can occur. Visual disturbances of various kinds can also be triggered. See blurred, Double vision or that sudden onset of opacity, as a kind of swarm of black dots can be perceived.
The latter indicates a vitreous hemorrhage down. This includes the Risk of tearing the retina of the eye. If more Flashes of light can come this one Sign of a retinal tear that has already occurred be. A doctor should be consulted immediately! Furthermore, an eye that protrudes and in addition Vision deterioration occur on a bruise behind the eye called a retrobulbar hematoma Clues. If such a suspicion exists, a doctor should be consulted immediately.
Even if permanent or recurring side effects such as headaches and visual disturbances occur, the causes and, if necessary, the underlying diseases should be clarified by a doctor.
When should you see a doctor and how does he diagnose the disease?
When a bruise in the eye does not go back after 2 days or it Concomitant symptoms such as headaches, visual disturbances or other complaints a doctor should be consulted. Even if the bruises appear repeatedly in the eyean investigation should be carried out. It starts with a targeted survey.
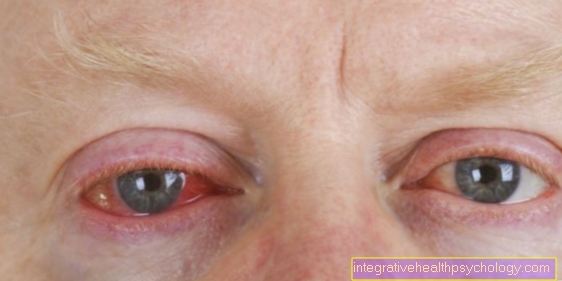
Then the doctor takes a close look at the eye. Furthermore, he can differentiate extensive eye bleeding from eye reddening. If blood collects on the eyeball, it can be seen as bright red spots. If, on the other hand, the iris is colored red, this is a sign that the blood is in the Vitreous spacecollected behind the lens of the eye. If the entire eye appears to be “bloodshot”, it is usually due to bleeding under the conjunctiva. The doctor literally takes the eye “under the microscope” when examining it with the slit lamp. Additional examinations are carried out depending on the accompanying complaints. In some cases you will be referred to another specialist if, for example, a so-called neurological cause is suspected.
Bruise on the outside of the eye
An external bruise (Hematoma) is usually not dangerous. However, it is important to note that no important structures, such as parts of the eye, are injured or restricted in their function. On the other hand, the bruise should not get so big that it takes on disquieting proportions. Sometimes it can also happen that the amount of "leaked" blood is so much that the hematoma exerts strong pressure on the eye structures, which can then lead to impaired vision (see also Symptoms of injuries to the eye). In some cases it may be necessary to surgically remove the bruise above or below the eye in order to relieve the pressure.
Bruising around the eye is quite common. They mostly come about as a result of trauma, for example fights or accidents, if there is blunt trauma in the area of the eye (see also Bruised eyeball). This ruptures blood vessels that supply the outside of the eye, including the skin of the face. If the bruise is around the eye like a ring, it is also known as a monocular hematoma. The blood always flows downwards due to the force of gravity, which means that even if a bruise occurs in the upper area of the eye, it will over time settle on the lower eyelid.
Bruise inside the eye

Bruising in the inside of the eye is proportionate Rare before, but they are riskier due to their area of spread. Within the eye there are very important structures that are indispensable for the visual process. The lens with the ciliary muscles, the vitreous humor, the retina and the optic nerve are the components of the eye that enable perfect vision.
Bruising in these areas can lead to displacement of these structures and thus to injury and severe impairment of vision. Furthermore, it must be noted that when the bruise occurred, such a great force may have already acted on the eye that structures in the area of the eye were injured.
Hematomas in the eye need to be carefully examined by an ophthalmologist and their effects on the function of the eye must be weighed. In some cases, treatment is not necessary as the bruise will clear on its own within a few days. But it may also be that the bruise has to be removed by surgical measures.
See also:
- Eye surgery
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Eye pain
Causes of a bruise in the eye
The most common cause of hematoma inside and outside the eye is trauma. As a rule, it is blows or blunt injuries in an accident that accelerate the position of the eye in such an unphysiological way that the smallest blood vessels tear and bleeding occurs.
A bleeding under the conjunctiva called a Hyposphagma, can be caused by broken veins. This can be done by taking so-called Blood thinners (e.g. ASA) occur increasingly. A cough or sneeze can easily cause bleeding in the eye. The cause is usually increased blood pressure, which creates this type of bruise in the eye. This can look terrifying, but is usually harmless and painless.
Also bleeding disorders, which among other things in the context of a Alcohol disease can occur, the veins in the eye can burst. This is known in technical jargon as Hyphema. This can disrupt the drainage of water and lead to increased intraocular pressure.
Increases in blood pressure in connection with metabolic diseases can also lead to small hemorrhages on the retina, which can then also lead to visual disturbances (read about this Diabetic retinopathy). In this case, however, one does not normally speak of a bruise. In young children, the bruise that is inside the eye is almost always trauma-related.
Surgical interventions also lead to bruising. The Cataract surgery (Cataracts) also causes bruises outside and inside the eye, usually quickly receding.
Bruise in the eye from a blow
The blow to the unprotected eye is the most common cause of a bruise outside and inside the eye. Depending on the force acting on the eye and in which position the eye is at this point in time, severe structural injuries can occur in addition to a hematoma in the eye Eye emerge. Some of these can also endanger eyesight. Tears of the lens and ciliary muscles, optic nerve or vitreous body injuries with accompanying hemorrhage make a particularly careful approach necessary when making the diagnosis.
Usually the first symptoms after a blow to the unprotected eye are temporary blindness, which disappears within a few seconds or minutes, as well as a flash in the eye (here it goes Causes of blindness). The most important measure after a forceful act on the eye is to clarify the extent of the injury. Ultrasound or MRT examinations are used here. It may be necessary to surgically remove a hematoma caused by a blow to the eye. If no structures are at risk, a wait-and-see approach can be chosen.
Bruising in the eye from contact lenses
The edges of contact lenses can injure the eye, cause the veins to burst, and bruise the eye. If pain and visual disturbances occur at the same time, a doctor should be consulted.
In addition, awkward handling of the contact lenses can cause the Cornea of the eye to be abraded. This is also known as the so-called Erosio cornea. The affected person usually has severe pain because not only blood vessels but also corneal nerves are affected. In addition, strong tears occur Eyelid cramp and Eye redness on. The corneal abrasion is often invisible to the naked eye. If this is ignored and untreated, a Corneal infection develop. If a vein has already burst for other reasons, wearing contact lenses can in some cases increase the bruise in the eye.
If the edge of the contact lens presses on the injured blood vessel, this can lead to renewed or further damage. Therefore, it is Recommended to use glasses as a visual aid instead of contact lensesuntil the bruise in the eye has subsided. If the combination solution causes a burning sensation when inserting the contact lens, a doctor should be consulted. If you already have wounds and injuries, you can secondary bruising through contact lenses arise in the eye.
Bruising in the eye after Lasik surgery
As Lasik surgery This is a term used to describe a surgical procedure with which, through laser treatment, ametropia can be treated within a few minutes. A part of the cornea is opened up using a laser and the corneal structure is removed, which then changes the refractive power of the eye. Sometimes there may be a small bruise inside the eye shortly after the operation. As a rule, patients notice this bruise through impaired vision (for example, through a dark spot when fixing a point).As a rule, the bruise will recede within a few hours or days and will no longer cause discomfort.
Therapy for a bruise in the eye

In particular, the external bruise of the eye usually does not need to be treated. On the one hand, this is due to the fact that the space outside the eye is more generous than inside the eye. The blood can expand without displacing or injuring important structures in the eye. On the other hand, the hematoma often breaks down by itself and does not require any further treatment. In some cases, however, the bruise may cause so much blood to have spread around the eye that the pressure on the eyeball increases. This is dangerous as it becomes a Damage to the optic nerve can come.
Bruises that do not resolve themselves and are outside the eye must be surgically removed. This measure is rarely used, but it is sometimes necessary. For this purpose, the spread of the bruise is first determined by an ultrasound examination in an ophthalmology clinic. A small incision is then made in the area where the most blood has accumulated and the effusion is removed by rinsing. The skin is then closed again. The procedure takes place under local anesthesia and takes about ten minutes to an hour, depending on the extent of the bruise.
Bruising that occurs inside the eye must first be visualized with regard to blood volume and spread. Before starting any treatment, it is particularly important to find out how big the hematoma is and which structures in the eye it is likely to press or constrict. Ultrasound and MRI are used for this. If no important structures are constricted by the bruise and the visual process is not endangered, one can first wait.
Please also read our article on this MRI of the head
In many cases, the bruise will clear itself within the eye as well. But it is important to check the size and spread of the effusion from time to time. If a bruise increases in size and circumference or if important structures such as the lens, vitreous humor, retina or even the optic nerve are at risk, a minimal surgical clearance operation must be performed.
In an ophthalmology clinic, small incisions are made next to the eyeball to create access to the eye. Then the hematoma is slowly suctioned off with the smallest of instruments. The procedure can take up to two hours, depending on the location and size. It is important to proceed very carefully so as not to endanger important structures in the area of the eye.
Please also read our article on this Therapy of a blue eye
Alternative therapy through homeopathy
No treatment is required if the eye bruises is harmless. However, some sufferers find accompanying homeopathic treatment supportive. Treatment should be guided by a professional. Homeopathic treatment does not replace conventional medical therapy. In particular for bruises on the eyethat are associated with pain and swelling, but also with harmless bruises in the eye Arnica have a soothing effect. For the first hour after the causative event, adults are recommended 5 globules with a potency of C5 every 15 minutes and then 5 globules every hour. Arnica in a potency of C9 can be advisable for children. At Bruised eyeballThat can be accompanied by dull aches and pains and problems opening the eyes or bleeding in the eye or eyelids, in some cases Ledum support the healing process. As a rule, 3 globules in the corresponding individually agreed potency are recommended here 3 times a day. If Arnica and Ledum do not provide relief, it may be possible Symphytum also support the healing of earlier injuries on and in the eye.
Duration of the bruise
Depending on the cause and size of the bruise on the eye, the length of time it takes for a hematoma to break down varies. Smaller hematomas break down faster than larger ones. The breakdown time for internal and external bruises is usually about the same. Bruising can take up to two to three weeks to disappear. In this case, one of the decisive factors is whether the bleeding has stopped or whether oozing bleeding repeatedly occurs in the area of the eye. A constant run of blood would lead to an extension of the healing time.
Bruising on the eye in the baby
Bruising on a baby's eye are to be taken seriously in any case. The cause can be trauma in the sense of an accident or violence.
The procedure for treatment is the same as for adults. First, it must be assessed whether and which structures in the area of the baby's eye are injured. Appropriate wait-and-see or operational behavior should therefore be aimed for. Eye tests are difficult to do in babies, so it's especially important to do it with ultrasound and imaging Injuries to the eye to exclude.
Bruising within a baby's eye is often caused by what is known as shaking trauma. In the case of child abuse in the sense of shaking the child, the child's head is set in a very fast back and forth movement, which can cause the smallest blood vessels in the eye to tear and begin to bleed. In the area of the vitreous body and the retina, you can then see the smallest bleeding that can temporarily limit the child's vision (see also Vitreous hemorrhage). This bleeding can indicate that abuse has taken place.
The extent to which treatment must be carried out also depends on the extent, on the visual impairment of the baby and on the displacement of other structures of the eye. If no other reason for the occurrence of the bruise is evident, a criminal investigation should be initiated with regard to the origin of the injuries.
Also read our topic: Bruise in the child


.jpg)