Denture
introduction
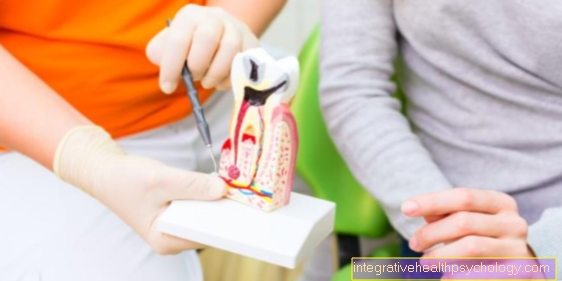
A Denture serves to replace a lost one Tooth or multiple lost teeth. In the Dentistry A distinction is roughly made between removable, fixed or combined dentures. The group of fixed dentures belongs above all Inlays, Crown and bridges. Partial and full dentures are among the removable forms of dentures.
The decision as to whether a partial or a full denture needs to be made is based on the number of missing teeth.

Denture
Partial dentures
A partial denture can be made in different types and with different materials. The basic version consists of a plastic mixture onto which the teeth to be replaced are applied.
The fixation in the jaw is ensured by wire clips specially made for the individual patient.
In addition, so-called support mandrels can be attached as supporting and holding elements; they offer significantly better stability. In Germany, partial dentures based on plastic are usually only used as temporary dentures (Interim prosthesis) applied. The manufacture of such a dental prosthesis may be necessary in the course of a surgical tooth extraction, it remains in the oral cavity for the entire healing time and is ultimately replaced by a permanent dental prosthesis.
Read more on the topic: Interim prosthesis
Model casting partial dentures are produced in the dental laboratory using a jaw model. The attending dentist has to make an impression of the patient's jaw in advance, which is then poured out in the dental laboratory.
In the dental laboratory, a metal framework, together with the holding and supporting elements, is then formed for the future dental prosthesis. The advantage of this method is the relatively precise adaptation of the prosthesis to the patient's jaw conditions. This ensures an enormous accuracy of fit, high stability and fewer pressure points.
After the metal frame and the holding and supporting elements have been made, the dental technician applies teeth molded from plastic. In order to avoid later discomfort, it is important that a distance of several millimeters is maintained between the remaining teeth and the partial denture.
In addition, partial dentures can be distinguished on the basis of the circumference and the position of the teeth to be replaced.
Switching prostheses are dental prostheses in which a tooth gap is closed. This means that there is at least one natural tooth both in front of and behind the tooth to be replaced.
A cantilever prosthesis, on the other hand, ends freely in the Temporomandibular joint, there is no further natural tooth behind the tooth to be replaced.
Full dentures
In the case of complete tooth loss, i.e. in cases where there are no more natural teeth jaw are present, the supply will be a total Denture necessary.
In contrast to partial dentures, full dentures are not created by clasps but by negative pressure and adhesive forces in the Oral cavity held. In order to ensure this, a so-called functional impression must be made for the prosthesis production.
This means that the jaw and parts of the oral cavity are shown in different states of motion.
In most cases the correct fabrication of a full denture of the upper jaw is much easier than the fabrication of a full denture of the lower jaw. This fact may sound a bit unimaginable at first, because one could assume that dentures of the upper jaw offer less support due to gravity.
But since it is in Lower jaw there are fewer contact surfaces with the jaw and the mobility of the tongue has a negative effect on the adhesive forces, this phenomenon can be easily understood.
How much does a full denture cost?
The removable full denture is considered to be Standard supplywhen a patient no teeth has more. Per jaw becomes a prosthesis prepared. This standard care is also called regular care. Health insurance usually pay the Half the cost for such a prosthesis.
If there has been a check-up at a dentist every year for at least five years, and these check-ups always in one Bonus booklet have been noted, then most health insurances increase the proportion of the costs that are covered.
The dentist creates one Treatment and cost plan, in which he writes exactly how much money he is asking for the denture. This plan is submitted to the health insurance company, which then decides whether the planned dental prosthesis can be made and how much of it it will pay. Such a healing and cost plan is made up of the Fee for the dentist, the fee for the Dental technicianwho has to make the prosthesis and the cost of that materialthat the dental technician and dentist consume in the course of treatment.
Because there are no very precise rules for this, it is possible that two dentists charge different amounts of money for the denture. So it can be worth going to two or three practices and comparing the costs. For two dental prostheses (i.e. upper jaw and lower jaw), a patient must reckon with at least 600 euros personal contribution.
If the patient's income is too low, the dentist may apply for a hardship case. If this is approved by the health insurance company, the insured person does not have to pay anything for his full denture because all costs are covered by the health insurance company.
Denture of the upper jaw
In the upper jaw, the palate, with its relatively large area, provides a good base for anchoring a prosthesis. If the bone level of the upper jaw is sufficient, anchoring elements such as implants or teeth are usually not even necessary to fix the prosthesis in a satisfactory manner. The upper jaw prosthesis holds by one Suction effect. Due to its viscosity, the saliva produced acts like a lubricant between the plastic base and the palate and thus creates a negative pressure that fixes the upper jaw prosthesis. Therefore, it can often only be removed from the upper jaw with external force.
However, it is only one poor bone level which the prosthesis has no chance of holding Holding elements necessary so that the prosthesis is adequately fixed. Implants, mini-implants or, if still available, your own teeth offer options. If there is not enough bone to anchor the implants, external grafts can be used to transplant bone to the desired location so that the implants can grow into place. However, this procedure is associated with a high level of stress on the patient.
Mini-implants are a good alternative, which are associated with a moderate operative load. They can also be implanted with a lower bone level and offer a satisfactory hold of the prosthesis.
Denture of the lower jaw
The denture has a much smaller area in the lower jaw through the tongue to be attached. It is only held on the alveolar ridge. This fact is the reason that a good hold in the lower jaw is very difficult to achieve and depends heavily on the individual situation. If there are still implants, mini-implants or teeth as holding elements, the prosthesis can be hung on them so that it is firmly fixed.
Once the lower jaw is toothless, the bone tends to recede, to atrophy. This makes it all the more difficult to produce a well-fitting prosthesis with which the patient is satisfied. If the atrophy of the jaw has progressed, there is usually far too little bone available to attach implants, unless bone is surgically created with transplants.
This procedure is very costly and uncomfortable for the patient, so that it scares off most of those affected. Therefore, the only alternative is the implantation of so-called mini-implants, which are much shorter than the conventional ones and thus allow a lower jaw level. If these artificial holding elements are in function, the jawbone no longer retracts because it is in use. Thus, a certain level of the jaw can be obtained with the mini-implants and creates a variant of the attachment that is satisfactory for the majority of patients.
Read more on the topic: Denture of the lower jaw
Combined dentures
A combined dentures is a mixture of fixed and removable dentures. The stuck part can be made Crown, bridges, so-called Telescopes and / or webs exist, and the attachment of the dental prosthesis to implant pins is no longer a rarity these days.
A particularly good hold in the oral cavity and the reduction of the additional load on the remaining remaining teeth are among the advantages of such a combined denture.
Dentures with push button
The term push button stands for mini implants, which are shorter than conventional implants. They are drilled into the upper jaw and, as a counterpart, locators are incorporated into the prosthesis, into which the mini-implants snap. The principle is like a push button. However, 6 mini implants in the upper jaw are also necessary to create freedom of the palate.
What to do if the denture is loose?
If the prosthesis rocks or no longer holds it properly, the source of the problem must be found out. Those affected have to go to the dentist's practice, self-treatment is not possible. Reasons for the prosthesis rocking are numerous and can be serious. Even not wearing the dentures can lead to a bad fit or even a non-fitting of the prosthesis after a few days. Also the sudden weight loss or one rapid increase can impair the hold of the prosthesis.
Furthermore, there is the possibility that mucous membrane or bone changes of any kind can adversely affect the hold and fit of the prosthesis. To find out and treat the various causes, which can also include malignant diseases such as tumors, the dentist should be consulted. If the prosthesis is still not in place after medical clarification and treatment, for example with a relining, the patient has the option of including the prosthesis Adhesive cream to fix or to create artificial holding elements with an implantation, which are associated with high costs.
What to do if the denture hurts
Pain from a denture mainly occurs as soon as it is new and settles in first. Pressure points arise on the soft tissues that are displaced by the new prosthesis. In this case, the person concerned has to go to the dental practice so that the denture can be ground free at the pressure points.If pain occurs even though the prosthesis is several years old, the dentist must definitely be visited, as a change in the bone or mucous membrane may have formed, which creates a pressure point.
These changes can be quite malignant and should be examined by a dentist as soon as possible so that a tissue sample can be taken for examination if necessary. In the event of any form of pain caused by the prosthesis, it is advisable to visit the dentist in order to find out the cause as quickly as possible. If the prosthesis is not worn for a long time due to the pain, soft tissues and bones can form so that the prosthesis no longer fits.
Also read the article on the topic: Inflammation under a denture
How can you reline the denture?
If the fit of a prosthesis is no longer one hundred percent guaranteed, the dentist recommends relining it. There are two methods of relining. In the first, an impression is taken with the prosthesis, which shows the places on the ridge and palate where material is missing. The prosthesis is hollow and wobbles at these points. The technician then fills in the areas that are missing material and the jaw has receded with plastic. This described procedure is the indirect relining.
The other approach, the direct relining, the liquid plastic is applied directly to the denture base and placed in the mouth until it hardens. Then the new edges are worked out by the technician.
Read more on the topic: Relining a dental prosthesis
How can you glue a denture?
If a denture is broken, it must be repaired. Providing it with an adhesive does not work, as in many cases the fragments cannot be put together without gaps and the prosthesis no longer fits. It is not uncommon for the dentist to take an over-impression over the fragments in the mouth in order to determine the correct position of the prosthesis. The dental technician knows exactly from the impression how the prosthesis has to be assembled.
A plaster model is made in the laboratory to fix the fragments in the correct position, the fragments are roughened at the fracture point and the technician lets new plastic flow into the fracture gap. After hardening, this is worked out, smoothed and polished. This is the only way to restore the stability of the prosthesis. Glue cannot fill the fracture gap stably and in the correct position. In addition, it is toxic, harmful to the oral cavity and must not be swallowed. Therefore, it is generally not advisable to attempt repairs yourself.
What adhesives are there?
Adhesives are aids for prosthesis wearers, without which many users would have virtually no prosthesis hold. This mainly affects users who have little or no salivation, which is crucial for the suction effect of the prosthesis. The most popular adhesive is the classic adhesive cream, which is characterized by a very thick, almost pulpy consistency. This adhesive cream is distributed on the denture base in portions the size of a hazelnut and increases the viscosity and hold of the denture.
If teeth or implants are still present, the adhesive cream should only be applied to the areas where there are no retaining elements. There are also adhesives in powder form, which are simply sprinkled in a thin layer on the base of the prosthesis and then provide the prosthesis with an optimal hold for hours when it is inserted.
The powder consists of Sodium alginate and is particularly suitable as an adhesion promoter. For particularly sensitive mucous membranes that tend to form pressure points, there are adhesive pads that are cut and moistened for the prosthesis. The adhesive pads ensure optimum hold and pad the prosthesis at the same time. This protects the mucous membrane from inflammation, pressure points and fills hollow areas like a relining material. In general, a prosthesis should not need any adhesives for an optimal hold.
What is the palatal plate on a denture?
The palate plate is made of plastic and covers the entire palate of the upper jaw between the rows of teeth. On the one hand, it is there to give the prosthesis support, as the prosthesis creates a negative pressure through the suction effect of the saliva on the palatal jaw, which prevents it from falling. On the other hand, the palate plate distributes the pressure load over a relatively large area so that the bone does not regress, because only stressed bones remain, unloaded ones recede.
Is it also possible without a palate plate?
Without a palate plate, an upper jaw prosthesis is only possible if there are still at least 6 retaining elements that support it (teeth, implants, mini-implants). If there are fewer teeth, the palatal plate must distribute the chewing pressure so that there is enough hold. Without a palate plate, the prosthesis would fall down with a smaller number of holding elements and would not guarantee any hold.
What does a denture cost in the upper jaw and / or in the lower jaw?
A prosthesis for a toothless jaw costs around 400 euros per jaw, which means 800 euros for both jaws. This includes the portion taken over by the health insurance company. If this prosthesis is anchored to teeth or implants, this anchoring must be paid for separately for a better hold. Anchoring to existing teeth with telescopes is relatively expensive, since each tooth has to be supplied with a metal telescope and the matching counterparts, also made of metal, are incorporated into the prosthesis. This supply can cost several thousand euros, but it promises a good hold and comfort.
If there are implants in the upper jaw instead of teeth, the implants have to be paid for privately in advance, and around 1000 - 1500 euros per implant should be expected. The superstructure that is placed over the implants has to be charged again with several thousand euros, so that an implant-supported variant often has the value of a small car.
Mini implants are slightly cheaper than normal implants. Locators are incorporated into the prosthesis so that the mini-implants lock into the prosthesis using the lock and key principle. This care can cost from 3,000 to 7,000 euros, depending on the dentist. In the case of implants, the difference in costs is very large, since every dentist can determine the costs privately, because any form of implant is a purely private service, for which the health insurances do not subsidize anything. Only the prosthesis that is worn by the implants is subsidized, but not the implants themselves.
AOK will assume the costs
In the AOK health insurance fund Insured patients are always reimbursed part of the costs that their dentures cost from their health insurance company. Lost tooth replacements always cost the insured person money if they want to replace them.
Of the Treatment and cost plan the dentist sends to the relevant health insurance company. The latter processes the application, decides what percentage of the costs it will cover and then sends the completed application back to the patient. In this letter, he will find out exactly how much money he has to pay himself.
For those insured with the AOK, it pays off, a so-called Bonus booklet respectively. The dentist records every inspection visit in this. Find this Check-ups regularly instead, the AOK pays in the event of a necessary denture more fixed grant.
After five years of regular checks, the insured person receives 20 percent more fixed allowance, after ten years this amount even increases to 30 percent.
This fixed subsidy amounts to AOK always 50 percent of the standard supply. This means that if a patient no longer has any teeth in their mouth, the standard supply is a dental prosthesis. The AOK always pays half of the cost of this denture, unless a bonus booklet was kept regularly. Then the proportion that the AOK pays of the cost of the denture increases. The health insurance always pays this amount, even if the patient prefers to have implants, for example. Dental implants cost much more money, the difference between the standard dental prosthesis and the implants has to be paid for by the patient himself.
At the AOK there is the possibility of a Additional insurance complete for dentures. In the first year in which this supplementary insurance is paid, the insured person receives 250 euros in addition to the money that the AOK would have to pay for the standard care. In the second year of this additional insurance, the insured person receives an additional 500 euros. From the third year onwards, the AOK pays twice as much as the fixed allowance would have been. So the patient gets reimbursed twice as much for their dentures. The monthly premium for this supplementary insurance is based on age. For people over 60 years of age, 15, 60 euros are due per month.
If the income of an insured person is below a certain limit, the dentist can submit a hardship application. In these cases, the cost of the dental prosthesis is covered in full and the insured does not have to pay anything himself. Hartz4 recipients, for example, are below this limit. You get the standard care, a removable denture, paid for in full.
Techniker-Krankenkasse will assume the costs
The Techniker-Krankenkasse (TK) basically has one similar cost regulation for a dental prosthesis like the AOK. She usually always pays 50 percent from standard care, i.e. a removable denture for a patient without teeth.
The Techniker-Krankenkasse also applies that it pays off regular check-ups to have it carried out by the dentist. After five years, the portion that is covered by the health insurance of the costs increases by 20 percent, after ten years of regular checks, the portion that is covered by the health insurance is 50 percent of the standard care and an additional 30 percent more.
The TK increases the grantShe pays for the dentures if the insured is a very low income Has. If the TK insured is below the limit, the fixed allowance is doubled. The gross monthly income for this double allowance must not be higher than EUR 1,134 for a single person, EUR 1,559.25 with a relative and an additional EUR 283.50 for each additional relative.
At TK there is also the possibility Supplementary insurance complete.
cleaning
Regardless of whether a patient has been fitted with a partial or full denture, an extensive, careful one dental care should not be neglected in any case. Lack Oral hygiene can cause lasting damage to the tooth supporting structure and the gums as well as the materials from which the dentures are made.
Some patients developed intolerance to the materials used due to inadequate care of the prosthesis, including the development of Inflammation of the gums and / or one Periodontal disease is possible.
In the course of periodontal disease, if the Jawbone, it can happen that no Denture can be made with sufficient hold.
To minimize this risk, it is advisable to remove the denture from the mouth at least once, better twice a day and with the toothbrush and something toothpaste scrub off.
In addition, the weekly use of special cleaning tabs is necessary to prevent unsightly deposits on the prosthesis material. (See also Denture cleaning)
Which denture cleaners are there?
There is a wide range of cleaning options for dentures. The well-known cleaning tablets that are dissolved in water are very popular. However, it has been scientifically proven that they can attack and damage the plastic. There are also specially concentrated solutions made from acetic or citric acid, which can be used as short baths to loosen and clean the denture deposits. The best way to clean the prosthesis daily Ultrasonic baths that do not damage the prosthesis, but merely clean it. There are special ultrasound devices for household use that can also be used to clean glasses and jewelry.
Can you clean the dentures with baking soda?
You should keep away from baking soda as a cleaning option, as the coarse particles inside the powder not only remove food residues and deposits such as tartar, but also gradually rub off the plastic. The plastic is strongly attacked and thinner, so that it becomes unstable and more likely to break.
Can you clean dentures with vinegar?
Table vinegar is used as a cleaning agent for dentures not recommendedbecause it is too concentrated and attacks the denture resin, making it porous and more prone to breakage. However, there are special vinegar baths for cleaning dentures, which are so low that they can be used. The prosthesis should only remain in the bath for 10-15 minutes so that deposits can loosen. Then it should be rinsed off thoroughly.
Durability of a denture
The durability of a dental prosthesis is individually variable. Depending on the chewing load and the grinding and pressing behavior of the patient, the plastic teeth are worn out faster or slower and must be replaced accordingly. If the patient loses a lot of weight quickly, the maxillary bones and soft tissues also decrease. The prosthesis may no longer fit, meaning that a new one has to be made. As a rule, the durability of a prosthesis can be a good 10 to 20 years, but it has to be relined from time to time in order to guarantee the hold.