Bed sicknesses
Synonyms in the broadest sense
- Puerperium bleeding
- Uterine inversion disorders
- Subinvolutio uteri
- Traffic jam of the weekly flow
- Lochialstau
- Lochiometra
- Uterine inflammation in the puerperium
- birth
The morbid puerperium
During the puerperium, the body and psyche changes in the body and mind after the birth can lead to some complications.

Increased bleeding and bleeding disorders
If the weekly flow is excessive, it may be a Bleeding from a wound of a (possibly not yet discovered) vaginal, cervical or Perineal tear (Lazerations on vagina, Cervix or perineum). The blood is bright red.
The bleeding can also occur poor after-labor (Contractions of the myometrium) and no pressure (compression) of the vessels of the uterine lining (endometrium).
Another reason can be trauma in terms of a Injury to the uterus (Uterus) during the birth process.
Remaining in the uterus Remnants of the mother cake (Placenta) can also lead to bleeding.
Bleeding disorders can occur during the puerperium and after the puerperium, especially in non-breastfeeding mothers when the menstrual cycle tries to settle in again. If these bleeding disorders last longer and cause discomfort, oral Smelting agents (oral contraceptives) can be controlled.
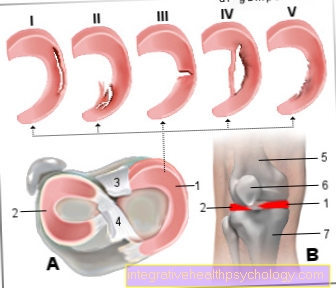
Disorders of the degeneration of the uterus (uterine involution disorders = subinvolutio uteri)
One speaks of a uterine regression disorder when the fundus (upper part of the uterus) does not sink by a transverse finger every day and the uterus is not reduced in size accordingly.
The reason may be decreased after-labor (uterine contractions). Decreased after-pains may be present in the presence of benign muscle growths of the uterus (myomas) or due to congenital or acquired muscle weakness of the uterus (hypometrium). Acquired muscle weakness is present in multiparous women, for example. The after-labor pains in the event of overextension of the uterus in multiple births or increased amniotic fluid (Polyhydramion) be reduced. Weaning also promotes reduced after-labor.
Therapeutically, the women who have recently given birth are given a short ocytocin infusion or ocytocin nasal spray, which promotes after-labor.
Damming of the weekly river (Lochialstau, Lochiometra)

A congestion of the weekly flow can occur if the Cervix (Cervix) arise. The obstruction can be caused by blood clots or kinking of the cervix with the uterus pointing backwards (retroflexio uteri). Remaining membranes can also obstruct the cervix.
The symptoms usually begin around the fourth to seventh day after delivery. She can go with high fever in the puerperium (> 38 degrees Celsius) and / or with Abdominal pain or. Abdominal pain in the puerperium accompanied. However, there can also be unspecific and minor symptoms such as a headache or Earache prevail, which the women who have recently given birth misinterpret and do not consult their gynecologist.
In any case, the women who have recently given birth also notice a reduced or no weekly flow. If there is some weekly flow, it smells pretty bad. Many women who have recently given birth and who have unspecific symptoms attribute the foul-smelling weekly flow to poor hygiene and try to improve through increased hygienic measures. This improvement does not happen, however, as the weekly flow cannot drain and is steadily increasing bacteria accumulate, which ultimately becomes a Inflammation of the uterus (Endo (myo) metritis) and in the worst case also the Fallopian tubes and Ovaries (Adnexitis) to lead.
Please also read our page Abdominal pain after childbirth.
Note: Lochialstau
Therefore, every woman who has recently given birth should consult a gynecologist if there are symptoms of any kind with an additionally reduced or absent weekly flow.
Therapeutically, a short oxytocin infusion or oxytocin nasal spray is given. You may widen the cervix (cervical canal).
Uterine inflammation in the puerperium (endo (myo) metritis puerperalis)
Inflammation of the uterus in the puerperium usually arise through ascending infections out of the vagina. Reasons for this can be a congestion of the weekly flow, a premature rupture of the bladder, frequent vaginal examinations (possibly without prior disinfection of the genital area), delayed uterine regression (uterine subinvolution) and a long birth process.
Rarely can it become one inflammation of fallopian tubes and Ovaries (Adnexditis) come.
Even more seldom, a rarity since the introduction of antibiotics, it can become one Blood poisoning (Puerperal sepsis) through carried pathogens or pathogens that get into the bloodstream. It used to be a common cause of mothers to die after giving birth.
Symptoms include increased temperatures, possibly attacks of fever, abdominal pain and reduced, bad-smelling weekly flow.
In sepsis it comes to a very high level fever, chills, Magnification of the spleen (Splenomegaly) and one increased heart rate (Tachycardia). The symptoms can worsen and lead to death if no therapy is initiated.
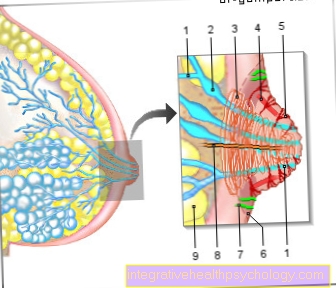
Inflammation of the mammary gland in the puerperium (puerperal mastitis)
Through small cracks and wounds on the Nipples, which often arise with an incorrect breastfeeding technique, pathogens can penetrate and lead to a Inflammation of the mammary gland (mastitis) to lead. The chest becomes red, hot, thick and painful on pressure (painful on pressure). In addition, there is a fever, possibly chills. In the initial stage, moist compresses (quark compresses) are sufficient for relief, in the advanced stage it must be treated with antibiotics. If there is no treatment, abscesses (pus cavities) develop in the further course, which then require surgical opening.
- See also Problems in breastfeeding (mother)
Milk congestion
Also read on this topic: Milk congestion
Additional information can be found here: Milk Obstruction - What Can You Do?
A few days after the birth, milk production in the mother's breast is very strongly stimulated so that there is enough milk for the newborn. However, if the baby does not empty some parts of the breast, milk will remain and the constant new production can lead to a blockage of milk.
As a result, the otherwise very soft breast tissue hardens and is often very sensitive to pain. Sucking the baby in particular is a great pain stimulus.
Milk congestion usually occurs in the first few weeks after birth, but can in principle cause problems during the entire breastfeeding period.
Read more on the topic: Pain when breastfeeding
The cause of the blockage can be an excessive milk production that exceeds the drinking requirements of the newborn. A change in the baby's drinking rhythm or a bra that is too small and too tight can also lead to blocked milk.
If the blocked milk is not treated, it can develop into breast inflammation (mastitis puerperalis).
The best therapy for congestion of the milk is to let the baby keep drinking despite the pain in the chest, so that the chest is relieved and as much milk as possible comes out. Special techniques should be discussed with the midwife to optimize breastfeeding and to increase the amount of water the newborn needs to drink if this is too little.
Thrombosis and embolism
In pregnancy and in Puerperium the probability is one Leg vein thrombosis to get increased significantly. The cause lies in the Changes in the circulatory system during pregnancy to adapt to childbirth.
Postpartum fever
The Postpartum fever, which is also called puerperal fever, is caused by a Inflammation in the woman's genital area after giving birth.
Small injuries occur in the birth canal during birth, which gives bacteria an easy entry point. The cervix, which is still wide after the birth, also helps bacteria to ascend from the outer vagina towards the uterus. Usually it is bacteria from the groups staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli or Neisseria gonorrhea that are responsible for puerperium fever.
Is there a infection before, the postpartum fever usually goes through fever, a poor general health, Pain in the lower abdomen and a foul smelling puerperium flow. In addition, you can Bleeding and Nausea or vomiting occur.
Often there are symptoms of shock, which means, in addition to a fast heart rate and accelerated breathing, there is low blood pressure. The postpartum fever should be quick antibiotic treated as it becomes a Spread of inflammation can come on the peritoneum. Then there is a high risk of developing blood poisoning.
Sheehan Syndrome

The so-called Sheehan syndrome occurs when there is a significant loss of blood during or after the birth, which leads to an insufficient supply (ischemia) of the pituitary gland (anterior pituitary gland = adenohypophysis). Necrosis (tissue death) occurs in the anterior pituitary gland and this leads to a Less education or a lack of education of the hormones formed there.
A lack of the hormone Prolactin leads to the fact that there is no milk production (lactation) and breastfeeding becomes impossible. A lack of hormones FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (Luteinizing hormone) causes poor release of sex hormones. A lack of sex hormones leads to the absence of menstrual bleeding (secondary amenorrhea), to a certain extent to the regression of breast development (hypotrophy of the mammae) and the uterus (superinvolutio uterii) and in some cases to the loss of secondary hair (pubic and axillary hair) .
In addition, there may be a lack of interest in sexual intercourse (loss of libido). Due to lack of the hormone TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), the thyroid (Hypothyroidism).
Decreased levels of the hormone ACTH (Adrenocorticotrophic hormone) in the blood lead to an underactive function of the adrenal cortex (adrenocortex). Symptoms of this are low blood sugar levels (hypoglycaemia), low blood pressure values (hypotension) and sluggishness (adynamia).
Nowadays all missing hormones can produced and replaced (substituted).
Depression in the puerperium (postpartum depression)
This must be distinguished from a mood depression (post-partum blues) that sets in immediately after the birth and which usually lasts for a maximum of a few days depression in the Puerperium (postpartum depression; see also Pregnancy depression). The depression in the puerperium usually does not set in until a week after the birth, when the woman is usually already discharged from the hospital. This is why it very often goes undetected and untreated. The depression lasts about three months beyond the puerperium. The patients appear listless, sad and dissatisfied, and their drive is disturbed.
Postpartum psychoses
0.1-0.2% of all women develop puerperal psychosis like one depression, one mania or the schizophrenia (accumulated around the 5th week)
Tips and advice for the puerperium
Hygiene is important during the puerperium Avoiding infection. Since the weekly flow (lochia) is always infectious, full baths should be avoided. This is to prevent the infectious weekly flow from coming into contact with the breast, which may have small tears on the nipple and represent a gateway for pathogens. Women who have recently given birth should also use a separate towel for the lower half of the body and one for the upper half to dry off after bathing. As long as the weekly flow is flowing, visits to swimming pools should also be avoided for reasons of hygiene.
Sexual intercourse during the weekly flow is also not advisable due to the risk of infection.
Note: contraception
It is essential to use contraception immediately when sexual intercourse is resumed, even when breastfeeding. As a rule, during the breastfeeding period (see Breastfeeding) no ovulation and therefore no menstrual bleeding. However, in some women who have recently given birth and who are breastfeeding, one may nonetheless Menstrual period (Menstruation) come with or without ovulation or ovulate without a menstrual period. For this reason, breastfeeding is not suitable as a Contraceptive method and women who have recently given birth should always be on one during sexual intercourse Contraceptives To fall back on.
However, shouldn't be on that oral birth control (contraception) as the pillthat was used before pregnancy should be used as this is not suitable. A progestin preparation should be used. In any case, you should consult with the Gynecologist to use an appropriate contraceptive.
When symptoms arise, such as Headache, earache, abdominal pain during the Weekly flow, should always be one Infection of the uterus should be thought and the gynecologist should be consulted immediately. You should also be examined for bleeding that is greater than the normal weekly flow.
An early failure of the weekly flow can indicate an obstruction in the drainage and secondarily lead to infections. Thus, if the weekly flow is low or if there is no weekly flow, the Gynecologist be consulted.
Painful, red, and overheated breasts can indicate inflammation. Quark compresses can bring relief in the early stages. If the findings do not change after one or two days, you should see a gynecologist in order to be able to treat with antibiotics at an early stage and to avoid the development of abscesses (pus cavities).
Because through the birth the Pelvic floor muscles pelvic floor exercises should be sought.
If a depressive mood is suspected, a depression or puerperal psychosis, patients should not be afraid to talk to a doctor about this, as in most cases the symptoms are overlooked and not treated.



.jpg)