Brain cysts
introduction
Brain cysts are demarcated cavities in the brain tissue, which can either be empty or filled with fluid. Sometimes they are also divided into several small chambers.
Brain cysts are generally benign and, provided they do not cause symptoms, do not always need treatment. In this case, they are often an incidental finding.
However, if the patient has deficiency symptoms, headaches, or other symptoms caused by the brain cysts, they must be treated.

causes
There can be many different causes for the development of brain cysts. Generally, cysts can develop following previous damage to the Brain tissue form. If that brain for example, the blood supply is too poor at one point, for example through Calcifications in the vessels, this leads to a stroke. The affected brain tissue is severely damaged because it was temporarily undersupplied and may even die. This leads to the liquefaction of the affected tissue. A cyst can then develop from this.
Also clot In the evacuating cerebral vessels, blood congestion can lead to brain tissue damage, which can also manifest itself as reactive cyst formation.
Brain cysts were also found increasingly in people who had suffered from high blood pressure for a long time. Patient with high blood pressure are particularly at risk for Bleeding into the brain tissue (intracerebral haemorrhage), as the vessels at some point can no longer withstand the high pressure and tear. Brain cysts can also develop following such bleeding, if survived.
Arachnoid cysts
Ultimately there is still that Arachnoid cysts. The naming comes from the fact that these cysts are in the Arachnoid, the so-called cobweb skin. This is the middle layer of the meninges that surround the brain from the outside.
Most of the time, the arachnoid cysts are congenital and usually occur randomly in one MRI- or CT-Examination discovered. They are benign and usually filled with fluid (usually with liquor, i.e. normal cerebral fluid). If they do not cause discomfort to the patient, they do not necessarily have to be treated. If, however, the location of the arachnoid cysts compresses important areas of the brain and prevents them from functioning properly, treatment must be given.
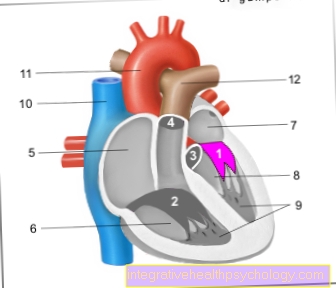
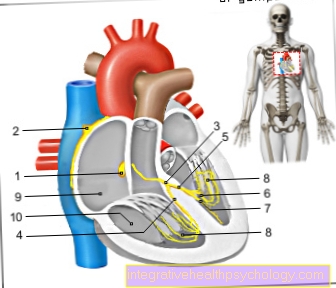
Figure brain cysts

Brain cysts
- Skull roof -
Calvaria - Hard meninges (dura) -
Cranial dura mater - Subdural gap -
Subdural space - Cobweb skin of the brain -
Arachnoid mater cranialis - Soft meninges (pia) -
Pia mater cranialis - External cerebral water space -
Subarachnoid space - Cerebrum = endbrain -
Telencephalon - Head artery - Carolis
Causes:
Damage to brain tissue
(poor blood circulation, clots,
High blood pressure, calcifications
in the vessels)
A - arachnoid cysts
in the cobweb skin
(Arachnoid) -
benign, usually with liquor
(Brain fluid) filled
B - cysticercosis
(parasitic disease) -
from infection with the
Tapeworms Taenia saginata
and Taenia solium raised
Echinococcosis
(parasitic disease) -
most often from infection
with the dog tapeworm and
Causes fox tapeworm
Therapy:
A - only for complaints
(e.g. when compressing the brain areas)
B - surgical resection
(surgical removal) of the cysts,
chemotherapy
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medicineche images
Cysticercosis
The Cysticercosis is a parasitic diseasecaused by infection with the Tapeworms Taenia saginata and Taenia solium is triggered.
The tapeworms only use humans as intermediate hosts and not as final hosts, which is why they store their eggs in different tissues. As a result, the characteristic cysts form in which the new tapeworms develop into fins, the larval stage.
In principle, any tissue can be affected by cysticercosis, but tapeworms prefer to use it Subcutaneous tissue, the Musculature, the Peritoneum, the liver and the brain.
The disease is usually treated by surgical resection of the cysts or a chemotherapythat is supposed to kill the Finns.
Echinococcosis
The Echinococcosis Like cysticercosis, it is parasitic Tapeworm disease and is of the genus Echinococcus caused.
Most often, people are from Dog tapeworm and from Fox tapeworm infested. Again, however, humans are not the final hosts of the tapeworms, but merely act as intermediate hosts.
The worm genera mentioned are rather rare in Germany. Mostly, the sick are people from southern countries or tourists who have spent their vacation in the Mediterranean region.
The infection with the Parasites is done either by Smear infectioni.e. Contact with excretions from infected animals and subsequent contact with the mouth or through consumption Echinococcus-Eggs contaminated food or drinking water.
Here, too, the tapeworm lays its eggs in various tissues, where the fins then develop in the characteristic cysts. Typically, these cysts can consist of several small chambers. If the disease remains undetected for a long time, the worms develop in many small vesicles into the so-called hydatids, which move freely in the fluid-filled cavities.
Is preferably attacked in the Echinococcosis the liver, followed by the lung and less often spleen, kidney and brain.
The cysts can be im roentgen, MRI, Ultrasonic or CT be detected. Will the brain from the Echinococcosis affected, depending on the location of the cysts, there may be neurological deficits.
The therapy takes place as with the Cysticercosis also especially through surgical removal of cysts and chemotherapeutic medication.
Symptoms
The Symptomsthat can be caused by brain cysts are very variable. The most important factors here are the number of brain cysts, their size and their exact location.
Possible symptoms are a headache, Dizziness, Nausea, seizures and Impaired consciousness.
Brain cysts can also lead to motor failure, i.e. to Signs of paralysis, Coordination problems and Difficulties in the sequence of movements to lead. The sensitivity of various parts of the body can also be impaired by brain cysts. Last but not least are too Speech and vision disorders possible.
With the parasitically caused brain cysts can also infection-related symptoms occur, e.g. fever, to cough (with lung involvement) or a general feeling of illness and weakness.
In addition, there is the Risk of bursting the cysts when the tapeworms hatch and get too big. The parasites then freely enter the tissue and can violent allergic reactions until allergic shock cause. Furthermore, when the cysts die, cavities can remain into which it can bleed. This can happen with heavy bleeding also through a headache, weakness, Dizziness or Circulatory failure express.
diagnosis
The diagnosis from Brain cysts can by means of an imaging of the brain CT or MRI of the brain be asked. If the patient has no symptoms due to the brain cysts, these are usually an incidental finding within the scope of an examination arranged elsewhere.
Once the brain cysts have been diagnosed, there is a subsequent one neurological examination absolutely necessary. The Functions of the brain and des Backmarks checked. This is important in order to detect possible impairments that are caused by the brain cysts and that may have gone unnoticed up to now. The doctor checks both motor functions, as well as the sensitivity and the Reflexes of the patient. A blood sample can also provide information about the cause of the brain cysts. So can certain in the blood Ignition parameters can be determined, e.g. in infection-related brain cysts can be increased.
therapy
So far the Brain cysts do not cause discomfort, they do not have to be treated in every case.
An observation and regular control is sufficient initially.
This does not apply to Brain cyststhat through a parasitic infection have arisen. These are either removed surgically or additionally treated with medication. Currently used Medicines for worms e.g. are for example Mebendazole, Albendazole and Praziquantel.
Operation of the brain cyst
Whether and how an operation is performed depends on the location and type of the cyst as well as the type of symptoms.
In general, cysts are only operated on if they cause symptoms, since only then is the risk of an operation acceptable.
There are various methods available to remove the cyst or, for example, to improve the drainage of cerebral fluid.
Just at Arachnoid cyststhat are filled with brain water, the cyst is often not removed, but only connected to the actual cerebral chambers.
This will reduce the pressure on the cyst and relieve symptoms. It may also be necessary to drain off the cerebral fluid to the outside, for example to relieve a hydrocephalus that has developed. The operation can be open, after opening the skull with the aid of the surgical microscope, or endoscopically. The choice of the surgical procedure depends primarily on the location of the cyst.
During the operation a number of aids are used to minimize possible complications.
Computerized software helps navigate the instruments in the brain. In addition, the brain function is continuously monitored during the operation to ensure that there is as little permanent damage as possible.
prophylaxis
The making of Arachnoid cysts cannot be avoided by prophylaxis because they are innate and therefore have a genetic component.
To avoid the parasitic infections with the tapeworm, it is advisable to deworm pets regularly. This is especially true if the animals are brought from abroad (especially the Mediterranean region). Adequate hygiene should be observed after contact with animals, such as thorough hand washing and avoiding direct contact with the mouth or mucous membranes. When staying abroad, well-cooked food should be used. Raw meals, especially those sold on the street, should be avoided as the hygiene standards there are sometimes poor.
Brain cystsbased on an underlying medical condition, such as the high blood pressure, can be avoided primarily by treating the underlying disease. Therefore, if you have known high blood pressure, you should lower your blood pressure by changing your lifestyle and, depending on the severity, a medical therapy respectively. Vascular protective drugs can also have a protective effect. In addition, people with diabetes should ensure that their blood sugar levels are well adjusted.
Brain cysts in children
There Strokes or Parasites (at least in Germany), which can lead to the formation of cysts in adults, are usually less common in children, most cysts of the brain are congenital in children.
These are cavities that arose in the course of brain development in addition to the normal brain chamber system and often with it Brain water are filled. These include, for example, the so-called Arachnoid cysts.
In principle, these cysts are not dangerous. Depending on the location, however, they can lead to the cerebral water, which can normally flow freely in the brain, being dammed up. In this case, a so-called Hydrocephalus (Water head), which must be treated acutely and can lead to further damage.
In very rare cases, a brain cyst can even deform the skull. As a rule, the cysts are not noticed at all and are often only discovered by chance in later life.
In addition to the hydrocephalus, the size of the cyst be a reason for surgery in young children. For example, very large cysts are often operated on to make room for the brain to develop further.
In the further course, a known cyst should then be checked regularly, as e.g. If the growth is strong, it may be necessary to remove it later. Even if symptoms later, like a headache or epileptic seizures occur, the cysts should be included in the diagnosis, but in many cases they never cause problems.
The group also plays with unborn babies Choroid plexus cysts a special role. These cysts form in the areas of the chambers of the brain that are responsible for producing the cerebral water. They can often be found during the prenatal ultrasound scan. As a rule, however, they themselves have no disease value.
Only in the case of very large bilateral choroid plexus cysts should further prenatal diagnosis be considered. In this case one speaks of a so-called soft marker.
This is understood to mean an abnormality that could indicate further malformations and disabilities, but is not conclusive or exclusive. Unilateral cysts usually go away on their own before birth and are not an indication of other diseases.
congenital brain cysts
Since congenital cysts in the brain often appear without specific symptoms, they are often diagnosed as incidental findings even in adulthood.
Many people live with these brain cysts without ever having any problems with them. If the cyst is known, however, it should be checked regularly in order to notice rapid growth in good time.
Despite their basically harmless character, congenital cysts can also lead to problems in the further course. This is mostly the case when the cyst starts to grow and affects important structures in the process. In this case, symptoms such as headaches, concentration disorders, deliberate failures, personality changes, epileptic symptoms or even disorders of the cerebral drainage can occur.
The symptoms depend on the location of the cyst and do not have to be permanent. Depending on the localization, these symptoms then represent an indication for surgery.
Read more on the topic: Therapy of the water head
parasitic brain cysts
Cysts in the brain that can be traced back to parasites are rather rare in Germany.
The main areas of distribution here are the Mediterranean countries. Typical pathogens are worms from the group of tapeworms. Here especially the dog tapeworm.
This can be transmitted especially when there is close contact with animals, especially dogs. The infection takes place through smear infection, via the dog's excrement, which first gets on the hands and then on the food, drinking water or in the mouth. The cysts then arise from the fins of the tapeworm.
These form a fluid-filled bladder, which is then separated from the body by connective tissue and thus forms a cyst. As with all cysts, the diagnosis is made using imaging techniques.
From the infection with the dog tapeworm, so the so-called Echinococcosis, but mostly not only the brain is affected. Cysts can also form in the liver or lungs and cause symptoms. The infection itself is usually not noticed. Symptoms then vary based on which cysts are predominant.
The brain cysts have various neurological failures. During therapy, it is particularly important to surgically remove the entire cyst, otherwise the fins can spread further. The whole thing is then supplemented by drug therapy or radiation.
other topics
You might also be interested in the following topics:
- Brain tumor
- Brain metastases
- Anatomy brain
- Cerebral hemorrhage
- a headache
- stroke
- high blood pressure
- Speech disorder
- Increased intracranial pressure