Stomach acid
definition
The term gastric juice refers to the acidic liquid that is in the stomach and which is of great importance for the digestion of all food components. A human body produces per day, depending on
- frequency
- Amount of food intake and
- Composition of food
about 2 to 3 liters of gastric juice.
Composition of stomach acid
The gastric juice is made up of many different components. Be the most important component is probably stomach acid. This is a (when sober) 0.5% hydrochloric acid, the only from one cell type the Gastric mucosa, the Parietal cells, is formed.
How much hydrochloric acid is formed there is depending on food intake. The gastric acid is released according to a very special principle: around the Epithelial cells to protect them from that attacked even by stomach acid and are destroyed, the acid will settle only outside the cells together.
In the Parietal cells arises from:
- water (H2O)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- carbonic acid (H2CO3), (Protons (H + ions) and Hydrogen carbonate ions (H2CO3-)
The protons created can now in exchange for potassium ions (K +) with Help of a pump be carried inside the stomach. That now still needed for the stomach acid Chloride ion the cell receives in exchange for the hydrogen carbonate ion from the blood plasma.
Now the chloride ion can also get out of the cell by passive transport into the stomach lumen, where it is then with the proton to hydrochloric acid (HCl) connects. This process requires a lot of energy.
A increased secretion of Chloride ions takes place under different influences, like one Activation of the parasympathetic nervous system or the release of histamine or Gastrin (i.e. following an intake of food).
Stages of digestion
There are three phases in gastric secretion:
1. Head phase (cephalic phase): Here will the stimulus for hydrochloric acid production through the Vagus nerve, so ultimately that Seeing, tasting, or smelling food set.
2. Stomach phase (gastric phase): the formation of hydrochloric acid over the Stretching of the stomach through the ingested food and special ingredients like spices or Egg whites promoted.
3. Intestinal phase (intestinal phase) She is kind of a negative feedback mechanism, through which from the Duodenum Enzymes are released when the chyme has migrated to there, which will eventually be the Limit gastric acid production.
Apart from their main function, which is Denaturation (splitting) of proteins and with it the digestion of protein, the stomach acid activates that Enzyme pepsinogen to pepsin, which is then also able to break protein bonds.
In addition, stomach acid is there, with the help of hers low pH of 1 to 1.5 on an empty stomach and 2 to 4 on a full stomach, Kill microorganisms.
Other ingredients of stomach acid
In addition to gastric acid, gastric juice contains other substances that are essential for digestion. These include, for example, a Variety of enzymes, below Pepsinogen or pepsin from the cells of the stomach, which is responsible for breaking bonds in the protein. There are also lipases that help digest food fats.
That is also important Intrinsic factor, which also arises in the parietal cells, which is responsible for the proper uptake of the Vitamin B12 in the Small intestine is needed by forming a complex with it that protects the vitamin from being destroyed by gastric acid.
Another important component of gastric juice is mucus. Mucilage (Mucin) are produced, among other things, in surface cells and secondary cells. These cover them entire inner wall of the stomachwhich protects them from being digested by stomach acid.
That which is also produced by the surface cells also makes an important contribution to the protection against gastric acid bicarbonate which is in the Mucous membrane is stored and there the Stomach acid partially neutralized.
pathology
If the protective mucous layer of the stomach by certain factors such as:
- Drinking alcohol
- certain Painkiller (e.g. Ibuprofen®)
- Food components such as Tannins (e.g. contained in coffee beans)
- hot spices
- Infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
are attacked, it can lead to acidification, which causes the Cells of the stomach wall through the Gastric acid are attacked, which among other things has a Inflammation of the stomach lining can train. In the case of an attacked gastric mucosa there is also the development of Stomach cancer favored.
It is also possible that with a lack of function of the lower esophageal sphincter (Esophageal sphincter) or one Overproduction of stomach acid in the esophagus which leads to a burning pain, also known as a heartburn designated. In the case of permanent damage to the surface of the esophagus, the so-called long-term occurs Reflux disease.
To the Limit gastric acid secretion, one usually uses so-called Proton pump inhibitors how Omeprazole® back, which is the transport of the H + ions from the Parietal cells into the gastric lumen and thus prevent the formation of hydrochloric acid. You will be at both Inflammation of the gastric mucosa as well as at heartburn used.
The state of a insufficient or completely missing Production of gastric juice is known as Achylie. This disease mostly arises in the context of the Complications of gastric cancer. Since now kproper digestion more can take place, those affected suffer from recurrent diarrhea and (through the lack of absorption of the intrinsic factor and thus from Vitamin B12which for the emergence red blood cells matters) one Anemia (pernicious anemia).

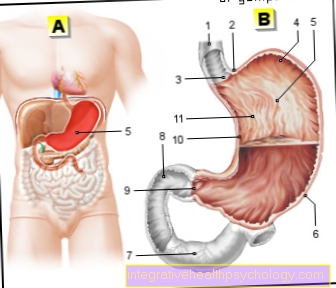
- Esophagus - Esophagus
- Incision at the stomach entrance -
Incisura cardialis - Stomach entrance -
Ostium cardiacum - Gastric dome -
Fundus gastricus - Stomach body -
Corpus gastricum - Great curvature of the stomach -
Curvatura major - Duodenum,
horizontal part -
Duodenum, pars horizontalis - Duodenum, upper part -
Duodenum, pars superior - Stomach porter - Pylorus
- Small curvature of the stomach -
Curvatura minor - Stomach folds - Plicae gastricae
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations