Inflammation of the salivary glands
introduction
Under an inflammation of the salivary gland (medical: Sialadenitis) one understands the inflammation of one of the salivary glands, which mainly affects elderly or immunocompromised people.
It is a very painful disease that is usually caused by bacteria or viruses.

definition
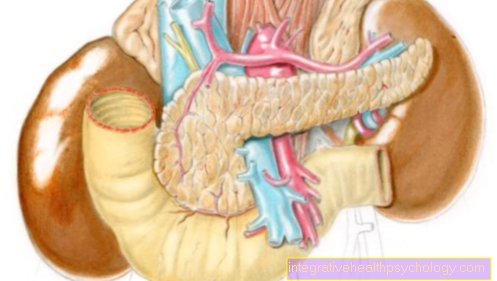
A Inflammation of the salivary glands refers to the inflammation regardless of which of the many salivary glands in humans.
At the most common are by far the big three Salivary glands affected:
- Sublingual salivary gland,
- Mandibular salivary gland
- Parotid gland
However, inflammation can also occur in the smaller ones Salivary glands in the throat, at the Buccal mucosa or the Lips occurrence.
causes
Most Salivary gland inflammation come about either through:
- bacteria: usually staphylococci or streptococci or
- Viruses: especially mumps or Coxsackie viruses
Often one arises Inflammation of the salivary glands but also by the presence of Salivary stones or their formation is at least facilitated by these stones. This is because the saliva becomes due to salivary stones backwards and obstruct the duct of the gland. As a result, the secretion can no longer drain away.
This pent up forms a perfect one fertile soilon which bacteria and Viruses can reproduce extremely well.
Restrictions due to other reasons (for example Tumors or scar) lead to an inflammation of the salivary glands.
In addition to these common causes, there are less common once Autoimmune diseases (e.g. that Sjogren's syndrome), certain medications, poor oral hygiene or Inflammation of the oral mucosa (Stomatitis) Trigger for a salivary gland inflammation.
Certain underlying diseases can also promote the development of a stone and thus an inflammation of the salivary gland:
- Diabetes mellitus,
- gout or a
- Excess on Calcium ions
Symptoms
As a rule, only one side is affected by an inflammation of the salivary gland, with the exception of mumps, which tends to occur on both sides.
The inflammation usually occurs very suddenly and is accompanied by a, sometimes massive, swelling of the face and hardening of the diseased side. In addition, in some patients, the skin over the gland may be red and feel warmer.
Read more on the topic: Swelling on the side of the neck
If it is a purulent inflammation, pus can drain into the mouth, creating an unpleasant taste. There is also typically severe pain. These often become stronger when chewing (because the chewing muscles and the temporomandibular joint are near the glands) and eating (because during this time saliva production increases, causing the saliva to press even more on the inflamed tissue). The consequence of this is that many of those affected no longer like to eat or even cannot open their mouth (wide) at all.
You might also be interested in the following topic: Symptoms of inflammation of the parotid gland
diagnosis
The suspicion of one Inflammation of the salivary glands results from the typical symptoms described above and is usually provided by the person concerned.
In order to ultimately confirm the diagnosis, a doctor to be visited. This will first perform a detailed examination of the affected gland. The gland must scanned become. Occasionally, this causes a purulent fluid to evacuate, which is sent to the laboratory. A Pathogen detection respectively. In addition, it is checked whether there are other abnormalities in the oral cavity that could possibly explain the salivary gland inflammation.
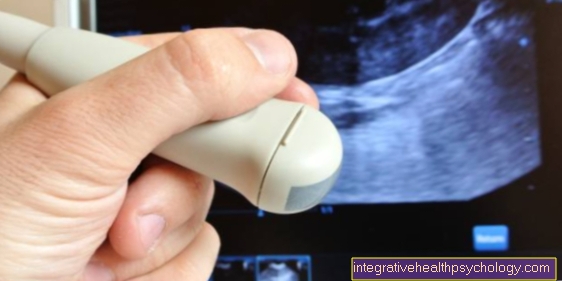
In some cases, an examination of blood further to be able to make a diagnosis. To rule out or detect a salivary stone, a Ultrasound examination carried out. This examination is able to detect stones with a size of 1.5 millimeters with a certainty of over 99%. It also serves to between one Salivary stone and one tumor or to differentiate abscess.
Another way to represent Salivary stones (Sialolite) is the so-called Sialography. A liquid containing a contrast medium is injected into the affected salivary gland, which causes you and your entire duct system to use a X-ray image can be made visible. In exceptional cases, one of the following examinations can also be useful:
- Computed Tomography (CT),
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),
- a reflection (Endoscopy) or one
- Fine needle puncture be performed.
therapy
Against a Inflammation of the salivary glands you can already do a lot yourself. In principle, help:
- cooling envelopes containing alcohol,
- a thorough one Oral hygiene and a
- increased Hydration.
It is best to avoid solid food in the acute phase.
Otherwise, the specific therapy depends on the cause of the inflammation. At a bacterial Infection come Antibiotics for use. Otherwise one treats more symptomatically, especially with anti-inflammatory drugs and Painkillers.
In addition, so-called "Saliva loosener" recommended. These are substances that stimulate the formation of saliva:
- These include, among other things chewing gum,
- acid sweets and beverages (for example with lemon juice).
The increased saliva flow “cleans” the gland from the inside out. If there is a stone underlying the inflammation, the saliva loosener can sometimes even move it out.
If this does not work, there are other ways to remove the stone:
- Some stones (especially if they are at the end of the execution aisle) can already be passed through massage be solved.
- Otherwise usually a extracorporeal Shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) carried out.
In this treatment are from the outside Shock waves aimed at the stone, breaking it into small pieces that can then come off by themselves. In the case of extremely large stones, the same applies to AbscessesAs a rule, surgery cannot be avoided.
course
Most Salivary gland inflammation take a good course. Only if they persist for a very long time and are inadequately treated, it can happen that the bottom of the inflammation develops abscess forms. This is the collection of pus in a capsule. If this spontaneously empties into the tissue, this can be a Blood poisoning (sepsis) cause. Chronic inflammation can also become a long term Die of tissue (atrophy) and Scarring to lead.
prophylaxis
There are measures by which one can reduce the risk of developing one Inflammation of the salivary glands can decrease.
Above all, this includes:
- a good Oral hygiene (Rinses) and
- quality dental care.
In addition, one should be sufficient drinkas this makes it more difficult for bacteria to settle. Special ones also help Vaccinations (for example against mumps) against salivary gland inflammation caused by special pathogens.

-buschmcke.jpg)