Surgery for a coccyx fistula
introduction
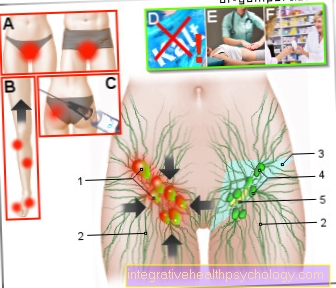
In the case of a coccyx fistula (in technical terms Pilonidal sinus or Pilonidal sinus), it is an inflammation in the gluteal fold between the tailbone and the anus (Rima ani).
Probably the most common cause of this is hair growing into this part of the body. which can lead to inflammation of the skin and hair follicle (boils). It is not uncommon for bacteria to migrate into the inflamed hair root and increase the inflammation.

If this inflammation progresses without the pus that has formed draining away, it develops cavity filled with secretion (cyst) under the skin. Once a Drain to the outside exists, one speaks of a fistula. Starting from a cyst, several such drains can develop to the outside, and a real duct system develops under the skin.
Due to the increased hair are especially very hairy men affected by a coccyx fistula.
Depending on the severity of the inflammation, any intermediate stage can develop between complete freedom from symptoms and the inability to sit or walk.
Because the inflammation mostly difficult to treat and not infrequently occurs repeatedly, is one surgery often the the only optionto treat the coccyx sinus permanently. However, a recurrence must often be expected even after an operation.

Duration of the operation
There are different methods of treating pilonidal sinus (coccyx sinus). The choice of procedure depends on the extent and type of the coccyx fistula. Therefore the duration of the procedure can vary. There are both open Operations as well as semi-operative, so-called minimally invasive, Surgery to treat a coccyx fistula. However, all surgical options have the same goal, namely the fistula to relieve, one if present Drain abscess, as well as to remove the fistula ducts comprehensively. Usually the duration of such an intervention is between half an hour and an hour.
Interventions carried out on an outpatient basis are usually of shorter duration as the treatment is Local anesthesia can be carried out and thus induction and diversion are not necessary. Compared to general anesthesia, the patient's time in the operating theater is shortened. The Regional anesthesia is also a possibility in which the duration of the procedure is shorter on average than with general anesthesia. However, it should not be overlooked that not every procedure and every type of anesthesia is equally suitable for every case and every patient, so that ultimately the surgeon and the patient have to determine the appropriate procedure.
The exact duration of an operation depends on the anatomical conditions and the type of coccyx fistula, so that a somewhat longer course of surgery may be possible in the case of complicated fistula tracts or extensive abscesses. Overall, however, it can be said that the duration of a coccygeal fistula operation is approximately one half an hour to an hour can be appreciated.
Surgical procedure

- Operation according to Karydakis
- Pit picking
- Laser treatment
1. Operation according to Karydakis
In the conventional surgery or the modified form Karydakis the patient lies in general anesthetic on the stomach, and all parts of the fistula are removed. This type of complete removal by cutting out the affected tissue is also called Excision (Ex= out, caesare= cut). Only with smaller fistulas can the operation be performed under local anesthesia (Local anesthesia) be performed.
In order not to leave any parts of the duct system and the cyst, the dye methylene blue is often used after the cyst has been cut open to stain all parts and present them in the surgical field.
It is not uncommon for the entire tissue to be removed down to the coccyx, and a "hole" is even created in the gluteal fold. By removing the tissue is a simple sewing is often not possible, and additionally at high risk for Wound healing disorders and the recurrence of another coccyx fistula. That is why the wound becomes in these cases left open and not sewn up.
In this open procedure, the wound is covered with special bandages or wound sponges, and heals from the depths out over several months to.
In the case of the Karydakis operation that will Cut out the tissue from the side of the buttocks carried out because the Greek doctor Karydakis had found that the conditions for wound healing are very unfavorable due to the high temperatures, bacteria and other factors directly in the gluteal fold. This procedure was modified by various other doctors. In its basic principles, the Karydakis operation is still carried out today.
The wound is then covered with sponges or other materials, often within the so-called Vacuum therapy (engl: Negative pressure wound therapy = NPWT) covered airtight, and it will be a small one suction pump to the Drainage system (Drainage is the name given to the hoses that drain the wound fluid to the outside), and a negative pressure is created in the wound when the pump is switched on. The vacuum therapy (NPWT) improves wound healing, since by sucking in the secretion the The wound stays clean remains, and the negative pressure the Promotes blood flow to the tissue.
2. Pit picking
The "pit picking" is that smallest intervention in the treatment of coccyx fistulas that currently exists and can always outpatient under local anesthesia (Local anesthesia) be performed. With pit picking, too in the prone position cut out the fistulas with small incisions, and an incision about two centimeters long is made on the side, from which the wound secretion should drain. The procedure, which was developed by John Bascom in 1980, is always carried out on an outpatient basis under local anesthesia. The postoperative period is called almost painless and uncomplicated so that most patients can go back to their daily life immediately after the procedure (including sport and work) can pursue. It is based on the knowledge that the fistula ducts (pits) of the gluteal folds are lined with skin over a few millimeters into the depth. This provides a kind of rail for pathogens, dead skin cells and hair to migrate under the skin. There these can be deposited and cause inflammation. Based on this theory, during “pit picking” the open fistula ducts (pits) are “picked” and scarred. This closes the “pits”, thereby closing the inflamed cavity. The "pits" of the gluteal folds are made with very small incisions (1-3 mm in size) "Picked out", if necessary (advanced inflammation) a small relief incision of 10 to 15 mm is made on the side of the gluteal fold, which allows inflammatory secretions to drain off. The entire pit picking procedure only takes a few minutes.
A bandage is applied after the procedure. In some patients there is a small circulatory weakness postoperatively, but this is harmless. Small secondary bleeding is also possible, but is then immediately stopped. It should be noted that the Recurrence rate in this procedure at approx. 20% lies. This means that statistically one in five people can suffer a relapse. In contrast, the risk for women is only 4%. Smoke and Increase excess weight the risk by a further 10 to 15% each time.
After the operation, all daily activities are possible without restrictions. After about 2 to 3 weeks, the wound should be dry. However, there may also be delays. However, the wound should be healed after 6 weeks at the latest.
3. Laser treatment
In principle, it is possible to treat a coccyx fistula with a laser treatment. However, it should be noted that laser procedures are based on the current state of medical recommendations no real importance in the primary treatment of coccyx fistulas. Compared to conventional procedures such as surgical excision or minimally invasive intervention, laser treatments are negligible. It is not certain to what extent a laser treatment can prevent a relapse of the disease and therefore no recommendation for such a treatment can be made. However, there are clinics that offer laser surgical procedures. It is about microsurgical interventions, for which only a small cut of a maximum of 5 mm in size is usually sufficient. The tissue of the fistulous duct is then effectively destroyed with the laser, the surrounding tissue should be spared as much as possible. The follow-up treatment of such interventions is very easy, as only small wounds are created that heal quickly. Laser treatment is currently still of particular importance in the post-treatment of coccyx fistulas. Hair can be removed from the affected area using laser epilation. No recommendation has been made for this at the moment either, as it has not been sufficiently clarified whether laser hair removal actually prevents the formation of a new coccyx fistula or whether the use of laser epilation is obsolete.
Juxtaposition
The Karydakis method is a surgical method in which the ends of the tissue are sewn together again under compulsory general anesthesia after the entire fistula system has been removed, or the wound heals open. This type of surgery can be performed on almost any patient, while pit picking is not always possible.
Also with the Pit-picking method decisive how long the fistula has existed, because the earlier it is treated with this surgical method, the lower the relapse rate.
In the case of the Karydakis operation, the period does not matter and Fistulas of all ages can be treated.
How to proceed after the operation

After a conventional operation (according to Karydakis) is almost always a inpatient hospitalization about three to four days necessary.
First upon discharge the drainage inserted during the operation (the tube that conducts secretion from the surgical wound) is pulled out. If Threads have been sewn in, these will be Removed 10 days later by the family doctor.
If the surgical wound is not closed and the wound is treated openly, a very long treatment time must be planned. Of the Association has to go through a large amount of wound exudate changed at short intervals or the sponge for vacuum wound treatment (NPWT) be replaced. For a time set by the doctor, the patient becomes are not allowed to sit or lie on their back. Sitz baths can be taken to aid wound healing, and the wound should be removed after a bowel movement carefully washed out with water become.
If the procedure was performed under general anesthesia, the patient is prohibited from driving or driving other vehicles or machines on that day or for 24 hours.
For the Pit picking is a healing time of about 4 weeks scheduled. After this time one should also control examination occur. After these four weeks, after a successful operation, no more wound secretions should be found in the underwear or the insert. Before that, this is completely normal, even if it sometimes contains pus.
During the healing period after pit-picking, patients are allowed to do anything in terms of sport, bathing, sauna etc. However, it should Avoid shaving on the treated area become. There the wounds through the small pits are comparatively small special wound treatment is usually unnecessary. Only Of course, cleanliness should be ensured.
If a coccyx fistula occurs again, the pit picking can be repeated.
Pain
Especially minimally invasive procedures such as the "Pit picking“Or other outpatient procedures can be relative for the patient painless be. Intraoperatively, the area is numbed with either regional or local anesthesia so that there is no pain during the operation, even in awake patients. Occasionally you feel a kind pressureBut not pain. With general anesthesia, the patient is also pain-free during the procedure. Postoperatively, the minimally invasive interventions tend to be relatively painless. If necessary, usually Ibuprofen prescribed for pain relief. Open surgery or complicated wound healing can lead to more severe pain, but this does not necessarily have to be the case.
Whether there is pain and how severe it is varies greatly from patient to patient and should be discussed individually with the attending physician. With good wound healing, one is usually sufficient Reliever medication With Ibuprofen out. The pain intensity is greatest in the first postoperative days and sounds after about 3 to 4 days clearly. Often times, the pain does not start until the second postoperative day. However, there are also many patients whose healing process is largely painless, so that great pain is not necessarily to be assumed. The size of the wound also shows no linear relationship with the pain intensity.
However, if very heavy bleeding, pain or other complications such as a wound infection occur, it is advisable to contact the treating doctor immediately and discuss this.
Rebleeding
Secondary bleeding can occur in the postoperative wound care of a pilonidal sinus occur. They are more common with the secondary (open) Wound healing. If the wound is closed with a suture intraoperatively, secondary bleeding is somewhat less common and postoperative care is easier. With primary wound closure (wound is closed with a suture), however, the recurrence rate is significantly higher than with open wound healing, so that the latter is often preferred.
In order to avoid or prevent secondary bleeding, it is important to be careful and careful Care of the wound important. This will usually be showered once a day or with one Octenisept ointment creamed and freshly bandaged. There are sometimes different opinions about wound care. Some doctors do not recommend showering the wound, as this leads to mechanical stress on the healing tissue and thus possibly to secondary bleeding. It is important to carefully loosen the bandage in order to seal the wound save. Postoperative care is often provided on an outpatient basis in the treating practice or clinic in order to ensure good wound management and to minimize the number of secondary bleeding. If care is provided at home and you are unsure about care, it is advisable to contact the treating physician. In addition, strict wound healing should be ensured Abstinence from nicotine to be available. This also promotes quick and good wound healing.
How long can I not do sports after the operation?
For an operated coccyx fistula to heal, it is necessary to care for and close the wound as well as possible save. Otherwise wound infections, pain and bleeding can occur. In terms of postoperative care and rest periods, there are primarily differences in the treatment of open wounds compared to primarily closed wounds. It is not possible to give precise information in advance about how long the definitive healing will take. Usually it takes time at least two weeksuntil medium and small wounds have healed. In addition, however, you should also ensure that the tissue is not stressed too much during sport.
At a open wound healing however, wound closure can also up to 8 weeks last. In the first few weeks after the operation, the healing process can be better assessed so that more precise statements can then be made about the duration of the sports leave.
At a "Pit picking"-OP, however, it is possible Exercise again immediately after the operation close. However, not all fistulas are suitable for this. In particular, patients who in the past have often presented to the doctor with coccyx fistulas and have been operated on are less suitable for this procedure, as it is up to 20% to Relapses can come.
Complications
As with any operation, the operation of a coccyx is of course not without risk.
Secondary bleeding are particularly to be feared with the open type of operation and wound treatment. Due to the open wound treatment, improper treatment can easily cause germs to move into the wound and wound infections can occur.
If this is the case, the risk of renewed fistula formation elsewhere also increases. Up to 10% of those affected are affected by wound healing disorders after an operation.
Depending on the place where the fistula occurs and the size of the area of the fistula ducts and the cyst underneath, it is not infrequently unavoidable to remove parts of the sphincter with what the Fecal incontinence has the consequence, i.e. the inability to hold the stool and controlled bowel movements.
In the case of the Karydakis operation, the removal of tissue over a large area can lead to a persistent numbness on the bottom caused by injury to superficial skin nerves.
All possible complications are discussed with those affected in an informed consent discussion.
Alternatives to surgery
The alternative therapy methods include therapy with Anoint or with corresponding Sitz baths, which are also supposed to alleviate the inflammation.
If a coccyx fistula has healed, one can improved hygiene in the buttocks area prevent a fistula from recurring.


.jpg)