Damp pleurisy
introduction
The Pleura is a thin skin that lines the inside of the chest (pleura) and also covers the outside of the lungs (pleura). The Pleura is traversed by many nerves. Because of this, it is also extremely sensitive to pain.
The function of the pleura is to form a sliding layer for the breathing movements of the lungs.
In medical parlance, the pleura is called Pleura designated. A pleurisy becomes consequent pleurisy ("Pleura": pleura; "-itis": inflammation) called. Wet pleurisy (exudative pleurisy) is a subgroup of pleurisy in general. In contrast to this is the dry pleurisy (Pleurisy sicca).

causes
As root cause for one pleurisy there are many different options. Microorganisms (often bacteria, less often viruses or fungal infections) can be involved in the development of pleurisy. In the past, pleurisy often occurred in the course of tuberculosis Disease, but has become rare in everyday life in Western Europe today.
In addition to these infectious forms of pleurisy, there are also causes that are non-infectious, such as toxic substances that can be both chemical and physical in nature and trigger pleurisy. For example, it can happen that a pleurisy after a Radiation treatment occurs.
Also as a result of one Vascular occlusion (Pulmonary embolism) lung infection or pancreatitis, pleurisy can occur when the pathogens spread to the pleura.
If the person concerned suffers from a malignant disease, so can the Lung tumor cause pleurisy. Other non-infectious causes can be rheumatic diseases, processes after trauma or operations.
Symptoms
At a moist pleurisy collects liquid (Pus, blood) between the pleura and pleura, these are called Pleural effusion. In contrast to dry pleurisy, it may well be that those affected hardly feel any pain, the pleural effusion is primarily responsible for this.
Depending on how extensive the pleural effusion is, a Shortness of breath occur because the lungs have less space to expand.
Unspecific symptoms such as fever, cough, or feeling very sick can also occur. The breathing with pleurisy is usually flat in order to keep the respiratory-associated pain as low as possible. Due to the flattened breathing, the inflamed parts of the lungs lie on top of one another for longer than usual and there is a risk, especially with moist pleurisy, that the pleura and the pleura will grow together.
diagnosis
First of all, the doctor will try to find out more about the symptoms through a conversation. As part of a physical examination, the breathing movements are analyzed and the sounds of the lungs are examined by auscultating with the stethoscope and tapping with the finger.
In the case of wet pleurisy, you can typically hardly hear a rubbing sound when listening, as is the case with dry pleurisy. The pleural effusion also changes the sounds when tapping the lungs.
Furthermore, fever should be measured and the blood examined in the laboratory in order to determine inflammation values.
Read about this too Pleural puncture
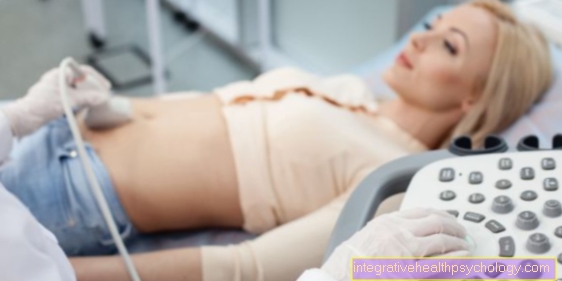
With the imaging diagnostics additional knowledge can be gained: In the case of a damp pleurisy, the typical Pleural effusion on ultrasound represent well. The pleural effusion can also be punctured under the sonographic display, i.e. the fluid is transported out of the body through a needle in order to relieve the pleura and lung pleura. The fluid obtained during the puncture can be examined in the laboratory for pathogens and be an important clue for the following treatment.
Also in one X-ray examination an accumulation of fluid in the lungs can be visualized and the diagnosis of wet pleurisy can be confirmed. One advantage of the X-ray is that concomitant diseases (pneumonia, tuberculosis, malignant processes). In any case, it is important to determine the cause of the damp pleurisy and exclude a tuberculosis disease by screening (tuberculin test, diagnosis of sputum and gastric juice). If necessary, a computer tomography can also be performed.
Complications
As complication pleurisy can lead to it Adhesions of the pleura (pleura). This is due to the shallow breathing of wet pleurisy, which means that the pleura and the lungs lie on top of each other longer than usual. If the two parts of the pectoral skin stick together, this results in a functional disorder in breathing, as the lungs are restricted in their ability to develop.
therapy
While the pleurisy is bed rest indicated to protect the body. If you get better with a Breathing exercises started to train the lungs and prevent the formation of rinds.
In the case of uncomplicated processes, the administration of painkillers can be helpful. Since coughing can be very painful with pleurisy, the urge to cough is suppressed by cough suppressants.
In the case of productive coughing with sputum, it does not make sense to inhibit the urge to cough, because the mucus should then be removed.
The other medical therapy depends on the Cause of pleurisy. A moist pleurisy caused by bacteria is treated with antibiotic drugs. The inflammatory process can also go through cortisone medication be contained. At the same time one tries to prevent adhesions. If the inflammation or effusion causes severe shortness of breath, oxygen can be administered through a nasogastric tube or mask.
The pleural effusion should in any case be drained from the chest in good time. This can be done through a Puncture happen. An operation may be necessary if the pleura and pleura are strongly fused and the function of the lungs is restricted. Unfortunately, in very late stages it is not always possible to restore the lungs' efficiency. The earlier and more effectively you begin to treat a damp pleurisy, the shorter the duration and the better the prognosis.

.jpg)