Paget's disease
Important NOTE:
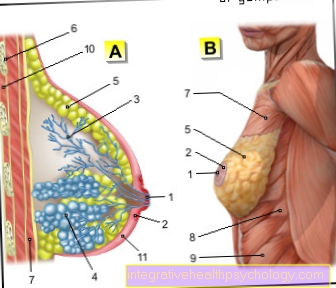
Paget's disease is used synonymously for two different diseases. On the one hand, Paget's disease is a disease from the field of gynecology and cancer.
Paget's disease from the field of gynecology is a malignant tumor (cancer) of the milk duct in the area of the female nipple.
The following topic deals exclusively with Paget's disease from the field of orthopedics.
Synonyms in a broader sense
- Osteitis deformans
- Osteodystrophia deformans
- Paget's disease
English: Paget's disease
definition
In which Paget's disease it is a localized osteopathy (= bone disease).
As part of this disease it comes to excessive bone remodeling. This conversion ultimately leads to a abnormal bone structure. It is through these bone remodeling and abnormal bone structures that the affected become bone prone to breakage (e.g. Femoral neck fracture) and deformations (deformation of the bones).
The clinical picture of Paget's disease can occur from the age of 40. The average age of those affected is 60 years. As the disease usually no particular or “typical” complaints causes and in most cases is diagnosed rather “by chance”.
At the beginning of the disease, an increased activity of the so-called osteoclasts (= cells that break down bone substances) can be demonstrated.
One distinguishes one asymptomatic and one symptomatic course the disease.
Under a asymptomatic course one understands that the disease was diagnosed as a so-called "incidental finding" and not a main place of manifestation (by this one understands a Cookwho suffers particularly badly from Paget's disease) can be fixed.
Patient with a symptomatic course to have Pain especially on the musculoskeletal system (especially: Spinal discomfort).
frequency
As already mentioned above, illnesses occur Paget's disease usually from the age of 40. The average age is assumed to be around 60 years.
The probability of illness is approximately 1 : 30 000, this means that on average there is one patient for every 30,000 people with an increased probability of Paget's disease.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
causes
Currently, the exact cause of the Paget's disease still unclear.
It becomes something called a Slow virus infection of the skeleton discussed, which is now also regarded as apparently likely.
Under one Slow virus infection one understands one Viral infection, which progresses slowly through months to years of incubation. As the cause of the Paget's disease in particular, a virus infection with something called Paramyxoviruses viewed.
This Paramoxy viruses promote the activity of Osteoclasts (Cells that break down bone substance). This overactivity accelerates the breakdown of the bones Osteoblasts (= Cells that form bones) then cause this increased bone breakdown Attempted reparations balance.
As a result of these attempts at reparations, a rushed and uncoordinated bone cultivation occurs. Upon closer examination of these bone additions, it becomes apparent that they are a under-mineralized bone structure exhibit, which is why there is deformation and very quickly and easily too Broken bones can come.
Symptoms
As already described above, one distinguishes one asymptomatic and one symptomatic course the disease.
An asymptomatic course is understood to mean that the disease was diagnosed as a so-called “chance finding” and no main manifestation site can be determined.
Patients with a symptomatic course have pain especially in the musculoskeletal system (especially: Spinal discomfort).
All two courses of the Paget's disease has in common that due to the increased activities of the Osteoclasts more waste products have to be eliminated from the body.
These "waste products" include, for example, amino acids (especially Hydroxyproline) and can be detected in the urine.
The Osteoblasts however, try to build bone mass and balance the osteoclast process.
This activity can be proven, for example, by a blood test / laboratory values. The increased activity of the osteoblasts leads to an increase in the enzyme "alkaline phosphatase"(= AP). Alkaline phosphatase is found in many organs, such as also the liver before, so it is important to use the "cooking-specific AP" = ALP or Ostease, im blood to determine.
Which parts of the body from Paget's disease affected can be different. Whether there is a main place of manifestation (symptomatic form of Paget's disease) varies from person to person.
Possible symptoms of the Paget's disease are listed below:
- Deformations of the bones
- Increased probability of fractures (risk of bone fractures)
- local pain
- Cardiovascular stress
- Muscle spasms through incorrect loads
- Overheating due to the formation of new blood vessels
- Varicose veins (Varicosis)
- Narrowing of various nerve tracts (nerve compression)
Formation of malignant relapses (= neoplasms) (rather rare: <1%), transition to a Osteosarcoma.
diagnosis
That is of the utmost importance X-ray image, because there in the early stages of the disease the Osteolysis (Bone dissolution) and later the coarse-stranded structure of the cancellous bone typical of the disease (= spongy structure of fine bone beams) can be demonstrated.
The increased bone remodeling can also be done with a Bone scintigraphy prove and represent. As a rule, these bone remodeling is confirmed by means of an X-ray image following the scintigraphy.

Scintigraphy Paget's disease
One can very well see the strong accumulation in the right thigh bone (Femur) through the high activity of bone metabolism
A increased osteoclast activity however, leads to increased degradation and consequently to the formation of waste products that have to be eliminated from the body.
These "waste products" include, for example, amino acids (Hydroxyproline) and can be in urine be proven.
As already described in the subsection "Symptoms", the increased activity of the osteoblasts can be demonstrated by the increase in the enzyme "alkaline phosphatase" (= AP), especially the "bone-specific alkaline phosphatase" ALP.
In terms of differential diagnosis, however, a Liver disease excluded, as this can also be held responsible for the increase in AP.
In cases where the diagnosis is still unclear after all examination methods, a Bone biopsy (Obtaining a tissue sample) can be carried out.
Furthermore, Paget's disease needs differential diagnosis
still from Bone metastases and other bone diseases such as the Osteomalacia (= increased soft tissue and bending tendency of the bones due to the inadequate incorporation of minerals into the osteoid).
General
Involvement of the skull bones mostly falls through one deformation or Increase in size of Skull because it becomes visible quite early on the head due to the lack of fat and connective tissue. For example, patients report that hats or helmets no longer fit properly.
roentgen
Is there a suspicion that the Skull bones from Paget's disease are usually affected first X-ray image made of the skull.
in the Early stage the disease are in it focal point, oval bright spots recognizable on a beginning Bone loss (Osteolysis) indicate. Later comes due to the "repair attempts" bone-building cells (Osteoblasts) excessive production of bone substance, which is reflected in the X-ray image by a Broadening of the skull bones with irregular bone structure ("Cotton skull") shows. The changes usually begin in the area of the Frontal bone and Occiput and can refer to the Temporal bone overlap (Osteolysis circumscripta cranii). Also Fractions of the skull, which can occur as a result of bone loss as part of the disease, can be visible in the X-ray image.
Scintigraphy
An x-ray of the skull should, however not by default with each patient Paget's disease only if there is evidence that the skull is affected.
In addition to the occurrence of symptoms, this is also the case, for example, if during the initial diagnosis a Scintigraphy is carried out in which an enrichment of the radioactive marked substance in the area of the head is noticeable. This means that a increased Metabolic activity close in the skull bones, which is typical of an infestation with Paget's disease is.
CT and MRI
A CT or MRI can be done to other medical conditions like osteoporosis or Metastases exclude cancer as a possible cause. Also possible for clarification Complications sectional imaging by means of CT or MRI makes sense. If the skull is involved, this is particularly recommended because of the deformation of the bones Brain tissue or annoy can be compressed.
Neurological examination
Therefore, if you have Paget's disease of the skull, you should also have a neurological examination as well as a Examination of hearing done because in 30 to 50 percent it comes to a Hearing loss because of a Narrowing of the auditory nerve or one Damage to the ossicles. A Damage to the optic nerve or other cranial nerves is less common but should still be excluded.
Bone biopsy
Relatively seldom does one have to Tissue sample of the bone (Bone biopsy) can be removed. This diagnostic method is only necessary if after CT and MRI exams continued suspicion of one Bone metastasis or a so-called Paget's sarcoma consists. The latter is one malignant bone tumor (Osteosarcoma), which at one percent of patients as a result of Paget's disease out degenerate osteoblasts arises.
Laboratory examination
As with all other forms of the disease, the Paget's disease of the skull an increase in the enzyme alkaline phosphatase (AP) or the bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in the blood and an increase in Hydroxyproline in the urine be detected. These laboratory values are an important part of diagnosis and can be used for process control therapy.
Therapy of Mobus Paget
Primary goals of therapy one Paget's disease is the elimination of the pain and beyond that the stopping of the further progressive deformations (bone deformation) as well as the Inhibition of the osteoclasts.
Not in every case Therapy for Paget's disease must be carried out. A patient with an asymptomatic course of Paget's disease, in whom no deformations could be detected, usually does not require any therapy.
To Ziegler The indication for the treatment of Paget's disease is divided into three different stages
- Absolute indication for therapy
- Strong remodeling activities with an AP> 600 IU / l
- Bone pain
- Deformities (bone deformation)
- High risk of fractures (risk of bone fractures)
- Failure of adjacent nerve structures
- Infestation of the skull base
- Relative indication for therapy
- Average disease activity
- Feeling of warmth
- Involvement of the skullcap
- Preparing for operative therapy measures
- Heart failure (heart failure)
- no confirmed indication for therapy
- The patient is older than 75 years
- no symptoms
- less renovation activities
- only a few bones are affected
The following forms of therapy can be used individually Paget's disease hold tight:
- Elimination of pain with anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics
- Calcitonin therapy (self-injection of the hormone; Nasal spray) to reduce osteoclast activity
E 100 for one month, then E 300 for another 6 months - Bisphosphonates (e.g. Fosamax -> not approved for the treatment of Paget's disease) to inhibit increased bone loss
- Pain therapy and / or physiotherapy to support drug therapy
- Operative therapy (Joint replacement operations, adjustment osteomies)
Bisphosphonates for therapy
The following bisphosphonates are currently approved for the treatment of Paget's disease:
- Etidronate 400 mg / day orally 6 months
- Pamidronate 30 mg / week i.v. over 4 hours 6 weeks
- Tiludronate 400 mg / day orally 3 months
- Risedronate 30 mg / day orally for 2 months
- Zoledronic acid 5 mg short infusion 15 minutes once
The choice of the form of therapy and therefore in particular the drug therapy for Paget's disease must always be determined individually with regard to the substances administered, the dosage and the duration of the therapy. Combinations of the various therapeutic measures are also conceivable.