Mesalazine (5-ASA)
Introduction - What is Mesalazine?
Mesalazine (trade name Salofalk®) is an active ingredient from the group of so-called aminosalicylates. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and is used for chronic inflammatory bowel diseases. Mesalazine is the gold standard, particularly in ulcerative colitis, but it is also used in Crohn's disease.
Mesalazine is used both in acute episodes and in prophylaxis and inhibits inflammation and its accompanying complaints such as pain and diarrhea.
.jpg)
Indications for mesalazine
Mesalazine is a drug used to treat inflammatory bowel disease. This includes ulcerative colitis, a chronic inflammatory disease of the large intestine.
Mesalazine is used in acute attacks, the phase of severe inflammation with symptoms such as violent, sometimes bloody diarrhea. Mesalazine is also used in relapse prophylaxis. The use of mesalazine also leads to a lower risk of colon cancer, which is generally higher for those affected.
Mesalazine is also used in the acute phase of Crohn's disease, a chronic inflammation that can affect the entire intestinal tract.
Read more on the topic:
- Therapy of chronic disease
- Therapy of ulcerative colitis
Mesalazine for diverticulosis / diverticulitis
Many people, especially in old age, are affected by what is known as diverticulosis. These are protuberances on the intestinal wall. These diverticula acquire a disease value when the fecal stones cause necrosis and inflammation of the mucous membrane. One then speaks of diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis is usually treated in the hospital with antibiotics and a zero diet at the beginning; depending on the course, an operation may also be considered. In the case of mild forms of the disease, according to recent studies, antibiotics may initially be dispensed with; in addition to mesalazine, spasmolytics and painkillers can be used.
Mesalazine also appears to lower the relapse rate in diverticulitis. Nevertheless, the use of mesalazine in diverticulitis has not yet been adequately investigated and has not been included in medical guidelines.
Read more on the topic:
- Proper nutrition for diverticulitis
- Stages of diverticulitis
Active ingredient, effect of mesalazine
Mesalazine is also known as 5-aminosalicylic acid or 5-ASA because it is an amine derivative of salicylic acid. Acetylsalicylic acid, known under the name aspirin, is also a derivative of salicylic acid.
The chemical, which used to be obtained from the juice of the sparrow and is now artificially produced, has anti-inflammatory properties, has an antipyretic and analgesic effect. This is why mesalazine is used for inflammation such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Specifically, the active ingredient inhibits the formation of inflammatory mediators and the activity of cells that are involved in the inflammatory response of the immune system. The tablets are gastro-resistant and only take effect in the intestine. This is where the inflammation occurs in the context of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, which means that mesalazine is very effective.
How quickly can an effect be expected?
How long an episode lasts and how long the patient has to be treated in the acute episode depends on the severity of the disease. Mesalazine is usually prescribed in the form of suppositories or tablets for mild, acute flare-ups. If there is no improvement after several weeks, additional corticosteroids are used.
Read more on the topic: Side effects of cortisone
In the severe episode, mesalazine and corticosteroid tablets are used simultaneously (at the same time). Treatment should last at least four weeks. Therapy with mesalazine should also be continued at a reduced dose after the relapse to prevent relapse.
Read more on the topic:
- Ulcerative colitis flare-up
- Chron disease episode
- Medicines for Chron disease (sulfasalazine)
Dosage forms of mesalazine
Suppositories
Mesalazine in the form of suppositories is used particularly when the inflammation affects the later sections of the intestine, i.e. the rectum and rectum. The SuppositoriesAs suppositories are also called, they are usually inserted rectally three times a day, in acute treatment suppositories with 500 mg of active ingredient, in prophylaxis 250 mg.
Mesalazine suppositories are mainly used in ulcerative colitis, and use in Crohn's disease may also be indicated.
Read more on the topic: Drugs for ulcerative colitis
granules
Granules are granular to powdery forms of administration of the active ingredient mesalazine. One dose corresponds to one sachet of granules; in an acute flare-up, three sachets are taken daily. The granules are placed on the tongue and swallowed whole with plenty of liquid.
Tablets
Mesalazine tablets are gastric juice-resistant, which means that they get undigested to the place where they are supposed to develop their effect. Mesalazine in tablet form is suitable for inflammation of the intestinal tract, unlike suppositories and rectal foam, also in earlier sections.
Rectal foam
In ulcerative colitis, which mainly affects the rectum and rectum, mesalazine is also used in the form of rectal foam. Usually the dosage is two sprays a day before going to bed.
The spray can is provided with an applicator tube that is inserted anally. The sprays are administered one after the other by pressing the pump head. The tube is discarded after the foam has been administered. After using the rectal foam, the bowel should not be emptied until the next morning if possible.
Side effect of mesalazine
As with any medicinal product, side effects can also occur with therapy with mesalazine. The side effects of taking mesalazine tablets include stomach pain, diarrhea, gas, nausea or vomiting. However, these can also be symptoms of the underlying disease.
Other known side effects are headache or dizziness, less often sensory disturbances. Renal impairment and impairment occasionally occur during treatment. The therapy can lead to changes in blood values and blood counts (decrease in white and red blood cells, platelets).
There are some intolerances and hypersensitivities to salicylic acid and its derivatives, which can be accompanied by serious side effects. Mesalazine should not be taken if there is such an intolerance. Rectal applications such as suppositories, enemas or rectal foam can cause discomfort in the anus or the application site.
Read more on the topic: Medicines for diarrhea and medicines for gas
stomach pain
Abdominal pain is one of the most common side effects of therapy with mesalazine. These complaints cannot be clearly distinguished from symptoms of the underlying disease, which speaks for inadequate therapy. Patients should inform their attending physician about any side effects they may experience.
Read more on the topic: Home Remedies For Abdominal Pain - Which Are The Best?
Particularly severe pain in the abdomen can also be an expression of an acute pancreatitis, which is a very rare but serious side effect of mesalazine.
Read more on the topic: Therapy of pancreatitis
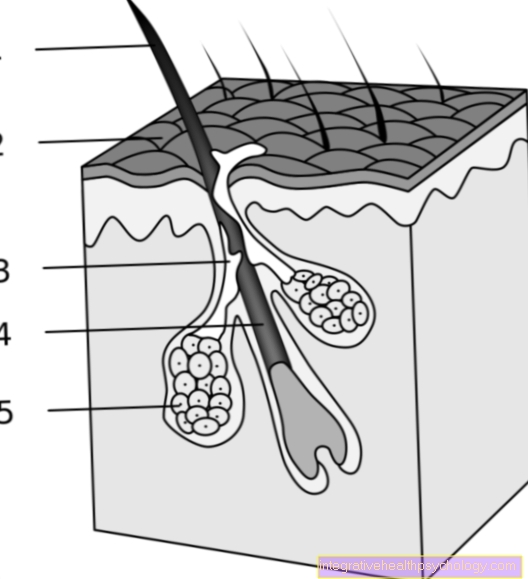
Hair loss
Hair loss is one of the possible side effects of mesalazine, which may affect less than 1 in 10,000 people (very rare). Both partial to complete hair loss have been reported. Hair loss can also be an expression of the underlying disease, since inflammatory bowel disease can also lead to a reduced absorption of minerals or nutrients.
Read more on the topic:
- Causes of hair loss
- Hair loss therapy
- Iron deficiency
What are signs of intolerance?
Intolerance to salicylic acid and its derivatives, including mesalazine, is an absolute contraindication for ingestion. Symptoms include, for example, itching and hives, i.e. the appearance of skin manifestations with redness and wheals. Fever, breathing problems or inflammation of the pericardium and heart muscle can also occur.
Read more on the topic:
- Wheals on the skin
- Symptoms of myocarditis
In case of uncertainty, patients treated with mesalazine should consult a doctor if similar symptoms occur and check for intolerance to mesalazine.
Interaction with other drugs
Mesalazine shows a wide variety of drug interactions.Patients should make the attending physician aware of the use of mesalazine when prescribing a drug. Interactions can reduce the effectiveness or increase the risk of side effects.
Mesalazine shows interactions with anticoagulants, the effect of which can be increased. The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding is increased. Mesalazine also shows interactions with sulfonylureas, blood sugar-lowering agents. This also applies to uricosuric drugs, agents that promote uric acid excretion. Diuretics such as spironolactone and furosemide also interact with mesalazine.
Glucocorticoids, which are used as anti-inflammatory drugs, increase the risk of unwanted side effects. Mesalazine also reduces the effects of rifampicin, an anti-tuberculosis drug. In combination with mercaptopurine, a cytotoxic and immunosuppressive agent, pancytopenia can occur, a severe reduction in all blood cell groups.
Effectiveness of the pill
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease repeatedly suffer from diarrhea. This can reduce the effectiveness of the pill and is not the first choice of contraception in the acute phase of the disease.
Mesalazine does not affect the effectiveness of the pill. Nevertheless, patients should discuss the possibilities of contraception with their gynecologist with regard to their disease and medication and, depending on the severity, resort to an alternative method. As alternatives to the pill, for example, hormone implants or hormone IUDs are conceivable. Effective contraception as long as there is no desire to have children is important, as particularly high-dose long-term medications in the course of severe disease carry a certain risk of damaging the baby.
Mesalazine and alcohol - are they compatible?
Alcohol has a negative impact on the course of inflammatory bowel disease and can promote an acute flare-up, which is why patients are generally advised not to consume alcohol.
The interaction between alcohol and mesalazine has not been adequately researched. Those affected should drink alcohol responsibly and in small amounts and, ideally, refrain from taking it. This is especially true for patients in an acute episode who are also being treated with cortisone.
Contraindications - When should mesalazine not be given?
Mesalazine must not be taken if there is hypersensitivity to salicylic acid and its derivatives (this includes aspirin). Serious liver and kidney dysfunction are also contraindications for use. Because of the increased risk of bleeding, mesalazine must not be used for existing gastric and intestinal ulcers (gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer). Mesalazine should also not be used in patients who have an increased tendency to bleed.
Mesalazine should only be taken on the advice of a doctor and under close medical supervision. In addition to blood and urine, monitoring of kidney function is recommended.
Dosage of mesalazine
Mesalazine should always be taken exactly as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. The usual dose of mesalazine tablets for the acute treatment of ulcerative colitis is between 1.5 g and 3 g mesalazine per day, divided into two to three individual doses.
In the acute treatment of Crohn's disease, between 1.5 g and 4.5 g are taken.
In the prevention of recurrence of ulcerative colitis, 500 mg are taken three times a day, i.e. a total of 1.5 g mesalazine per day.
Price of mesalazine
The costs of mesalazine vary depending on the provider and dosage form. Mesalazine tablets with an active ingredient content of 500 mg in a pack size of 50 tablets for around € 35, as a suppository of 500 mg in a pack of 30 for about € 57 and granulate bags with 1000 mg of active ingredient for about € 54 for 50 pieces.
Can be taken during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
Women who want to have children should definitely inform their doctor about this. Mesalazine should be taken after careful consideration of the risk-benefit ratio. While there aren't enough studies on this, mesalazine appears to be largely safe in pregnancy.
In general, women should wait for a phase of the disease when starting a pregnancy where no or only a low dose of the drug is required. If possible, treatment should be suspended for the last four weeks. Small amounts of mesalazine are excreted in breast milk, but breastfed infants show no abnormalities.
Read more on the topic: Medication in Pregnancy
Alternatives to mesalazine
Mesalazine is the first choice in the acute phase of ulcerative colitis. Patients with Crohn's disease also show a good response to the anti-inflammatory agent. In the case of particularly severe disease, the doctor will occasionally also prescribe cortisone.
If there is no response to the therapy, immunosuppressants are used that inhibit the inflammation. Medicines include azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, or antibodies such as infliximab. The last treatment option for both diseases is operative therapy.