Polymyositis
definition
A polymyositis is probably one immunological related disease of Muscle cells of the human body, which can lead to moderate to severe discomfort.
Also read more about the main topic Myositis and the related form, the Dermatomyositis.
Causes / forms

To date, the exact mechanism of the disease is not known. So far you are from a so-called autoimmunological The cause of the disease was assumed to be due to an excessive reaction of the human Immune system against endogenous Cells to corresponding Cell degenerations the muscles can come.
In any case, it seems to be correct that there is an infiltration of the disease white blood cells gets into the muscle cells. These have previously left the blood vessel and migrate into muscle cells. Why this happens is not known.
The discussion about the exact mechanism of development is still going on today and science is rather currently assuming various not yet fully explained causes why this clinical picture occurs. Besides the muscle cells can also Skin cells to be affected. In this case one speaks of one Dermatomyositis.
According to the current nomenclature five divided into different groups. In a group one will the idiopathic Polymyositis assigned. To the group two counts the idiopathic dermatomyositis. Idiopathic in this context means that the cause Not is known. To the group three become Polymyositides summarized, which are still accompanied by malignant neoplasms of the human body. These include on the one hand so-called neoplastic Syndromes (Tumors of the chest and the lung) such as Leukemias.
Do children suffer from polymyositis and is associated with it Vascular inflammation, one speaks of a group four classified polymyositis.
In the case of mixed images, this polymyositis belongs to the group five the division.
Symptoms
The symptoms of polymyositis are varied and therefore not easy to diagnose. The main symptom are Muscle achesthat occur for no apparent reason and that aching same. Also an accompanying one Muscle weakness can result from it.
General complaints such as exhaustion and fever as well as inflammatory changes in the Blood count. Also complaints in the field of Joints can occur and are common with Osteoarthritis or rheumatic diseases mistaken.
Depending on which muscle groups are also affected, corresponding complaints can occur in this area. Is the Larynx or the Respiratory muscles affected, swallowing or breathing disorders may occur; are rather the muscles of the extremities affected, impaired movement and reduced strength are often described.
In some cases the skin. One also speaks of one Dermatomyositis. In this case it comes to Skin irritation, Redness and Dandruff of the skin.
In addition to increased blood count Inflammation values sometimes too Muscle enzymes which are released into the blood due to the immunological process.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of polymyositis is difficult to make due to its diverse appearance. As a rule, a a flu-like infection, one rheumatological disease or one Drug reaction (e.g. Simvastatin) thought before the suspicion of polymyositis is directed.
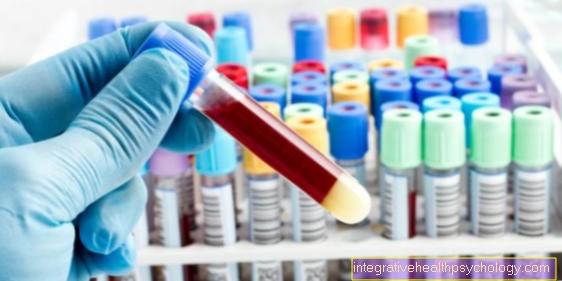
When making a diagnosis, it is first important to rule out the other possible causes. One of the most important diagnostic tools is that Blood test, in which inflammation values (white blood cells, CRP value, possibly rheumatoid factors) are determined. Only then can the diagnosis of polymyositis be made when viewed together.
Occurrence of antibodies in polymyositis
As a result of that Polymyositis some form of idiopathic Myositis and is therefore one of the autoimmune diseases, 90% of patients can have so-called Auto antibodies be found in the blood serum.
In about 60% of the cases, however, these are mostly antibodies that are directed against unspecific molecular biological cell components of the body's own cells, only in about 30% it is actually myositis-specific or myositis-associated antigens that the body falsely recognizes as foreign and fights .
The myositis-specific antigens include so-called tRNA synthetases, such as. Mi-2, SRP and Jo-1.
The corresponding myositis-specific auto-antibodies (MSA) which can exist and be detectable for these antigens in the patient's blood are therefore anti-Jo-1 antibodies, Mi-2 antibodies and SRP antibodies. The myositis-associated antigens include PM-Scl, SS-A-Ro.
These antigens are formed by the cells in a wide variety of different types of muscle damage and presented on the cell surface. In patients who are genetically predisposed to it, these antigens can then be recognized as foreign by the body's own immune system, so that an antibody-antigen immune reaction takes place, which leads to a chronic (muscle-) inflammatory process leads.
Blood tests for polymyositis
As part of the diagnosis of polymyositis, i.a. also the blood values determined, which in addition to the physical examination, tissue removal (Muscle biopsy) and the imaging procedures (Ultrasound, electromyography, MRI), represents a further investigation method.
Because it is a (muscle) inflammatory process that is triggered by the autoimmune reaction, the patient's blood usually contains increased levels of inflammation (CRP = C-reactive protein, ESR = blood sedimentation rate).
Elevated muscle enzymes that are released into the blood from the damaged muscle cells (CK-MM, GOT, LDH, aldolase, RF) are also noticeable. The level of these enzyme values also allows conclusions to be drawn about the extent of the disease or muscle damage and thus an impression of the current state of the disease can be obtained.
In addition, certain auto-antibodies that are involved in the characteristic autoimmune reaction can then also be found in the blood. A distinction is made between myositis-specific autoantibodies (MSA) and myositis-associated autoantibodies (MAA).
therapy
Due to the complexity of the clinical picture, the treatment of polymyositis is correspondingly difficult. Like all autoimmune diseases, treatment attempts are in the direction of Throttling of the immune system undertaken.
By cortisone and so-called Immunosuppressive the performance of the immune system is screwed down. Pain is treated with anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs (e.g. ibuprofen or diclofenac). Sometimes drugs known from rheumatology, such as MTX, are also used.
A physical one Protection can be useful if the muscle pain becomes very severe. However, it should be ensured that the muscles are not because of lack of exercise atrophy.
One of the last few approaches to treatment is that Filter of blood, from which plasma is withdrawn from the patient and purified before it can be infused again.
Is Polymyositis Hereditary?
Polymyositis falls under the broad umbrella of idiopathic myositis, a disease that is caused by an autoimmune reaction to the body's own skeletal muscle cell components.
Why the body initiates this wrong reaction in some patients has not yet been fully clarified, but familial clusters and certain hereditary characteristics indicate a possible hereditary component.
But in addition to the assumption that polymyositis is hereditary, certain environmental influences (e.g. Viral infections) and malicious Tumor diseases (e.g. lung, breast, stomach, pancreatic cancer) assumed to be the trigger for this autoimmune disease.