bruise
synonym
Contusion
Definition of bruise
A bruise is a painful event on bones or joints caused by trauma that is long-lasting and severe without visible injury. A bone contusion is usually associated with severe stress pain.
See also: How to treat a bruise

Causes / forms
First, one differentiates between a joint contusion and a pure bone contusion.
However, both arise from mostly blunt traumas.
The joint contusion occurs on the one hand during sport (e.g. soccer in duels), on the other hand in everyday life.
Most of the time, those affected hit a blunt object with the affected joint.
Knee joints, hips and elbow joints are often affected.
The most common cause is the edges of tables, chairs and cupboards.
A joint contusion also occurs in the form of a compression in complex injuries and is more of a side effect alongside serious injuries.
Furthermore, in the case of serious trauma, e.g. Car accidents or falls from great heights, in addition to frequent fractures, inevitably also bruises.
After a fall, the ribs or extremities are often bruised.
In addition to bone bruises, a distinction is also made between soft tissue bruises, in which the skin and the underlying tissue can often be sensitive to pain for several days to weeks due to blunt trauma.
The pain of a bruised bone is mostly triggered by irritation of the periosteum (periosteum) caused by the trauma.
The periosteum is very sensitive and excessive pressure or a bruise in this area can cause long-lasting pain.
In soft tissue bruises, the symptoms are triggered by the nerves running under the skin and in the tissue.
Furthermore, bruises in the bones, joints or even soft tissue areas lead to bruises in the overlying tissue and thus to an increase in pressure under the skin. This increase in pressure can also irritate the nerves and be painful.
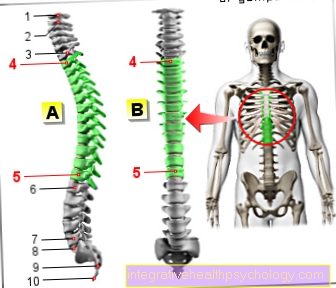
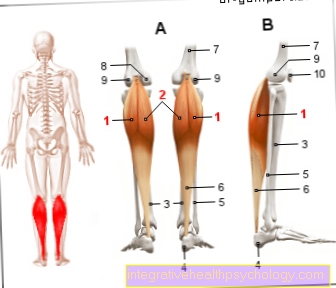
Figure bruise

Bruise - Contusio
A - joint contusion (1-6)
B - Bruised bone (7, 9, 14)
C - Bruises of internal organs (12)
D - muscle contusion (10, 13)
E - Nerve contusion (8, 11)
- Shoulder joint -
Articulatio humeri - Elbow joint -
Articulatio cubiti - Upper wrist -
Articulatio radiocarpalis - Hip joint -
Articulatio coxae - Knee joint -
Articulatio genus - Upper ankle joint -
Articulatio talocruralis - head
- Neck, shoulder, neck area
- Ribs
- Upper arm - Brachium
- Forearm -
Antebrachium (Ulnar nerve) - Internal organs
(Kidney, liver, spleen, intestine, etc.) - Thigh - Femur
- Shin - Tibia
Examples of a bruise:
Picture a - Knee joint contusion
Picture b - calf muscle contusion
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Symptoms
After bruises, those affected experience moderate to severe pain relatively quickly.
Most of the time there is swelling in or over the area of the bruise within a very short time.
In addition to the bones, soft tissues and muscles are usually affected by a bruise, so it can happen that the blood vessels in the affected regions are also affected by the injury.
There is bleeding - a bruise occurs.
When joints have been bruised, there is often not only swelling but also a pain-related impairment of function, i.e. certain movements can no longer be performed due to the pain.
Often there are also bruises of the rib cage and ribs. In this case, in addition to severe pain in the ribs, patients also complain of breathing problems. Because breathing and moving the chest move the affected ribs and the pain intensifies. Similar symptoms also show up with a broken rib.
Read more on the topic: Broken ribs or bruised ribs
diagnosis
A bruise is usually identified through a visual diagnosis and physical exam.
A swelling or the presence of a bruise in connection with the trauma described makes the examiner think of a bruise. Joints and bones are felt (palpation) and the areas that are particularly painful are identified.
The most important differential diagnosis of a bruise is the fracture (broken bone).
Patients who complain of pain, swelling or restricted mobility and who report trauma must first be examined and a fracture in the relevant joint or bone must be excluded.
X-rays are particularly suitable for this.
In the case of bruised ribs, broken ribs in particular must be ruled out. Here it is particularly important to prove that none of the ribs have loosened and injured parts of the lungs. Here, too, an X-ray is usually sufficient (so-called hemithorax = one-sided image of the chest and ribs).
Furthermore, a so-called pneumothorax must be excluded in the case of specified breath-dependent rib pain. This is a detachment of the lungs from the thorax and a purring together. A pneumothorax is excluded by an X-ray of the entire chest (chest x-ray).
Read more on the topic: Chest x-ray (chest x-ray)
If no trauma is reported, a heart attack must always be ruled out given the pain in the rib area (writing an EKG, determining the heart enzymes).
therapy
Most of the bruises can be treated conservatively.
This conservative therapy mainly consists of adequate pain therapy, which consists of drug-based pain therapy and physical pain therapy.
The physical measures usually include cold treatments, but heat treatment can also be perceived as pleasant by the patient. Since horse ointment has both a warming and a cooling effect, it can be used to relieve symptoms by applying it to the outside of the affected area.
Furthermore, the areas affected by a bruise should be immobilized and not stressed. A cast to immobilize is not necessary.
Elevating the extremities can also provide pain relief.
If the ribs are involved, respiratory therapy should also be carried out in any case, as the patient complains of pain with every breath and automatically starts breathing freely. Breathing therapy prevents pneumonia and respiratory insufficiency that may be triggered by this breathing.
Joint contusions in particular can often be accompanied by injuries to the joint, ligaments and capsule. In this case, surgical treatment should be discussed.
Should a bruise be warmed or cooled?
Initial and immediately after the injury occurred must have a bruise with ice be treated. Cold therapy is part of the acute measures according to the PECH rule for sports injuries such as bruises, strains or sprains: P = break, E = ice, C = compression and H = elevation. Are best suited Ice sprays or but Cooling pads. In order to achieve a simultaneous compression, a bruised area can also be used if necessary cold, tight-fitting compress be placed.
Cooling can also be achieved by applying the pain and inflammation-relieving drug Voltaren Emulgel® or quark wraps.
A few days after the bruise can from the cold to the Heat therapy change. In the further healing process, it is necessary to supply the bruised tissue with sufficient oxygen and nutrients and at the same time to transport away the inflammatory infiltrate. This can be achieved through increased blood flow due to vessel widening based on heat therapy.
In contrast, in the acute situation, the vessels contracted due to the cold, so that the blood flow was reduced and less inflammatory infiltrate and blood could penetrate the tissue. So one could Counteracts swelling and severe pain become. However, once the healing process has progressed, heat therapy becomes more important. Heat pillows, heat patches or a visit to the sauna are suitable for this.
Treatment of the bruise with Wobenzym®
The Wobenzym® is a drug which is added to the anti-inflammatory drugs counts. It consists of a combination of the two enzymes bromelain and trypsin as well as rutoside, a flavonoid. Usually it comes in the form of Tablets applied. The Wobenzym® is not only used for a bruise but also for example strain or also at Joint pain owing to rheumatism or arthrosis.
Namely, it has the property of reducing the symptoms of inflammation by a increased blood flow to improve. Due to the increased blood flow, on the one hand the inflammatory infiltrate is transported away more quickly and on the other hand the bruised area with it more oxygen and nutrients supplied so that regeneration takes place more quickly. The Wobenzym® stimulates the body's own healing processes, so to speak.
The advantage of the Wobenzym® is that by using both the Relieved pain as well as one Decongestion is brought about. Thus, Wobenzym® is superior to pure painkillers. The treatment of a bruise with the help of the Wobenzym® ultimately aims to eliminate the cause of the pain, i.e. the inflammatory process. Especially when after a bruise only one short regeneration time is desired, the Wobenzym® is used.
Please also read our page Wobenzym®.
Treatment of the bruise with Traumeel®
Traumeel® is a medicine from homeopathy, which is mainly used for bruises, but also for strains, sprains or severe bruises. Traumeel® is available as tablets, creams, ampoules or drops. It contains a total of 14 different active ingredients, which in combination show an optimal effect. These include comfrey (= Symphytum officinale), Bergwohlverleih (= Arnica montana), Monkshood (= Aconitum napellus), Yarrow (= Achillea millefolium), Daisies (= Bellis perennis), Johannis herbs (= Hypericum perforatum), Chamomile (= Matricaria recutita), Lime sulfur liver (= Hepar sulfuris), Purple coneflower (= Echinacea purpurea), Marigold (= Calendula officinalis), Narrow-leaved sun hat (= Echinaea angustifolia), Deadly nightshade (= Atropa bella-donna), Magic bush (= Hamamelis virginiana) and a mixture with the main component mercuroamidonitrate (= Mercurius solubilis Hahnemanni).
Traumeel® is very well suited to relieve the pain of a bruise and to promote the healing process. Traumeel® can be taken in the form of tablets or drops, but can also be applied directly to the bruised area as an ointment or gel.
Read more about this on our website Traumeel® .
Treatment of the bruise with Voltaren Emulgel
Voltaren® is a pain and inflammation relieving drug that has a wide range of applications. It is used very often, especially for bruises, as it can combat the main complaints such as pain and swelling. The active ingredient of Voltaren Emulgel® is diclofenac, an arylacetic acid derivative, which belongs to the group of so-called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition to relieving pain and inflammation, diclofenac also inhibits fever, so it has an antipyretic effect.It works by inhibiting a special enzyme so that certain substances for the inflammatory process can no longer be formed.
Voltaren should be applied locally to the area and lightly massaged in. It is important that the skin is intact, which by definition is actually the case with a pure bruise. In addition, Voltaren Emulgel® should be used as soon as possible after the injury so that it can achieve the best possible effect. Another positive side effect is the cooling properties of Voltaren Emulgel® due to its watery and alcoholic base.
Read more about this on our website Voltaren Emulgel®.
Home remedies for bruises
In treating a bruise, one can make use of some home remedies that the conventional therapeutic measures meaningfully complement or even as effective alternative can be used. With the help of various home remedies, it is possible to alleviate the symptoms of a bruise: Pain, swelling and bruises can thus be easily combated.
As part of a Cold therapy help to reduce pain and swelling particularly well Quark wrap. Depending on the location of the bruise, the curd can either under a bandage be wrapped or else in a sack be pressed on the bruised area. Alternatively, the use of peppermint oil a cooling effect.
Against the Pain There are also various essential oils, herbs, or other substances that can help relieve a bruise. These include, among other things Tea tree oil, the Marjoram leaves and a Combination of finely chopped parsley and whipped egg white.
The healing process of a bruise can also be accelerated or supported by fighting the inflammation, which is associated with a reduction in swelling and pain. A blood circulation-enhancing agent with just that effect is Rubbing alcohol. This contains, among other things, substances such as Mountain pine oil, Juniper berry oil, Spruce needle oil and menthol.
Creams or ointments that contain substances such as arnica, Comfrey, menthol, rosemary, Marigold and Horse chestnuts contain. In addition, the use of the Schüssler salt No. 3, the so-called "Ferrum phosphoricum“, Can be used in the treatment of a bruise.
Most of the components of the home remedies mentioned so far can either be found in your own herb garden or available at the pharmacy, so that you can make the appropriate remedies yourself if you need and if you are interested. In general, if Persistence of the complaints Home remedies should not be used alone, but a consultation with a doctor is advisable in order to rule out serious illnesses.
Duration of a bruise

The duration of the healing time can vary greatly from affected person to affected person if there is a bruise. In this context, the extent of the injury and the time at which treatment is started play a decisive role. In most cases, the pain felt by the affected patient can be effectively alleviated with simple measures. In addition, the rapid initiation of suitable therapy can significantly shorten the healing time of the bruise. Mild pain relievers (Analgesics) such as ibuprofen or paracetamol are taken. In addition, analgesics that contain the active ingredient diclofenac are particularly suitable for relieving bruise-related pain. Special ointments, creams and cooling gels can also be used to further accelerate the healing process and thus shorten the time it takes for a complete recovery.
Nevertheless, the exact duration of the healing process in the presence of a bruise cannot be determined even with extensive rest and the use of beneficial drugs. In general, however, it can be assumed that the pain typical of a bruise will subside within a period of a few days. After the pain has subsided, the affected area no longer needs to be cooled. From this point on, the duration of healing can be further shortened by using red light, heat pillows or therapeutic baths. People who have a bruise should definitely refrain from any sporting activity. Excessive use of the bruised area can lead to serious complications and significantly increase the time it takes to heal. Overall, it can be assumed that the average time it takes for a bruise to heal completely is around six weeks. After this period, the affected area can slowly be brought back to stress.
Types of bruise
Knee contusion
A Bruise on the knee (Technical term: Knee contusion) is usually caused by an external force acting directly on the knee joint. The skin surface is usually not affected by this force. However, the tissue immediately under the skin is due to the high pressure pressed against the hard tissue (e.g. bone or the joint capsule). In rare cases, forces acting on the side cause this kind of displacement of the tissue and thus lead to the development of a bruise on the knee.
Regardless of the mechanism of origin, the enormous pressure exerts on the tissue Cracks in small and medium-sized blood and / or lymph vessels. Due to the fact that the surface of the skin is not broken even if the knee is bruised, the blood escaping from the vessels cannot escape and seeps into the spaces between the cells. The seepage of the blood leaking from the damaged vessels is therefore the actual cause of the formation of a bruise.
A bruise on the knee occurs in most cases while exercising exercise. For this reason, athletic people are particularly often affected by a bruise on the knee. In most cases, the subcutaneous fatty tissue just above the knee joint is also affected. Since the enormous pressure that leads to the formation of the bruise on the knee may also tear vessels within the joint capsule, one of the risks of knee bruises is the formation of hemorrhages in the joint.
Also read more on the topic: Bruise in the knee
A bruise on the knee should ideally treated asap become. Immediately after the first symptoms (such as swelling or pain) appear, the affected knee should be treated with a elastic bandage supplied and elevated become. It can also be prudent Cooling the knee region help to prevent consequential damage and shorten sports downtime. If there is a bruise on the knee, it is essential to ensure that any physical activity immediately should be set. Those affected who continue to exercise despite a bruise on the knee run the risk of extensive vascular injuries due to an acute increase in blood flow to the joints. The actual treatment of a bruise on the knee depends primarily on the extent of the disease.
Due to the direct vicinity, the thigh can also be affected by the bruise. Further information can be found on our website Thigh contusion.
Bruised shoulder
The mechanism of injury when the shoulder is bruised is usually based on a blunt external force. The shoulder contusion is a typical sports injury, particularly in the area of contact sports such as handball or rugby. But also in cycling or skiing, some athletes suffer a bruise from falling on their shoulder. In addition to the pain, sufferers complain of bruising, swelling and redness over the shoulder area. The pain also worsens when you move your shoulder.
Nevertheless, the shoulder must be slowly practiced in the healing process with the help of physiotherapists so that all degrees of movement are maintained. It is important here that the load must be kept as low as possible. Since the shoulder consists of a complex muscle and ligamentous system in addition to the bony structures, if a contusion is suspected, it must always be ruled out that there is a more serious injury or that other structures are additionally affected. An X-ray is particularly suitable for bone assessment. The muscular apparatus can be assessed using ultrasound or, if necessary, even an MRI of the shoulder.
As with any other bruise, the PECH rule should be implemented immediately as the first therapeutic measure, i.e. pausing, cooling, compression and elevation. It also makes sense to tape the bruised shoulder. In addition, pain relievers and pain and inflammation relieving ointments can be helpful.
Read more about this on our website Bruised shoulder.
Bruise on the wrist

In most cases, a bruise on the wrist is caused by typical injury processes. Most of the patients with a wrist bruise report using their wrists for support while falling. Even in the case of a bruise on the wrist, no injuries can usually be found in the area of the skin surface. If there is a suspicion of a bruise on the wrist, a doctor should be consulted immediately. In the wrist area in particular, bruises are often particularly painful. The prompt initiation of targeted treatment can prevent further leakage of blood and / or lymph fluid from the injured blood vessels and positively influence the healing process. Depending on the severity of the bruise on the wrist, different treatment measures must be taken. In most cases, decongestant dressings and anti-inflammatory drugs are particularly effective at treating a bruise on the wrist. If the pain does not decrease significantly within a period of one to two weeks when there is a bruise on the wrist, a doctor must be consulted again urgently. The greatest risk of a bruise on the wrist is the development of the so-called "muscle compression syndrome" which can often lead to permanent damage. Quick action is required for the affected patients. The dead tissue around the wrist must be removed immediately. Consequential damage can only be avoided with early intervention.
Bruise of the finger
Smaller bones, such as the finger bones, can also be bruised. In most cases, a bruise on the finger is a sports injury. Ball and contact sports are particularly predisposed. Balls in particular, such as volleyballs, hand balls or basketballs, which unhappily hit individual fingers and compress or twist them in the process, result in bruises. But finger bruises are also not uncommon in martial arts.
The symptoms of a bruise range from severe pain and swelling to bruising and redness. The joint capsule is often affected.
As a complication of a severe bruise, nerve tissue can be injured or irritated, so that those affected complain of numbness and abnormal sensations in the respective fingers. In this case, it is important to conduct an accurate diagnosis in order to rule out serious injuries.
Then, as with other bruises, it is essential to start treatment according to the PECH rule immediately. If a finger is bruised, a splint is often put on afterwards. Not just one, but at least two fingers are fixed and stabilized, as this can lead to an optimal healing process. Especially with bruises of the fingers, those affected should be patient and allow themselves enough rest and protection, as the fingers tend to be stressed again much too early in everyday life.
Read more about the topic here: Bruise of the finger, sprain of the thumb
Bruise on the thigh
A bruise of the thigh is usually the result of sports. A classic course of injury is, for example, that in football the opponent is his opponent in a duel rams the knee into the side of the thigh. This characteristic bruise on the thigh caused by an external force is also called "Horse kiss" designated. This is a bruise of the muscles, which with Pain and one dominant bruise goes hand in hand.
Since the tendon plate of the iliotibial band at the outer edge of the thigh does not give much, those affected sometimes feel an extreme Tension or pressure pain. In severe cases, a bruise on the thigh can result in a complication Compartment syndrome come. This is a phenomenon in which blood flow is cut off because the pressure from the swelling compresses the vessels and surgery is necessary.
In harmless cases, the same treatment recommendations apply to a bruise on the thigh as to other bruises. Hence this is immediate Pause, Cool, Compress and Elevate makes sense. As soon as the symptoms have subsided, you can resume sporting activity.
Bruise on the foot
Most bruises occur in the area of the foot. Hobby athletes in particular are often bruised foot affected. As a rule, the bruise on the foot occurs strong pain noticeable. In addition, the affected patients develop severe swelling and Bruising (Hematomas) along the ankle. A bruise on the foot not only restricts those affected by physical activity. In most cases, due to the location of the bruise, the Severely impaired everyday life. Since enormous loads continue to act on the foot while walking and running, a bruise on the foot often requires one significantly longer healing time.
However, the affected patients can positively influence the healing process by following certain rules of behavior. In this regard, appropriate treatment should be initiated immediately following the underlying event. If you have a bruise on your foot careful cooling Help accelerate the healing process within the first 15 to 20 minutes of the onset of pain. During cooling, however, care must be taken to ensure that the coolant is never placed directly on the surface of the skin. To avoid cold damage, ideally a thin towel should be placed between the coolant and the surface of the skin. In addition, creating a elastic bandage help relieve the pain caused by the bruise on the foot. Through the Elevation of the affected foot further sinking of blood and / or lymph fluid in the intercellular spaces can be avoided and the symptoms can be alleviated. After a bruise on the foot, a targeted drug treatment actively support the healing process. Especially herbal medicines (for example arnica) have so far proven themselves in the treatment of bruises on the foot. Arnica can be taken in tablet form or applied locally as an ointment.
Bruised ribs
There is a bruise of the ribs very painful. The reason for this is that there is little skin and fatty tissue over the ribs, so that the pain is felt comparatively more strongly than with bruises in other areas. In most cases, the cause of a bruised rib is one Fall on the chest area as part of a sporting activity or simply in everyday life when climbing or descending stairs. The pain from bruised ribs is common breath dependentwhat those affected find incredibly uncomfortable.
Therefore, they often breathe more shallowly and less deeply. In this regard, the risk of insufficient ventilation and a Pneumonia.
In most cases, those affected can pinpoint the point of pain, but the painful area often extends over several ribs away. By to cough, Sneeze or Laugh The pain is usually aggravated by the tension in the muscles in the chest that are connected to the ribs.Since the ribs, like a bony cage, have a protective function for some internal organs such as the lungs or heart, it is essential to clarify the integrity of the ribs in the event of severe bruises. In addition, to make sure that it is actually only a bruise and not a rib fracture, a X-ray respectively.
The therapeutically meaningful immobilization turns out to be a little difficult with a bruised rib, since the ribs are moved with every breath. Generally, after the PECH rule traded. Since the rib bruise is one of the most painful bruises, it is also a good and sufficiently strong one Pain therapy indispensable.
Bruised back
In most cases, a bruise on the back is caused by a Fall or hard impact caused. Affected patients feel severe pain if there is a bruise on their back. In addition, extended ones occur a short time after the accident bruises (Hematomas). Due to fluid retention within the damaged tissue, it can immediately after the accident severe swelling come. Since the bruise is traditionally caused by strong forces acting on the back, a specialist must be consulted promptly. A simple bruise on the back can usually not be distinguished from serious injuries through the clinic alone. For this reason, the presence of a bone fracture (technical term: fracture) in the area of the spine must be excluded. This is typically done through a targeted examination of the back and spine. If the findings are unclear, additional imaging procedures (for example the production of an X-ray).
Summary
Bruises are usually caused by trauma, usually blunt.
Mostly in sports accidents (especially joint injuries) or after falls (bruised ribs).
Swelling and bruising are usually visible in the affected area. The patients often complain of severe pain and restricted mobility.
A fracture must first be ruled out diagnostically, usually by means of an X-ray.
Bruises of the chest and ribs are particularly painful. They are usually caused by falls or car accidents. Mostly depending on the breath, they often cause complaints that last for weeks to months.
In terms of therapy, bruises are treated conservatively. This treatment consists of a physical therapy, which consists of cold applications, as well as an adequate drug-based pain therapy, which mostly consists of the drug group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Surgical therapeutic approaches should only be discussed if parts of the joint, the capsule or the ligaments have been injured, especially in the case of joint contusions.
Bruises are sometimes more difficult to treat than fractures and sometimes at least as painful and lengthy.



.jpg)