radiology
introduction
Radiology is a specialty in medicine that uses electromagnetic and mechanical radiation for scientific purposes or in everyday clinical practice for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Radiology is a rapidly developing and growing subject area that began with Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen in Würzburg in 1895.

Initially only X-rays were used. Over time, other so-called "ionizing rays" have also been used. Also the Magnetic resonance imaging is an aspect of radiology. It does not use ionizing radiation, but electromagnetic fields. Also the radiotherapy in therapeutic medicine is a sub-area of radiology. It is used, for example, in the Cancer treatment.
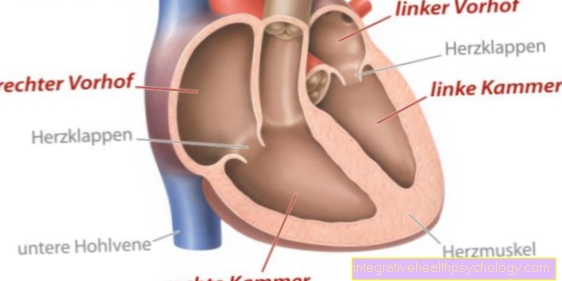
Radiology takes the largest part diagnostic Radiology in everyday clinical practice. The Ultrasound examination also represents a branch of radiology and is the most frequently used imaging radiological procedure. The simplest recording with ionizing radiation is the conventional one roentgen. An X-ray beam is generated with the help of two electrodes. A filament, the "cathode", sets small ones Electrons free and accelerates it strongly. The electrons hit the opposite second electrode, the "anode" and hit it so strongly that a so-called "Bremsstrahlung“Arises. The bremsstrahlung is the X-ray that is now directed onto the patient. The rays cross the patient and are recaptured and recorded on the other side. That used to happen on an X-ray film, today there is digital detectors for recording.
With the help of radiation, one takes advantage of the fact that structures in the body have different densities and consist of different materials. If rays hit them, they absorb part of the radiation. Depending on which areas of the body the rays cross, the stronger or weaker they are perceived and recorded on the other side of the body. These shadows then overlap to form a two-dimensional image and you get a snapshot of the inside of the body.
A Computed tomography (CT) works on a very similar mechanism. However, it provides more images from different levels and therefore more information about the inside of the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging is also frequently used in clinics (MRI). The MRI works with another, healthier ones Mechanism and mainly provides detailed information about the human Soft tissue.
Ultrasound, X-ray, CT and MRT have become indispensable diagnostic imaging methods in modern medicine. Some of them can be supplemented with the help of contrast media in order to be able to examine organ areas and structures with greater contrast.
roentgen
X-ray is the process of exposing the body to X-rays and recording the rays to convert them into an image. The CT examination also uses the X-ray mechanism. This is why CT is also correctly referred to as "X-ray computed tomography". If you mean the conventional simple X-ray in everyday clinical practice, it is also called "conventional x-ray"Or"Radiography". A conventional x-ray without contrast agent is called "native roentgen" designated.
Nowadays the X-ray image is registered on a photo film and chemically converted, but can mostly be digital Detectors can also be read in on the computer.
density Structures absorb the X-rays especially strong. With the help of this knowledge, the recordings can be quickly understood. bone thus cast a shadow on the film and appear whitish, air is on the other hand in the X-ray image black.
X-rays are particularly common in Broken bones applied. Since conventional X-rays only provide a two-dimensional image, depending on the fracture, a second shot another level. For example, a broken bone cannot be seen from the front, but can be seen from the side. There are standardized recording techniques known to doctors for this purpose.
The main area of application of conventional X-rays is therefore in the diagnosis of bone fractures.
It is also used to assess Heart- and L.unstructure, Mammography, Discovery of air-filled spaces in the chest or abdominal area or visualization of vessels. To represent Vessels the use of Contrast media on. Depending on how it works in the body, the contrast agent accumulates in the vascular or organ area that you want to display more precisely. For example, the representations of Arteries, Veins, Lymph vessels or from urinary system. The areas light up more strongly in the X-ray image and can be identified and assessed more precisely.
In the Dentistry X-rays are often made to identify caries between the teeth or the position of the wisdom teeth.
The rays used are for the body harmful to health. The dose for an X-ray is very small, but it should not be used too often. With the help of X-ray passports, patients can more consciously check the number of radiation exposures. Frequent radiation exposure increases the risk in life to a small percentage cancer to get sick.
MRI

Magnetic resonance imaging is also called "Magnetic resonance imaging" designated. The mechanism is different from that of X-rays. The harmful X-rays do not play a role in MRI. The effects of the magnetic field in the MRI have not been fully researched, but it is believed that they no health effects have on people.
The MRI is recorded with the help of a very strong magnetic field. The patient is in the tubular tomograph. The extremely strong magnetic field generated causes all atoms in the body to be stimulated to move. They emit a measurable signal. MRT enables extremely detailed, high-resolution and high-contrast layer representations of the body, as does X-ray CT.
In MRI, the distinction between individual organ areas does not take place via light and dark areas, as in CT, but mainly via the Contrasts between two foreign structures. In particular, the soft tissue is very rich in contrast. It is also a good idea to MRI images with a contrast agent to make. Above all, different types of fabric can be easily identified, for example Inflammation or Tumors.
The big advantage is that MRI scans manage without harmful ionizing X-rays. So you can repeat them without hesitation without having to take any health risks. The high soft tissue contrast also offers advantages in diagnostics, for example of Ribbons, Cartilage, tumors, adipose or muscle tissue.
A conventional one MRI examination takes between 20 and 30 minutes, which is why it quickly happens that the images are blurred by movements of the patient or the organs. However, new technologies promise to be able to make real-time recordings in the future, for example when examining the Heart.
Unfortunately, the strong magnetic field at the time of admission also causes patients with any kind of Implants, for example artificial joints or pacemakers, not suitable for MRI scans.
CT
The "X-ray computed tomography“, As it is correctly called, also uses the ionizing x-rays. Here, the patient is in a tube-like tomograph that produces x-rays many directions records. The images are digitally recognized and can be viewed on the computer. By recording a few pictures from different directions you can get Sectional images through the area of the body to be examined. This allows a much more precise diagnosis. The digital overlay-free images are also of a higher quality than the conventional X-ray images.
The CT images show the same absorption behavior as the X-ray images. Especially bone and air-filled areas can be determined exactly. With the help of contrast agents and higher quality images, vessels can also be made clearly visible. An important area of application for this is the so-called "Coronary angiography“, In which the vessels that supply the heart and are usually affected in a heart attack, are shown.
X-ray computed tomography recordings are also used to display lymphatic vessels and individual organ areas, for example the gastrointestinal tract or the urinary system.
The big disadvantage of the very high quality CT images is that high radiation exposure. In diagnostic radiology, CT images account for significantly less than a tenth of the examinations. Still, they are responsible for about half of the radiation exposure. Even a single CT scan in several slices increases the risk of secondary cancer by a small percentage.
Ultrasonic
The ultrasound, or "Sonography"Called, is the most frequently performed imaging procedure in everyday clinical practice. He used to make the pictures Sound wavesby different organ structures reflected and thus allows a distinction between the organs. It works without the harmful X-rays. The ultrasound examination can be carried out quickly, very easily and as often as you like. From the outside, the transducer, which emits the waves, is pressed onto the skin.
With the ultrasound can only Soft tissue because the bone does not let the waves through.
It is used for the detection of fluid or air-filled spaces, for the representation of vessels and abdominal organs. Also in the Pregnancy diagnostics the ultrasound device is often used to assess the child's development.
It is also often used to identify and diagnose the course of malignant tumors. Only experienced doctors can evaluate an ultrasound image well. The resolution and informative value of an ultrasound examination is very limited and depends on the experience of the doctor.
Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology is not part of diagnostic radiology, but rather helps with minimally invasive radiology therapeutic Measures. This sub-area of radiology has not been around for very long. Almost exclusively used in interventional radiology Vascular systems represented, often with the help of contrast media. These include arteries, veins, or lymph vessels Biliary tract.
The imaging procedures are performed at the same time as a minimally invasive Intervention carried out. These include above all the Dilation of vessels, the creation of Stents, the sclerosing of bleeding or the removal of narrowing (Stenoses) of the vessels. In order to guarantee that the minimally invasive treatment is carried out in the right place within the vessel, the position of the vessel and the implementation of the procedure can be precisely observed with the aid of interventional radiology.
The exact location of the therapy can also be determined and checked in organs, for example in the treatment of tumors of the liver, using the image recordings with contrast media.
In interventional radiology, it also applies to the Radiation protection to be careful, because it also works with ionizing, harmful X-rays.