Ring ear
Synonyms in a broader sense
Otematoma, ringer's ear, boxer's ear, cauliflower ear
English: othematoma, auricular hematoma
definition
(Ot = ear, hematoma = bruise)
An othematoma is a kind of bruise ("bruise") or swelling with accumulation of secretions in the auricle. Often the effusion is a mixture of both. Only the outer ear is affected. It is a build-up of blood or serum between the cartilage and the skin of the cartilage.
Summary
The othematoma is a swelling of the auricle. Blood or serum accumulates. Mostly the othematoma occurs in wrestlers, as it is primarily the result of direct violence. Therapy is by puncturing the effusion (pulling off the bruise with the syringe). If an othematoma is left untreated, a permanent disfigurement of the ear develops, which the expert calls a ring's ear.
Occurrence in the population (epidemiology)
The othematoma occurs particularly frequently in wrestlers and boxers, including the term ring ear. People who, for example, carry sacks on their shoulders to their ears at work, also suffer such a change. Simply lying on the folded auricle can also result in an othematoma.
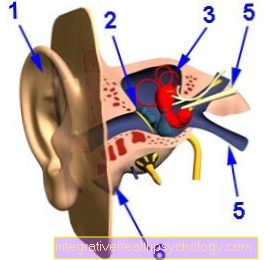
Figure ear
- Outer ear
- eardrum
- Balance organ
- Auditory nerve (nervus acousticus)
- tube
- Mastoid process
causes
The cause of the othematoma (Ringer's ear) lies in the force of force, which is tangential (directly hitting), shearing (brushing along the auricle). It is blunt violence.
Symptoms / complaints
The othematoma (ring's ear) rarely affects the patient. The swelling is usually painless, but clearly visible, so that there are cosmetic restrictions. Hearing is usually not impaired.
Complications
Untreated othematomas develop a remnant of connective tissue after a certain period of time. The bruise is replaced by connective tissue. The affected ears are then permanently disfigured. This appearance is also called "ring ear", "box ear" or "cauliflower ear".
diagnosis
The othematoma is usually easily recognized. It manifests itself as a bulging swelling on the front of the auricle. It is a serous, liquid effusion between cartilage and its connective tissue capsule.
therapy
The bruise is usually punctured (suctioned off with a syringe) or incised and the fluid is drained off. An antibiotic is often also given to prevent the bruise from becoming infected (hematoma). A pressure bandage can be applied instead of the puncture.
The individual therapy decision must be made on the basis of the findings.













.jpg)










