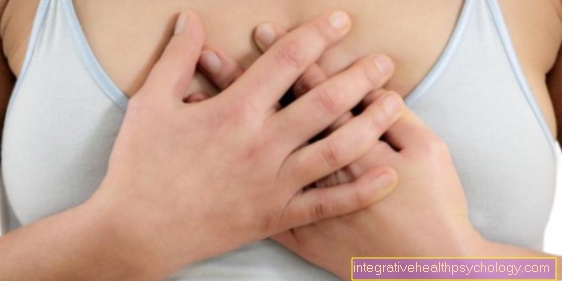
Chest pain
General
The word Chest pain means Chest pain and can have a number of causes.
Each organthat is in upper body ( thorax ) can in principle be ill and thus be the cause of the pain. For example, the pain can be caused by:
- the heart,
- the lung,
- the esophagus or also the Spine

Organs that are further down in the abdomen can also be the reason for chest pain, and vice versa, for example, pneumonia deep down can cause lower back pain.
Chest pain can be a sign of a serious illness or it can mean nothing. Due to the many possible causes, it is sometimes difficult to determine where the pain is coming from. Therefore, a very thorough medical history is important, because there are often certain indications depending on the organ, such as the exact location of the pain or the time at which the pain appeared.
Read more under: Painful breathing
Heart disease usually not only causes pain in the middle of the chest, but also often radiates into the left arm or back in the event of a heart attack, for example.
If the chest pain is breath-dependent, for example:
- the lungs or
- also on the ribs or
- the sternum (often described by those affected as a pain in the heart when breathing in)
Read more on the topic Burning in the lungs and burning behind the breastbone.
The organ heart as the cause

- Heart attack and Angina pectoris:
The pain when Heart attack and at the Angina pectoris are mostly Behind the Sternum and express themselves mainly as Feeling of pressure. They often radiate into the move, left arm, Upper abdomen or direction neck out. The pain depends on the type of angina load-dependent and through a Nitro spray easily treatable. However, the pain of a heart attack does not go away that quickly. With a heart attack can also nausea and Vomit to be available. If you experience these symptoms, you should see a doctor immediately. However, sometimes a heart attack can only go through one Feeling of pressure or a Drawing in the left chest to make noticable. Sometimes he is not even noticed, this is called "silent heart attack'. - Pericarditis: Here the pain is often stabbing and worsen in the Lie on the left. Since germs are responsible for the pericardial inflammation, the patient often complains flu-like Symptoms like fever and malaise
- Aortic dissection: An aortic dissection is a splitting of the wall layers of the aorta (Body artery) and can at first very much few symptoms run away. During aortic dissection, the various layers and separate blood occurs between you. The entering blood can make it strong move-, Chest pain or pain in the Leg area come.
The lungs as a cause of chest pain
- Pneumonia: With pneumonia, the pain is usually not particularly severe and depends on the breath. There is also often a fever, sputum, severe cough and malaise.
- Pneumothorax: Pneumothorax causes air to accumulate between the lungs and the chest. The pain comes on suddenly, due to the sudden crack in the pleura, for example from external injuries. The main symptom here is shortness of breath and unilateral chest pain. Pneumothorax is a disease that is only increasing and usually needs to be treated immediately.
Read more on this topic at: Pneumonia pain
- Pulmonary embolism: The pulmonary embolism occurs as a result of a blood clot that usually forms in the legs and then “flies” into the vessels of the lungs and blocks a vessel there. A pulmonary embolism can lead to death if left untreated and a doctor should therefore be consulted immediately. The main symptom here is also shortness of breath and chest pain, which are breath-dependent. Cardiac arrhythmias can also occur and are therefore easily mistaken for a heart attack. The main risk factors are smoking and taking the pill (see: Thrombosis risk of the pill). Long car journeys and long-haul flights can also lead to a blood clot, which can also lead to a pulmonary embolism, as the blood in the legs slows down due to the small amount of movement and can thus "clump".
- Lung cancer: Lung cancer can also lead to end-stage chest pain. More information on the topic: How do you recognize lung cancer?
Psychosomatic pain
Psychosomatic illnesses also play a role in chest pain. In contrast to some of the other illnesses listed, they are not dangerous, but cause great anxiety in those affected. If chest pain / heart pain is triggered by psychological problems, one speaks of a heart neurosis. In the case of this heart neurosis, the person concerned is convinced that they are suffering from a dangerous heart disease. Panic attacks can also cause chest tightness.
Chest pain on inhalation
Chest pain when inhaling suggests that the lungs are involved. Often the pain then occurs in connection with a Pleurisy on. The pleura, which covers the lungs, is stretched with every breath and thus further irritated. With shallow breathing the symptoms get better, but then one occurs shortness of breath on. The lungs do not always have to be primarily responsible for the breath-dependent pain, likewise Diseases of the heart can trigger this. The most typical example of this is Heart attackwhich causes chest pain and shortness of breath because the heart is no longer able to supply the body with sufficient oxygen. Even with one Bruising of the chest deep breathing can lead to pain, and coughing in particular often causes sharp pain. The reason for this is usually a Broken ribthat irritates the periosteum.
Left chest pain
If the chest pain occurs only on the left, it is obvious that this heart is responsible due to its location. Possible causes of left-sided chest pain are for example a Angina attack by constricted coronary arteries, a Heart attack, a Valvular heart disease or one Pericarditis. Also a very high blood pressure, such as severe arrhythmia can be the cause of discomfort in the left half of the chest. The is typical of unilateral breathing-dependent chest pain Pneumothorax. This can just as easily occur on the right side.
Chest pain on both sides
Chest pain sometimes occurs on both sides. This is especially the case with diseases that are not caused by heart disease. Chest pain triggered by Lung disease often occur only on one side, as only one lung is affected, but can also occur on both sides. Musculoskeletal complaints can also occur unilaterally and bilaterally. The common ones Diseases of the esophagus for example, they classically trigger a burning pain on both sides of the chest.
Chest pain on exercise
Chest pain after physical or mental stress are not uncommon. Especially with constricted coronary arteries in the context of a coronary heart disease, the symptoms often get worse or only appear with physical exertion. Because under stress, the heart has to work harder to pump enough blood into the circulation, for this the heart itself needs more energy and has to go through the constricted Coronary arteries are increasingly supplied with oxygen and nutrients, which is already difficult at rest due to the narrowed coronary vessels and then reaches its limits under stress. The same applies to psychological ones stress, where the Heart rate and the Blood pressure increased so that the heart has to work harder. In extreme cases, a load-dependent chest pain occurs in one Heart attack when one or more coronary arteries are already completely closed.
Chest pain after surgery

Especially with operations in the thorax area such as Heart valve surgery or in general at Operations on the heart or also at the lung pain can occur. A few days after the operation, however disappear again should. Often times this pain comes in the Area of the seams conditions. After an operation, chest pain can occur as part of a pneumothorax, which is unintentional during the operation was caused by the surgeon because Lung tissue injured so that air could enter the so-called pleural space between the outer and inner sheaths of the lungs. As a result, there is no negative pressure in the pleural space and the lungs collapse / contract. As other complications during surgery, there can be a Pulmonary embolism especially if the patient is at one during surgery Life-support-machine connected, there is an increased risk, which is reduced by the simultaneous administration of a blood thinner. It can also occur during an operation, for example due to the spread of germs Pleurisy or Pericarditis come.
Stomach and esophagus
- Inflammation of the stomach (gastritis): The chest pain can be more likely with an inflammation of the stomach diffuse be. They are mostly in Upper abdomen and have one stabbing Character. If the inflammation bleeds, it often occurs Vomit of black gastric juice and too dark stool. ( Breaking coffee grounds and Tarry stool)
- heartburn (Reflux): With reflux the chest pain is mostly only low. It'll be more of a Burning in the chest felt which at eat and gets stronger when you lie down. Often the pain is also in the throat. This type of pain is sometimes indistinguishable from pain emanating from the heart. The stomach acid flows back into the esophagus and damages it, this is partly due to a simultaneous occurrence heartburn accompanied.
- Organs outside the chest that are in the abdomen can also trigger chest pain, which is then referred to as one projected pain. This is because spinal nerves that emerge from the spinal cord often supply an organ and a skin area at the same time. Often times, this projected chest pain is caused by the Gallbladder or at one Gastric ulcer triggered.
Muscles, bones and co
- Broken rib or Bruised ribs: When breaking or bruising the Ribs It comes to breath-dependent, stabbing chest pain. The localization of the pain is similar to the localization of the bruise / break.
- Tietze syndrome: The Tietze syndrome also causes pain in the Chest area. Most likely they are caused by inflammation in the Costal cartilage caused. They are stinging and dependent on the breath.
- Shingles: The Shingles is a very painful condition caused by Herpes zoster viruses is triggered. The viruses travel along a nerve and also cause the typical ones Vesiclesthat follow the nerve segment. The pain is mostly called burning designated.
- Bechterew: ankylosing spondylitis is a disease of whirl and is particularly painful in the early hours of the morning and at night. The chest pain is usually deep in the chest-, or Lumbar vertebrae and is often described as dull.
Diagnosis of chest pain
Chest pain therefore has a diverse character and can be triggered by many organ diseases. The pain can also have a psychological reason, patients with depression often feel pain in the chest or stomach area.
The diagnosis and therapy of chest pain depend on the disease. A good and detailed medical history is very important for the diagnosis. Depending on the suspicion, it may be necessary to write an EKG, have an X-ray taken, a CT or MRT (a special MRI of the lungs must be performed here, especially in the MRI of the lungs, the problems between soft tissues and air in the lungs can be minimized ) drive, do an ultrasound (also swallowing ultrasound) or draw blood.
Read more on the topic: Chest x-ray (chest x-ray)
When taking a history of chest pain, focus should be on:
- Quality of pain (stabbing, dull, pressing) on which
- Location on which
- Intensity (pain scale 0-10),
- Spread and time of occurrence (sudden, breath-dependent).







.jpg)