Pubic branch
What is the pubic branch?
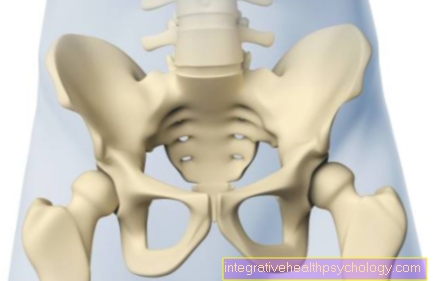
The pubic branch is a large bony process of the pubic bone (Pubis) and represents part of the bony pelvis. Overall, the pubic bone has two pubic branches, an upper one (Ramus superior ossis pubis) and a lower one (Ramus inferior ossis pubis). The pubic branches are at right angles to the pelvic entrance and are bony with the iliac bone (Os ilium) and the ischium (Os ischii) connected. Both branches form the so-called pubic angle (Angulus subpubicus / arcus pubis).
Read more about the topic here: Pelvic bones

anatomy
The pubic branches are anatomically a part of the bony pelvis.
The pelvis consists of the three fused ischial bones (Os ischii), Iliac bone (Os ilium) and pubic bone (Pubis). As the name suggests, the pubic branches belong to the pubic bone. This is made up of a body (Corpus ossis pubis) and two pubic branches together.
The pubic branches are bony processes that run across the pelvic entrance plane. There is both an upper and a lower pubic branch.
The superior pubic process (Ramus superior ossis pubis) passes into the iliac bone (Os ilium). In addition, two anatomical structures are to be emphasized there. The pubic crest (Pecten ossis pubis) forms the upper sharp-edged border of the upper pubic branch and is the origin of a muscle. In addition, it is the direct continuation of the Linea arcuata (rounded bone edge on the inside of the iliac bone). Together with the iliac bone and ischium, the upper pubic branch is on the structure of the joint socket (Acetabulum) for the thigh involved.
The second anatomical feature is the pubic bone (Pubic tuberosity), a small bony hump on which the inguinal ligament (Inguinal ligament) starts. The lower pubic branch (Ramus inferior ossis pubis) goes over into the ischium (Os ischii).
Both lower pubic branches limit the so-called pubic angle, which in men as Angulus subpubicus referred to as. It is around 70 ° and is therefore rather pointed. In women, the corner of shame becomes Arcus pubis called and measures about 90 ° to 100 °. It is therefore rather blunt and is an advantage during childbirth.
In addition, both pubic branches are together with the ischium on the formation of the Obturator foramen involved. The Obturator foramen is a large round opening in the pelvis through which various nerves and vessels run.
This article might also interest you: Structure of the pelvis
function
The pubic branches have different functions in the pelvis. On the one hand, they form anatomical structures together with other bones. This is how this comes about, for example Foramen obturatorium through the upper and lower pubic branches and the ischium (Os ischii). Vessels and nerves run through this large opening in the pelvis.
Furthermore, the pubic branches are the origin and attachment of different structures. The Obturator foramen is closed by a membrane (Obturator membrane), which attaches to the two pubic branches, among other things.
Particularly noteworthy is the pubic crest (Pecten ossis pubis) on the upper pubic branch, on which a muscle (Pectineus muscle) has its origin. Other muscles that are particularly responsible for pulling the thigh closer (adductor muscles) also use the pubic branches as their place of origin.
Another structure that represents a point of attachment is the pubic bone (Pubic tuberosity). Here the inguinal band (Inguinal ligament) on.
Diseases of the pubic branch
Pubic branch fracture
A pubic branch fracture is a fracture of the pubic branch and can be divided into a complete and incomplete pelvic ring fracture.
Symptoms of a pubic branch fracture are rather unspecific and are described as back or lower back pain that increases with movement.
Such a fracture is diagnosed with the help of an X-ray image or better still with a CT (computer tomograph).
Treatment varies depending on the type of pelvic ring fracture. In an incomplete pelvic ring fracture, either the upper or lower pubic branch is broken. In this case, the patient needs to stay in bed for a few days and take pain medication if necessary. However, the patient should be mobilized again as soon as possible to prevent secondary diseases such as Pneumonia can be avoided. The pelvis can be stabilized by wearing a special wide belt, which many patients find comfortable.
In contrast, a complete pelvic ring fracture affects both the upper and lower pubic branches. Other parts of the pool may also be damaged. In this case, surgery is essential.
Further information on the subject can be found here: Pubic branch fracture
Pubic cystitis
An inflammation of the pubic bone (Pubic ostitis, also called pubalgia) is a non-infectious inflammation of the pubic branch or surrounding structures, such as the pubic symphysis (Symphysis pubica), of the entire pubic bone (Pubis) or adjacent muscles (adductors, abdominal muscles).
This disease is particularly common in competitive athletes who run a lot (e.g. tennis players, soccer players).
The cause of an inflammation on the pubic branch is constant overload. Frequently reported symptoms are pain when walking and climbing stairs as well as when standing on one leg. The pain is often localized, but it can also reach the groin or lower abdominal muscles. This joking sensation is intensified if the doctor does a palpation examination (Palpation) performs.
An inflammation of the pubic bone or pubic branch is primarily treated conservatively. The patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs (anti-inflammatory drugs) and physiotherapy is prescribed. These are supposed to stretch different muscle groups as well as strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
Taking a break from exercise is also recommended to protect the site of inflammation, but it often encounters resistance from the patient.
Pubic branch pain
Pubic branch pain is a non-specific symptom and can have various causes. A precise history of the patient should be taken in order to find out more about the symptoms. The doctor also performs a palpation examination (Palpation). Nowadays, imaging methods such as x-rays and computed tomography are often used for a clear diagnosis.
Reasons for pubic branch pain are very diverse and can range from a fracture to inflammation. Fractures are more common in the elderly and can result from a fall. Those affected often describe this pain as deep back pain that extends to the tailbone.
Inflammation in the area of the pubic ramus is found mainly in competitive athletes who are exposed to high mechanical pelvic stress. These pains occasionally radiate to the groin or lower abdominal muscles.
Read more about the topic here: Pubic bone pain - these are the causes








.jpg)