Dizziness in the eye
General information about dizziness
Dizziness is generally understood to mean the perception of apparent movements, which those affected associate with a feeling of insecurity and drowsiness. Dizziness is caused by the interaction of three sensory systems: the balance organ of the inner ear, the eyes and the receptors for position and depth in the skin, joints and muscles.
- The organ of equilibrium in the ear provides information about the direction in which the body is moving.
- The eye complements the orientation in space, i.e. where we are.
- The so-called propioceptors of the skin, joints and muscles tell us something about the position of our body parts to one another. The
Gathering all information creates what is known as a sense of balance in our body.

If there is a disruption or contradiction in one or more of these systems, we feel insecure about our situation: dizziness.
There are a number of differences in the quality of the vertigo. There are roughly two major classes of vertigo.
- On the one hand, the systematic directed vertigo. In this case, the disturbance lies in the equilibrium system itself. This includes, for example, vertigo or vertigo, but also forms of vertigo in which one has the feeling of being in a lift or falling down somewhere.
- On the other hand, there is the unsystematic, undirected dizziness, which is more related to the classicTurning black before the eyes“Can be described. The location of the damage lies outside the organ of equilibrium.
Read more about this on our website dizziness.
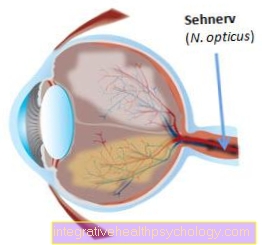
Eyes as a cause of dizziness
If the cause is in the area of the eyes, it is called ocular dizziness. The cause is usually a visual defect, paralysis of the eye muscles or a decrease in vision with increasing lens opacity, such as in cataracts.
Dizziness can also occur during the familiarization phase with new glasses or with incorrectly adjusted glasses. An increase in intraocular pressure and anomalies in the eyeball can also be considered as triggers.
Due to the ametropia and the consequent disturbed fixation of objects by our eyes, the interaction with the balance organ in the inner ear leads to absurd information to the control center in the brain, which ultimately leads to dizziness.
Dizziness from increased pressure in the eye
An increase in intraocular pressure is called glaucoma in medical terminology and is also known as "glaucoma". Glaucoma can be sudden and seizure or chronic.
While the triggers for chronic glaucoma are not yet known, there are some known risk factors for acute glaucoma: These include myopia, diabetes and circulatory disorders, such as those that can occur due to low blood pressure. An acute attack of glaucoma is very painful for the affected person and is also associated with headaches, nausea and dizziness.
Acute glaucoma is an ophthalmological emergency and should be treated as soon as possible.
Dizziness with Other Symptoms - What's Behind It?
Depending on the form of vertigo, this is perceived differently by the person affected. In spinning vertigo, those affected experience a feeling as if it was spinning inside themselves or the environment around them. Vertigo is associated with the discomfort, as if the ground was being pulled away from under your feet. If you have the feeling of driving in an elevator or even falling, it is mostly a question of elevator dizziness.
Attacks of dizziness are very often accompanied by unpleasant symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. In unsystematic forms of dizziness, such as those that occur with poor circulation and a drop in blood pressure, usually accompanied by "Blackening“In front of the eyes or a feeling of emptiness and lightheadedness add to it.
Systematic forms of vertigo, such as benign positional vertigo, tend to increase symptoms when moving in one direction and when closing the eyes. Depending on the cause of the dizziness, there may be a concomitant loss of hearing, the perception of additional noises in the ears, double vision, swallowing or speech disorders and feelings of numbness.
Attacks of vertigo can last for a few seconds. In extreme cases, however, dizziness persists for a few days and thus represents a very great burden for those affected. It is advisable to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Eye pain and dizziness
The most common cause of sore eyes is poor vision. The constant exertion and effort of the eye muscles to compensate for the weakness causes pain after a while. In addition, headaches and dizziness may occur as the disease progresses. A visual impairment such as farsightedness or nearsightedness can be quickly diagnosed by an ophthalmologist or optician and should be corrected with glasses or contact lenses, especially if the symptoms are concerned.
To do this, read: Symptoms at Myopia or farsightedness
Inflammation or increased intraocular pressure can also cause pain in the eye and, in advanced disease, headache and dizziness. If such a cause is suspected, attention should be paid to warm, reddened, or swollen areas of the eye. Reddened conjunctiva or a very hard eyeball can also indicate inflammation or acutely increased intraocular pressure (so-called glaucoma). If the latter could be the case, a doctor or an emergency room should be consulted, as glaucoma should be treated as soon as possible.
You might also be interested in this article on the topic: Eye pain or dizziness and blurred vision
Eye flicker and dizziness
Noticing fibrillation and dizziness is usually a sign of an acute migraine attack. The cause here is first an excitation wave, then an excitation blockage, which spreads over the cerebral cortex. Significant for migraines are, among other things, the unilateral headache and disorders of the senses, especially the eyes. The so-called flicker scotomes, which are reminiscent of the heat shimmer over an asphalt road in summer, are particularly typical.
But also the other way around, visual disturbances, such as eye flickering, can trigger dizziness in the affected person. During a medical consultation, it should therefore be found out which of these symptoms was present first and which could possibly have caused the other.
Read more about this: Migraines or migraine attacks
Eye twitching and dizziness
A twitch in the eye muscles usually indicates an overload. If the twitching of the eyes is an accompanying symptom of dizziness, attention should be paid to which symptom appeared first and whether one of the symptoms is perhaps the result of the other.
There is also the possibility that both eye twitching and dizziness are caused together by causes such as overexertion, stress or lack of sleep. If dizziness with eye twitching appears to occur frequently without cause and it causes restrictions in everyday life and the suffering of the person concerned, a doctor should be consulted for further diagnosis.
Read about this too: Shrug
Other causes
- In addition to the causes caused by the eyes, there are many other causes of dizziness. A classic among the forms of vertigo is what is known as benign positional vertigo. It mainly affects people over the age of 60.
This form of dizziness is triggered by a change in the position of the body, for example when turning from one side to the other in bed. This movement has the consequence that small crystalline stones in the coils of our inner ear loosen and cause irritation there. The result is vertigo. Fortunately, this dizzy spell only lasts a few seconds to minutes.
However, if the vertigo is persistent with a tendency to fall to one side and jerky eye movements, it may be an inflammation of the auditory nerve.
- A vertigo like "out of the blue“In connection with hearing loss and ringing in the ears should make one think of Menière's disease. This disease of the inner ear causes the smallest tears in the membranes of the ear, which separate two different fluids of the inner ear from each other. Due to their different composition, mixing these two substances leads to the symptoms mentioned above.
- The otitis media, which is particularly widespread in childhood, harbors the complication of the inflammation spreading towards the inner ear. The resulting irritation of the auditory cells can cause dizziness.
also read: Dizziness caused by the ear
- Dizziness can also occur due to circulatory disorders in the area of the cerebral vessels, as may be the case with slowly increasing calcifications of the arteries or a sudden stroke. Feelings of numbness in certain parts of the body, speech or vision disorders are common side effects.
Dizziness may occur under certain circumstances due to low blood pressure or hypoglycaemia. Such circulatory and metabolic attacks of dizziness are often caused by a "Blackening“In front of the eyes and accompanied by other vegetative symptoms such as cold sweat or paleness.
- Above a certain amount, the abuse of toxic substances such as alcohol can also irritate our sense of balance. What is usually provoked here is an uncomfortable vertigo that can last for a few hours. A number of certain medications, such as water tablets or sedatives, can also make you dizzy.
- It should not be ignored that the psyche also plays a major role in the sensation of dizziness. Fear or other emotional stressful situations can cause so-called psychogenic dizziness.
Read more about this on our website Causes of dizziness.
diagnosis

The first point of contact in the event of dizziness is usually the family doctor. If the suspicion of a specific illness is confirmed, the referral to a specialist will help. Basically, the medical professional will work for that Type of vertigo, the Duration, the triggering causes such as existing medical conditions interested. Also the Living conditions, possible stressful situations in work or family can be taken into account. Because even stress can be a trigger for dizziness attacks.
Then a physical examination, carried out with, for example, blood pressure and pulse measurement to expose circulatory disorders as a cause of dizziness. Also the Movement of the head in different directions and certain Positioning maneuvers are used to diagnose the cause of dizziness.
In addition, a Hearing test and a Examination of the eyes be performed. Because they too can be the source of dizziness. In addition, imaging recordings such as An MRI of the skull can be done to rule out a mass in the area of the brain with a displacing effect on the surrounding brain structures.
In Vertigo clinics, which are offered by some practices or clinics, a comprehensive diagnosis of vertigo is offered in cooperation with several disciplines.
therapy
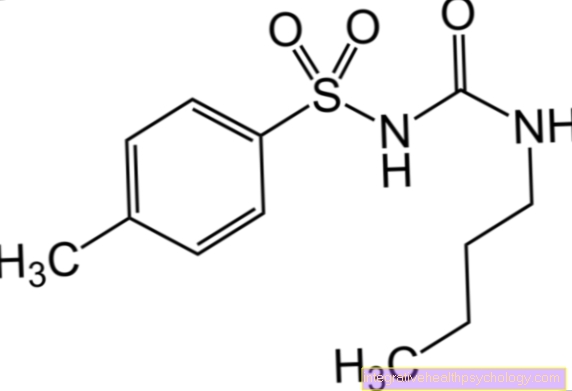
The therapy of vertigo depends heavily on the triggering cause. If drugs or other toxic substances are responsible for the dizziness, they should be stopped immediately. Medication can cause dizziness with so-called Antivertiginosa be treated. Under this "Anti-dizziness drugs“For example, some fall Antihistamines, like dimenhydrinate or the Calcium channel blockers Flunarizine. In their mode of action, they are primarily directed against nausea and the Vomit.
Drug treatment of dizziness should be mainly through physical exercises can be added. They serve that Storage training, avoidance of Bad posture as well as the correction of Incorrect movements. They also train the physical balance.
Targeted maneuvers to stop the vertigo attack are used, for example, in benign positional vertigo. Certain changes in the body's position return the small stones of the inner ear that have been detached from the semicircular canals to their original position.
If the basic problem lies in the area of the eyes should be done regularly specialist eye examinations be performed. Visual defects should be corrected as soon as possible glasses Getting corrected. An incorrectly calculated prescription for the new visual aid should always be considered and if necessary afterwards adjusted correctly.
The therapeutic spectrum of vertigo is far-reaching and should be given an appropriate treatment if the patient is under great stress Behavior therapy can be added. In rare cases, the operative elimination the triggering factor, for example through corrections to the eye, is the only solution to eliminate dizziness.
Duration and forecast
The duration of an attack of dizziness always depends on the precise cause, but in over half of the cases no organic cause for the dizziness can be found in the person concerned. However, if an underlying illness is detected, it can be treated and the dizziness can be reduced. In addition, the dizziness can be prevented from recurring. If one can at least identify risk factors for the occurrence of dizziness, the affected person can try to change their own lifestyle accordingly.