Which doctor treats a circulatory disorder?
These doctors treat circulatory disorders
Circulatory disorders are a very complex clinical picture. They can affect virtually all organs. Since the organs lack vital oxygen in the event of a circulatory disorder, malfunctions often occur. You can roughly remember that the doctor who is responsible for the organ also takes care of a circulatory disorder.
Cardiology, for example, is responsible for circulatory disorders in the heart. The neurologist treats circulatory disorders in the area of the brain and spinal cord. An internist can treat circulatory disorders in the internal organs. The ophthalmologist takes care of circulatory disorders in the area of the eyes. Angiologists are specialists in blood vessels. They mostly treat circulatory disorders in the legs or in the carotid artery. If a stent implantation is necessary, interventional radiologists can also be involved. The vascular surgeons or, for the heart, the cardiac surgeons perform surgical treatment of circulatory disorders. Therefore, the question of which doctors treat circulatory disorders cannot be answered in such a general way.
What does the internist treat?
Internists treat circulatory disorders in the area of the internal organs. This applies to circulatory disorders in the heart, but also circulatory disorders in the abdomen or in the liver and kidneys.
It is not always a question of circulatory disorders in the arterial system. The internist also treats venous outflow disorders in the abdomen. Most often it is a drug therapy. The internist can set risk factors for circulatory disorders well. These include high blood pressure, diabetes and a lipid metabolism disorder. These diseases are treated by an internist.
Find out more about the topic: Therapy of circulatory disorders
What does a cardiologist treat?
Circulatory disorders in the heart are the supreme discipline of cardiology. If there are circulatory disorders in the heart, one speaks of coronary heart disease. The coronary arteries are usually narrowed by arteriosclerotic plaques. This condition is treated by the cardiologist. On the one hand there is a drug therapy with platelet aggregation inhibitors (e.g. ASA). This must be taken for life. On the other hand, risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes and a lipid metabolism disorder should be treated.
The cardiologist also has interventional options for treating coronary heart disease. As part of a cardiac catheter examination, the narrowing of the coronary arteries (stenoses) can be shown. If necessary, small metal tubes (stents) can now be inserted into the vessel to keep the blood vessel open at this point. This improves the blood flow to the heart again. To keep the stent open, another blood-thinning drug (e.g. clopidogrel, prasugrel, ticagrelor) must be taken for a period of approx. 6 months. If a long vascular occlusion appears in the catheter that cannot be supplied with a stent, the cardiologist will refer the patient to a colleague in cardiac surgery to check the possibility of a bypass system.
Also read the article on the topic: Circulatory disorder of the heart
What does an ENT doctor treat?
The ENT doctor can also treat circulatory disorders. Most circulatory disorders in the ENT area are circulatory disorders in the inner ear. Circulatory disorders in the throat or nose area are rare. The hearing and balance organs are located in the inner ear. If the auditory cells are not supplied with blood well, a malfunction occurs.
Tinnitus occurs. Patients complain of ringing in their ears. Therefore, the treatment of tinnitus is to increase blood circulation in the ear. There are different possibilities for this. Infusions are used among other things. In addition to cortisone, these also contain drugs that stimulate blood circulation, such as the rheological agents dextran and pentoxiphylline. The results for acute tinnitus are very good. Chronic tinnitus is much more difficult to treat because other components often play a role as well.
Read more on the topic: Treatment of tinnitus
What does an angiologist treat?
The angiologist is a specialist in the field of angiology, a branch of internal medicine, and deals with vascular diseases. In addition to circulatory disorders in the arteries, this also includes venous and lymphatic diseases. There are, however, many overlaps with other disciplines, e.g. the cardiologist.
Angiologists usually do not treat cardiovascular disorders. Its domain is peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD) of the pelvic and leg arteries, as well as narrowing of the carotid artery (carotid stenosis) and narrowing of the renal arteries.
However, they not only treat circulatory disorders due to arteriosclerosis but also vascular diseases caused by inflammation (vasculitis) or radiation. Vascular sacs (aneurysms) of the main artery (aorta) or the pelvic and leg arteries are also treated by the angiologist. If these diseases are treated surgically, the vascular surgeons take over.
For laypeople, it is often not immediately obvious which circulatory disorders the angiologist is responsible for, so it is always worthwhile to consult your family doctor in case of doubt. This can then arrange for a forwarding to the correct subject area.
Also read our topic: Aortic aneurysm
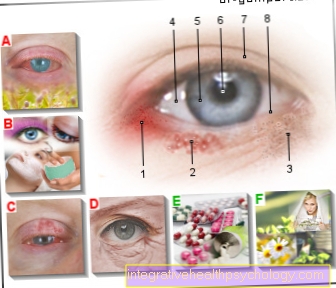
What does an ophthalmologist treat?
Circulatory disorders in the eye usually occur either in the area of the retina or in the area of the optic nerve (nervus opticus). They can either develop slowly or lead to sudden loss of vision. Chronic circulatory disorders in the eye are mostly caused by arteriosclerosis due to high blood pressure, diabetes and disorders of lipid metabolism. These diseases are treated by an internist.
The ophthalmologist's domain is the following diseases, more acute diseases such as central vein occlusion or the occlusion of a retinal artery. In the case of central vein occlusion, the therapy of choice is a blood-thinning drug (e.g. Marcumar) to dissolve the blood clot that is blocking the vein. In the course of the disease, laser treatment can be useful, especially if there are accompanying complications such as edema or new blood vessels.
The occlusion of a central artery is also an ophthalmological emergency. Here, the patient must be given the drug acetazolamide immediately. The eyeball should be massaged for 15 minutes. In the worst case, lysis therapy has to be carried out to dissolve the blood clot.
Read more on the topic: Circulatory disorder of the eye
What does the orthopedist treat?
Individual circulatory disorders in the area of the bones fall within the treatment of the orthopedic surgeon. However, this form of circulatory disorder is rather rare.
Nevertheless, they are a dangerous complication, if the bone is no longer supplied with sufficient blood, the cells die. In technical terms, this disease is called osteonecrosis. This can occur in the knee joint area, for example. The disease is also called Ahlbäck's disease.
The cause of this circulatory disorder has not yet been fully researched. The therapy consists of an operative measure. The osteonecrotic areas should be drilled open and the misalignment corrected. Circulatory disorders can also cause bone death in the hip joint area. In childhood, the disease is known as Perthes disease. However, it can also occur in adults after a femoral head fracture. This disease is first treated with medication and relief of the joint through mobilization only with forearm crutches. However, surgical intervention may also be necessary.
Read more on the topic: Ahlbäck's disease
What does the neurologist treat?
The neurologist treats circulatory disorders in the brain. Above all, there is certainly the clinical picture of the stroke.
An acute stroke should always be treated in the hospital on a specialized ward called the Stroke Unit. Neurologists and neuroradiologists work hand in hand here. Depending on the extent of the stroke, it is treated with medication (e.g. lysis therapy). Neuroradiologists can now also remove the blood clot in the brain directly. This procedure is called a thrombectomy. The resident neurologist then takes over the follow-up treatment after a stroke
Also read the article on the topic:
- Stroke therapy
- Circulatory disorder in the brain
What does a radiologist treat?
Radiologists can also treat circulatory disorders. They are mostly needed when it comes to inserting a metal tube (stent) into a blood vessel. On the heart, this intervention is carried out by the cardiologist. The constriction in the leg arteries can be bridged by the angiologist or the radiologist. This is very different and depends from clinic to clinic on the focus of the individual departments.
In principle, radiology is certainly not the first point of contact for circulatory disorders. However, it can be brought on board by other disciplines to expand any vascular occlusions, for example in the event of a stroke, the thrombus is removed by the neuroradiologist or if the hepatic or renal arteries are constricted, the radiologists can also place a stent there.

















.jpg)