Sexually transmitted diseases
introduction

Sexually transmitted diseases, also known as STDs, are among the oldest human diseases. In every place where people live in society and have sexual contact there will be one or the other sexually transmitted disease. Various pathogens, some of which can be attributed to viruses, some to bacteria, but also to fungi, can be considered as triggers.
What they all have in common is that they feel very comfortable in a dark, warm and humid environment and find optimal growth conditions there. The most common sexually transmitted diseases in Germany are infections with chlamydia, the Gonorrhea (popularly: gonorrhea), syphilis and infections with the HI virus; The HI virus has a special position due to the severity of the disease and the intensive therapy concept. It will therefore play a subordinate role in the following.
Read more about the topics: HIV and AIDS
The frequency of the occurrence of sexually transmitted diseases in general has decreased significantly in the recent past following increased awareness-raising and condom campaigns. Only in the last few years have there been more observations of sexually transmitted infections. This phenomenon can mainly be explained by a changed perception and a decreased awareness of the problem.
Since sexually transmitted diseases are no longer ubiquitous and the treatment options (in most cases!) Are quite effective, many underestimate the risk of infection and show a rather risky sexual behavior.
ly young, sexually active people who experience frequent partner changes are at risk. With most sexually transmitted diseases, the risk of infection is higher for men than for women of the same age.
There are dangers in not recognizing or not treating a sexually transmitted disease; as a rule, however, the majority of cases can be managed well. Most can be brought to complete healing with adequate therapy.
Symptoms
The symptoms of the different sexually transmitted diseases are diverse. Some signs can be seen very commonly and are common to almost all infections. These should be listed here for an overview at the beginning.
This is followed by some particularities regarding the course of diseases in the genital area that are common in Germany. The following list is of course not complete. When in doubt, should always a doctor directly be consulted. Venereal diseases often express themselves as Ulcers on the genital organs.
Pain in the genital area, which can occur both at rest and as Burn or cramps Make sexual intercourse uncomfortable as well Urination irregularities are clear symptoms. The situation becomes dangerous if no complaints arise. In the worst case, ascending infections can cause the fallopian tubes to stick together in women or chronic inflammation of the testicles in men, which can render the affected person sterile.
In women, the above-mentioned adhesions also increase the risk of a Ectopic pregnancy, that is, a pregnancy that does not take place inside the uterus.
If symptoms appear too late, there is also the risk of having infected other contact persons by then.
Symptoms in women

The main symptoms in women who have contracted an STD are abdominal pain and vaginal discharge (fluorine). This can be very purulent and tough, or rather fluid and light. In most cases there is a bad smell. Unfortunately, the discharge due to an STD is not always clearly distinguishable from the normal discharge that many women experience due to their cycle.
A heavily changed discharge, however, always points to an underlying disease and should be examined by a gynecologist. Furthermore, patients regularly report symptoms similar to those of a bladder infection or urinary tract infection; when urinating they feel a burning sensation and itching, they go to the toilet more often than usual.
You might also be interested in: Symptoms of vaginal thrush
Symptoms in men
Male patients with sexually transmitted diseases often experience severe testicular pain and problems urinating. Here, too, the genitals burn and itch.
In addition, the urine stream is usually somewhat weakened; despite the urge to urinate and the attempt, urination is only done in drops. In addition, there may be secretions of pus and secretions from the urethra. For some infections these are even characteristic (see below).
also read: The scrotum itches - what's behind it?
The most common STD in Germany and Central Europe is infection with chlamydia.
These are initially expressed in strong, mostly purulent discharge in women as well as severe itching and burning. If left untreated, the infection can spread to the upper sexual tract and the area around the liver. Fever and severe pain are the result. Slimy-purulent discharge also emerges from the man's urethra. Patients notice frequent urination and general symptoms of a sexually transmitted disease - as described above as an overview. If left untreated, the disease can also progress further in men, leading to infections of the intestines, testicles and epididymis.
The incidence within the population, the so-called infection rate, is relatively high. The reason is that 70% of infected women and 30% of infected men do not notice any symptoms and are therefore not treated. It is therefore possible that within certain age groups a great many (with rapidly changing intimate partners) become infected without a single one ever having shown symptoms. Since the disease is asymptomatic in these patients, one speaks of a "silent" infection.
In addition to chlamydia, there is another bacterial disease that is also widespread: infection with Gonococci (N. gonorhoeae) causes a Gonorrhea (also: Tripper).
Even with this type of sexually transmitted disease, the identification is not always clear; Affected women only show symptoms in around 50% of cases, which are then often so weak that they are not even perceived as conspicuous.
Classic signs are a discharge that can smell unpleasant and under certain circumstances a slight burning sensation when urinating.
Spotting and a slight fever are rare. If left untreated, chronic pelvic pain and infertility can develop.
Affected men are usually easier to diagnose: pain and burning sensation when urinating as well as a yellowish-greenish discharge from the urethra, which can sometimes be observed constantly and sometimes only appears as a single drop in the morning after getting up. Nevertheless, there is also a risk that men will miss an infection.
After a few days, the symptoms of the Gonorrhea again without treatment, which gives the patient a false sense of security. Instead of healing, the infection is expected to worsen at this point; inflammation of the prostate and / or testicles occurs. There is still a risk of infertility.
Read more on the topic: Chlamydial infection
Another common sexually transmitted disease, which should not go unmentioned for reasons of clarity, is syphilis, which has now become somewhat rarer.
The disease, which is also called syphilis is known, runs in batches with partially long symptom-free intervals between.
Because syphilis without therapy as chronic progressive disease can be seen, each interval is more symptomatic than the previous one.
At the start small ones appear at the place of infection (genitals, oral cavity, etc.) Nodules. The resulting ulcer is painless, but red and very hard. It's highly contagious. Even without treatment, this ulcer will regress in about a month.
After a symptom-free phase the patients notice a kind of flu-like infection, which has nothing to do with the actual respiratory disease, and rashes on and throughout the body. Characteristic nodules and ulcers are visible, which are also very contagious. These rashes can persist for a very long time without therapy; Healing occurs spontaneously only after about 2 years.
After a renewed symptom-free interval then the infestation follows internal organs.
Theoretically there is the possibility of tumor formation everywhere, some of which is associated with severe pain and / or functional impairment of the organs.
If there is no treatment at this stage either, the so-called complete picture of the disease develops Neurosyphilis with involvement of the nervous system. Affected patients become demented, show mental abnormalities and gait disorders. Neurosyphilis can lead to patient death. Thanks to good therapy options and mostly early treatment, processes as described above can hardly be observed today.
Genital herpes is the most common diagnosis among the non-bacterial sexually transmitted diseases. In this case it is the herpes simplex virus type 2, which is closely related to type 1, which is known to cause cold sores.
An infection expresses itself with painful blisters in the genital area, which may tingle or itch.
These vesicles usually heal spontaneously after a few weeks.
In contrast to other STDs, which can be completely cured with adequate therapy and only recur when there is a new infection, the herpes virus cannot be removed from the body with one hundred percent certainty.
After the initial infection, the virus remains in the body and can return at any time under certain favorable conditions (stress, weakened immune system, irritation or inflammation in the genital area). Even then, the rash is potentially contagious again.
Finally in this overview is the infection with warts, more precisely with Genital warts to call. The disease caused by human papillomaviruses (HPV) is triggered, turns out - if it comes to an outbreak - as reddish-brownish nodules in the genital area, which rarely itch and burn.
Usually, however, they cause no complaints.
These skin growths do not always appear as a visible sign after an infection.
The viruses (similar to the herpes virus mentioned) can last a long time symptomless remain in the body. Under these conditions, the visible disease only appears when the immune system is weakened or the skin in the genital area has already been damaged.
causes
The respective pathogens are just as diverse as the symptoms and signs of the venereal diseases described above.
What they all have in common is an infection with certain disease triggers before the onset of the disease must have taken place.
Viruses, bacteria and fungi can potentially be used.
In most cases it already is pre-existing mucosal injuriesthat can be used as a portal of entry that favor acute infection.
After the pathogens have penetrated the mucous membrane, they either remain in a narrow, local area or continue to spread in an ascending manner.
transmission

In addition to various kinds of sexual transmissions (see below), transmissions from mother to child also occur at different times (before or during the birth Breast milk) or rarely Smear infection or other sources of infection (e.g. insufficient chlorinated water in public swimming pools). Not all routes of transmission are possible and plausible for all diseases, so that a precise indication of the type of suspected infection can give the treating physician decisive information. The person concerned should not hesitate to give the doctor a hint sexual preferences and practices as infections that show up in the genital area may also have infected the inside of the mouth or the lining of the anal area. In this case, these parts of the body should also be given a careful examination and diagnostic steps.
Transmission genital / oral / anal
The most common place of manifestation of sexually transmitted diseases and also the most common place of infection are the primary genital organs and the corresponding mucous membranes. This means that the vulva or the entire area within and near the labia in women and the penis as well as the testicles in men often show symptoms.
Nevertheless, sexually transmitted infections can also be found in other sexually useful and stimulable areas.
Women in particular complain of independent inflammation in some cases Mouth and throat area (for example after a mild cold with hoarseness) about atypical symptoms that can be explained by a sexually transmitted disease. Due to pre-existing light mucosal lesions as ideal entry points, it is easy for pathogens to settle here as well.
The third possibility of the infection site should not be neglected Anal area as well as the rectum.
Aggressive sexual practices in particular, which are often associated with minor injuries, represent a considerable risk factor for infections.
In principle, every sexually transmitted disease that can occur in the genital area can also be observed in the anal area.
diagnosis
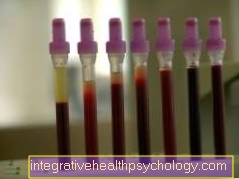
The diagnosis an STD is usually caused by a smear secured, which is examined by the treating doctor (gynecologist, urologist, family doctor) after the suspicion is expressed. The entire genome of the pathogen is often identified directly in the laboratory (PCR method).
Also a culture, so one Cultivation the pathogen on special culture media, or immediate microscopic observation is possible in some cases. However, these procedures are rather uncommon today.
In addition, there should always be a Examination of the urine done as an additional Urinary tract infection is not unlikely due to the great spatial proximity and may also have to be treated.
Rapid test

In addition to the diagnostic options described above, a quick test is also available to identify the most common diseases. Such reliable tests are offered by health authorities (also anonymously!), General practitioners, urologists, gynecologists and many dermatologists. If the first symptoms have already arisen or the partner has been diagnosed with an STD, the statutory health insurance will cover the costs of this test. Tests that are only requested for routine screening or in your own interest often have to be paid for yourself.
Rapid tests for STD diagnosis can also be ordered on the Internet. However, these tests should be used with caution. If there is a justified specific suspicion (clear symptoms, positive tested partner) or a positive rapid test, it is advisable to visit a doctor in person for further diagnosis and treatment, as explained above. A test for any genital infections can also be useful without any visible symptoms; For example, in the case of risky sexual behavior, frequently changing partners or sexual contacts in the context of prostitution. Pregnant women are also tested as part of the pregnancy examinations, because an infection that has not been noticed until then could have serious consequences for the unborn child.
Read more on the subject at: Rapid test for sexually transmitted diseases
therapy
Treatment approaches in sexually transmitted diseases result after a detailed examination and diagnosis depending on the type of cause; are bacteria the cause is one Antibiotic therapy Strongly recommended.
Depending on the doctor's experience and the level of resistance of the previously known bacterial strains, a Antibiogram the bacteria makes sense in order to be able to initiate a more specific therapy with a precisely fitting antibiotic.
In addition, there should always be a Examination and treatment of the partner respectively; If the intimate partner changes, it is advisable to inform all persons with whom within the last 30 days unprotected sexual intercourse has taken place.
If possible, sexual intercourse should be avoided completely during therapy. The risk of therapy failure or a so-called Ping pong contagion (from one partner to the other and back again) is otherwise extremely high.
In the case of other causes, such as genital herpes disease, viruses or warts in the genital area, antiviral ointments or tablets can accelerate the healing process and alleviate symptoms, but are not absolutely necessary. Therapy often only serves as support.
forecast
Almost all sexually transmitted diseases heal without consequences with consistent therapy or can be contained. Nowadays, almost none of these infections are acutely life-threatening.
Important exceptions to this are infections with HIV, which by definition also belong to the HOURS as the virus can be transmitted through sexual contact. Classical sexually transmitted diseases in the sense of the infections that were presented above usually respond well to therapy and are usually curable.
In this context, it is only important that a therapy is prescribed in the first place. False shame or other personal reasons should not be an argument against seeing a doctor.
prophylaxis
A venereal disease you have lived through does not give you Immune protection from new infections. Even a currently existing disease does not protect against further illnesses, but even promotes them through the existing irritation of the mucous membranes.
A good therapy therefore also includes a sensitive educational talk, which among other things should give the urgent advice to protect yourself and others during sexual intercourse. The only effective and at the same time very simple prophylaxis against sexually transmitted diseases are condoms. When used correctly, they not only protect against unwanted pregnancies but also against HIV and all infections in the genital area.