White skin cancer
What is white skin cancer?
In popular parlance, the term “skin cancer” is often used to refer to the dangerous malignant melanoma. However, many different types of skin cancer can be differentiated medically. The so-called "white skin cancer" comprises two different skin diseases that, in contrast to black melanoma, appear whitish. In detail, the term includes Basal cell carcinoma and spinocellular carcinoma.
The names already reveal that white skin cancer is also a malignant disease with the possibility of growing, spreading in the body and being life-threatening. However, it is far safer than the black skin cancer that is responsible for most skin cancer deaths. The name "carcinoma" implies that the cancer cells originate from the superficial layers of the skin, the so-called "epithelia". In contrast, there is black skin cancer, which originates from the pigment-forming cells.

Causes of White Skin Cancer
The causes that promote white skin cancer are lifestyle habits, genetic factors and contact with toxic substances. Injuries, burns, other previous damage to the skin or infections with certain pathogens can also trigger cases of white skin cancer.
However, the number one main cause of all white skin cancer is long-term sun exposure. The cumulative exposure to sunlight is primarily responsible, not individual damage in the form of sunburn. Severe sunburns are more of a risk factor for black skin cancer. Cumulative sun exposure is the lifelong, total sun exposure that a person collects over the years. This means that people who spend more time in the sun or in sunny regions of the world are more likely to develop white skin cancer. White skin cancer is thus by far the most common skin tumor.
Important causes of basal cell carcinoma, the more common variant of white skin cancer, are in particular genetic changes. For example, the disease Xeroderma pigmentosum favors this cancer. Squamous cell carcinoma, on the other hand, can develop primarily as a result of injuries, cuts, ulcerations, burns and skin irritations. More rarely, the papilloma viruses can also cause squamous cell carcinoma. Vaccination against many of these viruses has been available for several years.
What types of white skin cancer are there?
White skin cancer can primarily be divided into two different types, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, also known as spinocellular carcinoma. This distinction is based on the cells of origin of the tumor. These cells can degenerate and be stimulated to rapidly multiply and tumor formation. Each subspecies of skin cancer can be differentiated into further forms, depending on the external appearance and the form of growth.
Basal cell carcinoma can be nodular or flat, grow invasively or remain superficial, be colored or colorless and appear soft or hardened. Accordingly, for example, the most important variants are differentiated into “nodular and solid” or “superficial-multicentric” basal cell carcinoma.
Squamous cell carcinoma, on the other hand, is differentiated based on its stage and location. In contrast to basal cell carcinoma, it can metastasize and spread more frequently, which is why precise staging in diagnostics is crucial for prognosis and therapy.
More information can be found here: Basalioma - information about white skin cancer
You can recognize white skin cancer by these symptoms
White skin cancer can look very different depending on the exact type of disease, how it is spread, pigmentation or other factors. In contrast to the more dangerous and well-known melanoma, it is not pigmented black like a mole. Only in very rare cases of basal cell carcinoma can there be a black color.
Squamous cell carcinoma is often first recognized as a reddish point on the skin. This can appear rough and hardened. As it progresses, the point grows into a knot with small, hard, pearl-shaped protrusions. The lumps may later ulcerate and bleed. In rare cases, they can spread to other parts of the body and organs through deep growth. White skin cancer can only very rarely be life-threatening.
Basal cell carcinoma, the more common form of white skin cancer, often appears yellowish at first. It is also noticeable as a rough bump on the skin. Then the cancer can take many forms and be lumpy, scarred, or ulcerated. What these shapes have in common, however, is constant growth and, in contrast to moles and other skin changes, an irregularity in size, shape and delimitation.
Further information on the topic can be found here: Symptoms of a basalioma such as These are the symptoms of skin cancer
Itching in a white skin cancer
In the vast majority of cases, white skin cancer is characterized by the fact that only a few symptoms occur. The skin cancer is often only noticed by the externally visible changes and small lumps, at best by slight bleeding if the cancer ulcerates. Itching can only occur in rare cases due to some kind of inflammatory reaction. The affected area should not be scratched, however, as this can damage the skin, start to bleed and germs that cause inflammation can get under the skin. However, severe itching initially speaks against white skin cancer.
More information can be found here: Itching of the skin
White skin cancer pain
White skin cancer is largely symptom-free, especially in the initial stages. Pain in the skin or in the body is often only related to the cancer if it is well advanced. Well-advanced findings on the skin can be accompanied by ulcers and bloody changes. This can lead to pain. In the rare event that the white skin cancer forms deposits in distant organs, this too can lead to pain. As a rule, however, local pain is not one of the typical symptoms.
What does white skin cancer look like in the early stages?
The most important step in the treatment of all types of skin cancer is to identify the early stages and not to delay a visit to the doctor if there are any suspicious changes. Early stages hardly cause symptoms and therefore cannot be noticed by pain or itching.
In the early stages of white skin cancer, whitish-yellowish or reddish spots appear on parts of the body exposed to the sun, for example the face, décolleté or the back of the hand. These are located on the surface of the skin, which is why noticeable superficial changes occur early on. The spots can be raised, appear rough and coarse and grow steadily. The earlier a cancer is detected at this stage, the better the prognosis and the smaller the skin area that needs to be treated and removed.
This article might also interest you: How do you recognize skin cancer?
What does terminal white skin cancer look like?
The terminal stage of white skin cancer can be fatal. Cancer is an underestimated danger because, if it is discovered later and treated inappropriately, it can also cause damage locally to the skin and throughout the body through metastases. If left untreated, the findings on the skin can cause severe aesthetic but also functional damage to the underlying structures. On the face, where white skin cancer is common, the cancer can ulcerate and destroy the nose, lips, eyes, and ears, and even the bones of the face. Metastasis can affect and destroy all internal organs in the final stage. Even if the prognosis is good overall, therapy should not be neglected.
Diagnosis of white skin cancer
In the case of skin tumors, self-diagnosis and your own attention come first. For all forms of skin cancer, early detection improves the prognosis.
Superficial changes can occur anywhere on the skin. However, if a small lump appears, which changes and grows, this indicates a malignant change in the skin. A dermatologist should be consulted as soon as possible if there is justified suspicion. This can precisely examine the change in what is known as dermatoscopy. Factors to which special attention is paid are contour, size, color irregularities and structural unevenness. A suspicious finding must then be examined in a tissue sample under the microscope.
People over 35 have the opportunity to have a routine examination by a dermatologist every two years.
This article might also interest you: How can you recognize skin cancer?
Treatment of white skin cancer
Treatment varies with the stage and spread of the disease.
Since white skin cancer does not normally metastasize quickly and spreads comparatively slowly on the skin, detection and treatment in the early stages is likely. There are numerous therapeutic methods for white skin cancer today. However, surgical removal still comes first. In advanced stages, in addition to the superficial operation, the lymph nodes are also removed. The possibility of surgical removal depends primarily on the location and size of the tumor.
Alternative treatment methods must be considered especially in the case of very large tumors on the face, advanced age, and recurrent tumors. Therapies such as freezing, chemotherapy in the form of cream, photodynamic therapy, immunotherapies and radiation are also used. There are many innovations and good results, especially in local chemotherapy.
More information can be found here: This is how skin cancer is treated such as The best therapy for a basalioma
Does homeopathy make sense in treatment?
The basic idea of homeopathy is to stimulate the body's self-healing powers so that the body can heal the disease by itself. In the case of cancer, however, the body's own cells are degenerate and multiply rapidly so that they form an ulcer. In acute situations, skin cancer must be treated surgically or with chemotherapy and immunotherapeutic agents, otherwise it will spread further.
Homeopathic remedies can be taken as a support, but must not be the sole therapy.
Can White Skin Cancer Be Fatal?
White skin cancer is much safer than black skin cancer. Both types of white skin cancer have a significantly lower tendency to infiltrate and metastasize. The speed of their growth is also significantly lower, which is why treatment can often be carried out early.
Basal cell carcinoma does not metastasize in most cases. Even after many years of growth, there is hardly any risk of further spread. However, in order to check the local findings and to prevent the eventuality of metastasis, therapy should be given. However, squamous cell carcinoma is more likely to metastasize. In particular, tumors larger than 2 cm are at risk of colonization. Even then, death from white skin cancer is unlikely, but possible.
On which parts of the body can white skin cancer occur?
White skin cancer can theoretically develop anywhere on the skin. The most common parts of the body where white skin cancer occurs are listed below.
White skin cancer on the nose
The nose is a particularly common site of white skin cancer. It protrudes from the face and accumulates an above-average amount of sunlight over the course of life. Even when the face is covered, for example when skiing, the nose is often uncovered and exposed to the sun. However, white skin cancer can be recognized quickly on the nose. Here, both detection and treatment can often be carried out in the early stages. Surgery to remove the tumor is also the therapy of first choice here, but for certain reasons photodynamic therapy can also be considered as the first treatment, for example if several operations on the nose have already had to be performed after recurrences or if the affected area has been blocked is great.
You may also be interested in this topic: Basalioma of the nose
White skin cancer on the face
The face as a whole hosts most cases of white skin cancer. The nose and lips in particular are most commonly affected on the face itself. This is also due to the thesis on the development of white skin cancer. These areas collect most of the solar radiation over a lifetime. Exposed areas on the face such as the lips, cheeks, nose or forehead are therefore so-called "predilection points".
Read on here: Skin cancer on the face
White skin cancer on the scalp
Cases of white skin cancer on the scalp are generally less common but possible. Here, too, only exposure to the sun counts to a large extent. In people without scalp hair, the likelihood of cancer on the scalp is not only increased, but much more likely than on other parts of the body. For this reason, protection against UV light on the scalp is all the more important when someone is bald.
White skin cancer on the lip
White skin cancer on the lip is not only very uncomfortable but also very common. In contrast to other skin areas, the lip is not able to produce melanin, i.e. skin pigments. The lip is also often affected by sunburn. Even after long exposure to the sun, the lip is unable to adapt to the conditions and tan like the rest of the skin. Sunscreen must always be applied to protect the lips. These days there are also lip balms and lip balm sticks that contain sunscreen.
However, white skin cancer can be detected early. Due to the sensitive receptors in the lip, knotty, hard and rough changes are noticed particularly quickly and are annoying at an early stage.
White skin cancer on the forehead
As an exposed, large area of skin, the forehead is one of the typical "predilection sites" for white skin cancer. About 80% of all cancer cases occur between the forehead and lip. Important sun protection is essential when exposed to the sun.
White skin cancer on the ears
The ears are relatively often affected by white skin cancer. Although they are exposed on the head, many people are covered by hair. With long hair and good and constant sun protection, the likelihood of white skin cancer on the ears decreases. Protruding ears can also be a risk factor for cancer.
More on this: Basalioma on the ear
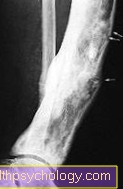
White skin cancer on the back of the hand
The back of the hand is also often affected by the cancer. The hands are rarely covered by clothing. The back of the hand is also often forgotten when applying a protective sunscreen, even though it is continuously exposed to the sun. White skin cancer is often recognized early on on the back of the hand and the treatment can also be carried out at this point.
White skin cancer on the back
The back is significantly less affected by white skin cancer than regions such as the décolleté or the head.
The skin on the back is a very large area and, under suitable conditions, can accumulate a lot of sunlight. Cases of white breast cancer are much more likely, especially in warm regions, where men and women are often bare chested in the sun. This can affect people who frequent the beach as well as workers who work topless in the sun. Adequate sun protection with sunscreen is extremely important. Many do not adhere to this, as applying cream to the back seems too time-consuming or difficult. Even if there are no sunburns on pre-tanned skin, long-term sunlight accumulation must always be considered.
How good are the chances of recovery in white skin cancer
The chances of recovery are good compared to other malignant cancers. As a rule, white skin cancer does not spread very quickly, which is why treatment in the early stages is quite possible. The main findings can be easily checked with the help of the operation and follow-up treatment.However, within the first two years there are very frequent relapses and small recurrences of the skin. Therefore, check-ups are recommended every three to six months.
Most recurrences occur particularly within the first two years. However, follow-up care is carried out over a period of 5 years. A complete cure is not possible in very many cases, but control over the tumor and the associated probability of life are very good.
Read more about this: The prognosis for a basalioma
How Fast Does White Skin Cancer Grow?
The different forms of white skin cancer are associated with different growth rates.
Basal cell carcinoma is not only less aggressive than squamous cell carcinoma in terms of its spread and metastasis, but also in terms of its growth rate. From the first appearance it usually develops over years. It grows slowly but steadily and takes many years for severe local damage or small settlements. Nevertheless, early treatment is advisable in order to keep the surgical and treatment area as small as possible.
Squamous cell carcinoma, also called spinalioma, on the other hand, grows much faster. It can cause noticeable and large local changes after just a few months or a year. A settlement and further spread in the body, however, happens very slowly. The squamous cell carcinoma only spreads locally to the lymphatics and lymph nodes at a late stage. Metastases in distant organs occur only rarely and generally much later, often only after years.
Metastases in white skin cancer
Metastases are relatively rare in white skin cancer. In contrast to black skin cancer, white skin cancer is also significantly less dangerous. Metastases describe settlements in distant organs, foreign tissues or lymph nodes.
In the case of tumors that grow deep, metastasis is very likely in the long term. Often the cancer cells attack the nearby lymph nodes and can spread over them or via the bloodstream to distant body regions. Statistically, the likelihood of colonization is much higher for a tumor larger than 2cm than for smaller tumors. Squamous cell carcinoma also spreads significantly more frequently than basal cell carcinoma. If there is already metastasis, the long-term prognosis is significantly worse. Even after treatment and removal, the likelihood of further previously unnoticed settlements is extremely high. This also reduces the overall likelihood of the cancer being cured.
Is White Skin Cancer Contagious?
Skin cancer, and cancer in general, is not contagious.
Infection is never possible even with direct contact with the cancerous areas. Only in the very rare form of virus-related cancer variants can the risk of developing cancer in the infected person increase through the transmission of the virus. In this case, however, one would not speak of an infection of the cancer.
What degree of disability (GdB) is there for white skin cancer
The German law for severely disabled people defines various degrees of disability. The grades start at 20 and can be increased in steps of ten to 100, with a higher grade being associated with higher impairments and thus higher compensation for disadvantages.
The presence of white skin cancer can justify a level 50 disability. This is determined by the Supply Medicine Ordinance. From a value of 50 onwards, one speaks of a severe disability with the associated compensation for disadvantages, for example a preferred setting, a certain tax exemption, protection against dismissal and many other facilities. In advanced stages, for example with metastasis of white skin cancer, the grade can increase to 80.















-braun.jpg)