What are the signs that my rash could be cancerous?
introduction
The cause of a rash is usually a bacterial, viral or fungal infection.
The likelihood that a rash is actually skin cancer is extremely small. A degeneration of a skin rash into cancer is excluded. Although rashes occasionally occur in the context of cancer, the skin changes are then an accompanying symptom as an expression of the weakened defenses of the entire organism, but not a cancer of the skin.
Still, any rash should be presented to a doctor. This is advisable not least because the possible risk of infection for contact persons can be reduced through adequate treatment.
Read more on the topic: Causes of a rash
Although the doctor will give the all-clear in most cases, a group of cancers is known to medicine that can actually be easily mistaken for a rash. These are the so-called cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. The cutaneous T-cell lymphomas are characterized by an uncontrolled reproduction of a line of defense cells. Like the name T-cell lymphoma already stated, the degeneracy affects the T lymphocytes, which are particularly common in the skin. The disease progresses slowly and over many years, sometimes even decades. It is a malignant cancer that can affect the entire organism in later stages. The most common T-cell lymphoma is the Mycosis fungoides, which gets its name from the former confusion with a fungal skin disease (Mycosis) Has. Another one T-cell lymphoma is this Sézary syndrome.
Read more on the topic: Skin lymphoma.

Symptoms
The Mycosis fungoides resembles the others in their course T-cell lymphoma. It runs in three stages, the first of which is one Skin eczema is easily mistaken for a common rash. It arise several round to oval, reddened foci of different diameter, which in some cases Blisters or oozing. In the second stage, the pre-existing foci enlarge and a plate-like, slightly raised pattern of the affected skin area is increasingly noticeable. Not infrequently there is one severe itching. Of the Loss of hair the diseased skin is possible and it persist occasionally Swelling of the surrounding lymph nodes. Only in the third stage, the so-called tumor stage, arise Tumor nodulesthat appear as bulbous or lobed elevations on the skin. These tend to disintegrate and form weeping ulcers.
The Sézary syndrome begins with a general, strongly pronounced one Reddening of the skin (Erythroderma), which is also severely flakes.
Diagnosing one cutaneous T-cell lymphoma is not easy and it often takes a long time to reach a final diagnosis. Especially in the early stages, the appearance resembles a normal rash. Of the Suspected lymphoma is for very long and therapy-resistant courses of skin eczema or abnormally persistent findingsthat one psoriasis resemble to pose. If the usual therapies that are used for eczema or psoriasis do not lead to an improvement in the complexion even after a long period of therapy, a further examination of the disease should take place. The definitive diagnosis is made after the pathological findings of a skin biopsy.
itching
itching is a common symptom of diseased skin. He occurs with bacterial, viral and for fungal infections and allergies frequently on and can have a lasting negative impact on the patient's well-being. Itching is a warning sign of diseased skin, but it is a symptom harmless in most cases. The unpleasant sensation provides indications of infections, dryness of the skin, excessive sun exposure or intolerance to certain foods or substances from the environment. Almost every rash is itchy.
Just in rare cases, chronic itching indicates cancer. In the case of the T-cell lymphoma already described, considerable, sometimes agonizing itching of the affected skin areas (Mycosis fungoides) or the entire skin (Sézary syndrome) occur. If severe itchy rashes or reddening of the skin persist over a long period of time despite intensive and adequate treatment, the initial diagnosis should be questioned and the cause of the disease should be re-examined.
Itchy birthmark

The birthmark, in medical terminology Nevus called, is a benign growth of pigment-forming cells (Melanocytes) of the skin. On average, about 30-40 birthmarks of different sizes or colors appear on each person. Occasionally, these can change their size, shape and appearance.
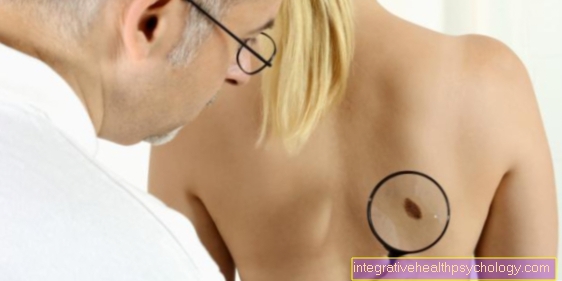
Also Itching around a birthmark can occur. Although the birthmark is a benign finding, occasional degeneration can occur and skin cancer can develop. This risk is particularly acute with very light skin types or with people with an unusually high number of birthmarks. A Warning sign for the Malignant degeneration of a birthmark is itching. However, this does not always mean that cancer is actually present. As a precaution, you should see your family doctor or dermatologist, who will look at the birthmark from various angles.
A Assessment of the presence of skin cancer becomes about the so-called ABCDE rule met. Birthmarks are considered suspicious pronounced asymmetry (A) exhibit, unsharp limited (B) are, several shades (F) show one large diameter (D, about 5mm) have or where there is a rapid development (E) of the points mentioned above. So the itching of a birthmark is by no means a sign of cancer. Rather, several parameters have to be considered and taken into account when assessing the risk.
Bleeding birthmark
A bleeding birthmark should In any case Give cause for a doctor's visit. In addition to itching, pain and oozing, there may be bleeding from a birthmark a sign of malignant degeneration the originally benign finding be. As with itching, however, a bleeding birthmark does not necessarily mean cancer. Rather, the area of skin may have been injured by an inadvertent movement or it may have got stuck on items of clothing because of its sublimity. The doctor will look at the suspicious mole from the point of view mentioned above and make an assessment.
At this point it must be mentioned that, according to recent studies, the likelihood of degeneration of a birthmark is only slightly higher compared to normal skin. In Western Europe around 10-15 / 100,000 people develop black skin cancer every year.