Asian (Japanese) bush mosquito
definition
The Asian or Japanese bush mosquito is native to parts of China, Korea and Japan and can transmit diseases to animals and people through its bite. In recent years, the insect has also been introduced to other parts of the world and has thus spread to North America and some regions in Europe, for example. Within Germany, the bush mosquito has settled on the Upper Rhine and in the Spreewald.
-buschmcke.jpg)
How dangerous is it?
In most cases, a mosquito bite by the Asian bush mosquito is harmless and only causes swelling and itching. In rare cases, however, a pathogen can also be transmitted through the bite, which usually leads to flu-like symptoms.
In individual cases, more serious consequences such as meningitis or nerve damage can occur. Dreaded transmitted diseases are the so-called Japanese encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain tissue, as well as the "West Nile fever".
In affected regions of Asia, the best way to protect yourself is with the usual insect repellants. The animals that have spread to Europe and North America do not pose any danger and special protective measures are therefore not necessary.
Read more on the subject below Japanese encephalitis and Asian tiger mosquito
What does the sting of an Asian bush mosquito look like?
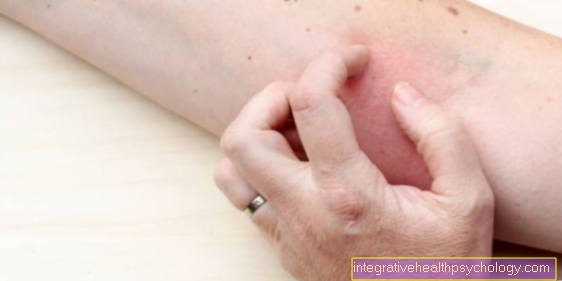
After being bitten by the Asian (Japanese) bush mosquito, a slight inflammatory reaction occurs in the affected area (see also: Inflammation after a mosquito bite). As a result, mostly round swelling and reddening develop. If you scratch the area because of the itching, swelling and redness are increased.
Also read the topic: Swelling after a mosquito bite
However, it is not possible to distinguish the mosquito bite by the Asian bush mosquito from the bite by another species of mosquito. The sting or bite of other insects also usually looks very similar. Likewise, allergic reactions, irritation from sunlight or skin symptoms after contact with certain plants can present themselves very similarly.
also read: Black fly
Accompanying symptoms with a sting
If you are bitten by the Asian bush mosquito, as with most insect bites, the affected area is primarily itchy. The mosquito bite can also be slightly painful. The symptoms are usually no different from those of a normal mosquito bite.
Since the Asian bush mosquito can also transmit a disease-causing virus in extremely rare cases, flu-like symptoms can also occur. These include, for example, fatigue, pain in the limbs or headaches, and a slight fever.
In very rare cases, nerve damage and meningitis can also occur. Possible accompanying symptoms are, for example, impaired consciousness or a stiffening of the neck muscles. In the event of such symptoms as a result of a mosquito bite, the family doctor should be consulted promptly.
In addition, it could lead to an allergic reaction after the mosquito bite, especially if you generally tend to allergic reactions quickly. In addition to nausea and dizziness, circulatory disorders and shortness of breath can occur. If you suspect an allergic reaction, you should consult your doctor.
Find out more at: Allergic reaction to a mosquito bite
How long does the sting cause symptoms?
In most cases the symptoms after a bite by the Asian bush mosquito do not differ in severity and duration from those caused by a normal mosquito bite. The redness and swelling as well as the itching recede within a few days.
However, if flu-like symptoms occur due to pathogens transmitted by the bite, these can last for several days to a few weeks. If symptoms do not improve after a week, a doctor should be consulted. In extremely rare cases, permanent damage is possible after a severe course of the disease with an attack on the nerves.
That could be interesting for you too: Mosquito repellent
What diseases does the Asian bush mosquito transmit?
In most cases, a bite from the Asian bush mosquito does not transmit any disease at all. There is only swelling, redness and itching at the puncture site. However, it is possible that certain diseases can also be transmitted through the sting. This includes, for example, West Nile fever. Even if a person is infected with the responsible pathogen, this usually goes unnoticed and there are no symptoms at all.
In some cases, however, the disease manifests itself through flu-like symptoms and fever. Even more rarely, meningitis with headache, impaired consciousness and possibly consequential damage can also occur. For the Asian bush mosquitoes that are widespread in Europe, however, no potential for transmission of diseases has been demonstrated so far, so that there is really no danger from the insects and special precautionary measures do not have to be advised.
Can you vaccinate against a bite?
So far there is no vaccine against the Asian bush mosquito or against the pathogens that can be transmitted by the insect. There are only vaccinations against other insects such as the yellow fever mosquito. If and when such vaccinations are useful or necessary, for example, the family doctor can tell in a consultation. Instead of vaccination, one can protect oneself from bites by the Asian bush mosquito by using insect repellent on skin and clothing. Mosquito nets, which are also best coated with insect repellent, provide protection during sleep. The danger posed by the Asian bush mosquito in Europe is considered to be extremely low anyway, so there is no need to be afraid of a serious infection and protective measures are not necessary in this country. However, when traveling to Japan or Korea, insect repellent measures are recommended.
Read more on the topic: Insect bite - first aid and immediate measures

-buschmcke.jpg)