Atlas correction
definition
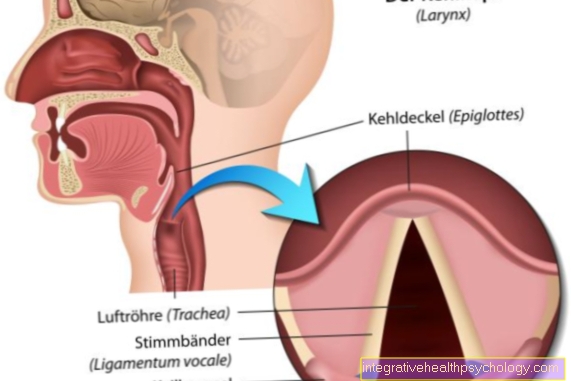
The atlas (C1) is the first vertebral body of the spine, which is located directly below the skull. Together with the second vertebral body, it forms a functional unit and enables the skull to move in a wide range of movements compared to the rest of the body. The movement of flexion (flexion) and extension (stretching) is only made possible by the shape and arrangement of the joint surfaces on the atlas.
The atlas correction is a form of therapy that realigns an unphysiological position of the atlas and returns it to its anatomically meaningful position. For this purpose, the local autochthonous and secondary back muscles are loosened and can thus enable repositioning (reorientation).

Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
indication
Misalignments of the atlas can occur from the beginning of life. These can already be caused by the physical stress of the birth process.
Other reasons can be a traumatic accident while doing sports, in traffic or falling. To secure the airway, an atlas misalignment can also arise during intubation.
Indicated is a measure for chronic complaints, which mainly occur in the area of the musculoskeletal system. Back pain, scoliosis, bad posture, pins and needles, regularly occurring headaches, migraines, herniated discs, lumbago, pelvic obliquity with leg length differences as well as hip and knee pain are possible. The therapy of an atlas correction can be an option if no other reasons for the complaints could be found after clarification of further causes.
Due to the interaction of the cervical spine with nerve cords, as well as the blood supply to the head and the brain, constant inexplicable tiredness or unclear dizziness can be further reasons for this therapy. The proximity to different nerve cords can also affect the independent / autonomous nervous system (Vegetative) so that, for example, digestive problems with a previously unknown cause can represent a further indication for an atlas correction.
Concomitant symptoms
Symptoms of an atlas deformity can be very variable and present locally in the form of headaches (tension headache), migraines, dizziness or jaw deformities. In relation to the entire musculoskeletal system, incorrect loads can arise, which in turn can be associated with pain. The areas of the hip and knee joint, as well as the spine (back pain up to the clinical picture of herniated disc, scoliosis, lumbago, as well as pelvic obliquity and the resulting leg length difference) are predestined.
Read more about this under How long does a lumbago last?
In the context of the vegetative nervous system, symptoms can also result by influencing the vagus nerve (vagus nerve). Above all, this results in possible dysregulations of the internal organs such as the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, gastrointestinal tract or spleen.
In the area of the spine, excessive kyphosis or lordosis can develop in the context of incorrect posture, so that compressions can result. These in turn can trigger disorders of the vascular supply, as well as lymph drainage and nerve disorders (nerve disorders), so that symptoms of reduced blood flow, lymph drainage and sensitivity disorders can result.
Read more about this under
- Lordosis
- Kyphosis
In relation to the abdomen (stomach), an atlas malposition can possibly cause a passage disruption, which can be associated with a reduced outflow of digestive secretions from the glands of the intestine.
dizziness
A symptom appearing that can be seen as a disturbance of balance due to uncoordinated information to the brain.
Different Etiologies (Origins) can be seen as the reason for the dizziness. With reference to the atlas correction, it can be mentioned that in the area of the neck area the vessels supplying the brain flow in and out and important pathways for motor skills and sensitivity run. Baroreceptors are also located here as a mechanism for regulating blood pressure. Manipulation in this area may cause circulatory disorders in the brain, irritation of receptors or mechanical stress on nerves, which in turn can cause dizziness.
Read also on this topic Causes of dizziness
Diagnosis of an atlas malposition
A detailed anamnesis discussion as a basic diagnostic measure can confirm the suspicion of an atlas malposition and rule out other clinical pictures. Support can be done using buttons (Palpation) a preliminary report can be made. If there is any suspicion, an atlas deformity can best be clearly demonstrated by means of computed tomography (CT). Reference should be made here to the high radiation exposure that occurs in comparison to a classic X-ray image. However, clear evidence can only be provided by computed tomography. Magnetic resonance tomography proves to be rather unsuitable in this case.
Treatment / therapy
The treatment usually takes place in one session. It is a gentle and painless treatment, without invasive or chiropractic methods. There are no maneuvers, such as lowering the head by turning the head, stretching or bending. Only the muscles in the area of the first and second cervical vertebrae and in the area of the skull are loosened by shock wave therapy. The lack of direct access to the muscles that support the atlas makes shock wave therapy necessary. If the muscles are released from their hardening by vibration of a vibrating device, the atlas can be corrected using massage technology. This improves the usually reduced range of motion of the head. The aim of the therapy is to put the "blocked" / "dislocated" neck joints back into their imaginary anatomical position. The restored physiological position can reduce incorrect posture of the entire body. The success of the treatment differs from patient to patient and can be accompanied by a direct therapeutic success immediately after the treatment or it can drag on for a few weeks afterwards.
Read more about this under Shock wave therapy
possible side effects
The atlas correction is not a guarantee of freedom from symptoms. On the one hand, this means that after the treatment there is not always an improvement.
On the other hand, symptoms can reappear even after successful treatment. Side effects are mainly known in the area of the musculoskeletal system. Painful conditions can occur particularly shortly after therapy. These express themselves in the form of muscular lesions (muscle soreness), which occurs more frequently after excessive stress on the muscle, as well as signs of fatigue / exhaustion. As part of healed injuries in the neck and neck area, pain can be caused again here.
In the case of pre-existing damage to bones, ligaments and spanning muscle tendons, an atlas correction can cause further side effects. With regard to the bones, spontaneous fractures and dyspositioning cannot be ruled out. This means that the atlas correction itself can cause non-physiological positions. Torn ligaments or painful soft tissue injuries to the muscle tendons can also fall into the spectrum of side effects. In the case of chronic muscular diseases, such as Becker or Duchenne muscular dystrophy, an atlas correction is clearly not advisable.
How common is an initial worsening?
As part of the atlas correction, increasing tension, including severe muscle pain, can be recorded for the first time after the treatment. Patients report that dizziness and nausea can also occur as part of the tension. The exact number of cases about the aggravations mentioned is not known. According to experience reports, the spectrum is drifting far apart, from immediate improvement to severe muscle pain.
How dangerous is an atlas correction?
As already described, an atlas correction is a rather gentle form of therapy. As there is no direct mechanical manipulation of the vertebral body, the risk is assessed as low. Since whiplash injuries after accidents or other traumatic events with uncontrolled forces acting on the musculoskeletal system can cause marginal misalignments up to and including fractures (broken bones), a clear diagnosis should be made in advance. The clarification should distinguish a soft tissue injury from anatomically changed conditions in order to enable adequate medical care.
If there are no endangered defects in the spinal column, an atlas correction can be carried out with a low risk. In the context of chronic diseases such as osteoporosis, severe scoliosis, deformities, spinal stenosis or after orthopedic / trauma surgical care, medical advice should be obtained beforehand. It is conceivable that in the cases mentioned, shock wave therapy or similar applications can result in spontaneous fractures or other consequences. Due to the location of the central nervous system in the spine, great caution is advised here in unclear circumstances.
Duration of therapy
The therapy is carried out as part of a session, so that a one to two-hour session results here due to the subsequent treatment scheme. In order to then wait for reactions from the body, a period of four to eight weeks is recommended in which the body can adapt. After the specified period of time, a control appointment is recommended in which the current position of the atlas is determined again and, if necessary, corrected again. The check-up appointment is about an hour.
How often do you need to correct?
No figures have yet been published on this. What is certain is that in some cases corrections will be carried out in the second session if it is established that the complete final position of the atlas has not yet been reached.
Can you do an atlas correction independently?
The atlas correction is a gentle and sensitive matter that should not be carried out if the patient is suspected of having an independent diagnosis. The cervical spine area is a vulnerable area that should only be treated by people with the appropriate training. For an adequate treatment, a precise knowledge of the anatomy of the bones as well as the muscles and ducts is necessary. Since the therapy is carried out with different devices depending on the provider, one is not even able to carry out an atlas correction due to a lack of knowledge and without technical support.
What about assuming the cost of the atlas correction?
In principle, the atlas correction is a controversial topic in science, for which no agreement on the benefit has been reached until today. There is no scientific background that could not be proven by serious studies. As a result, this form of therapy has not yet been recognized and is not in the catalog of items of the statutory health and health insurance companies. In rare cases, the therapies are covered by supplementary insurance after an examination of the cost coverage has taken place.
How do I find a good atlas therapist?
Since the therapists are usually not doctors, no information about this can be obtained from the German Medical Association or via platforms on specialist doctors. Following recommendations in forums as well as personal recommendations therefore remains one of the limited ways to get advice. In addition, certificates can be used by the providers as a guide.










.jpg)