Herniated disc of the cervical spine
introduction
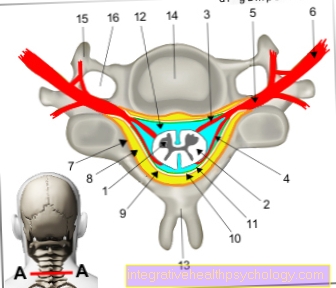
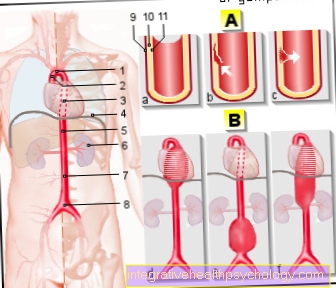
The Cervical spine consists of 5 Vertebral bodies plus two apex vertebrae, the Atlas and Axis to be named. Two vertebral bodies are replaced by one Intervertebral disc separated, which on the one hand are supposed to make the movement in the cervical spine more frictionless, on the other hand to dampen forces that burden the spine.
Herniated discs the cervical spine (Cervical spine) are a little less common than herniated discs ESPE or Lumbar disc herniation. One reason for this is that the strenuous movements of the spine are mainly carried out through the lower part of the spine (Lumbar spine, thoracic spine).

Causes of a herniated disc of the cervical spine
A herniated disc of the cervical spine can be triggered by e.g. heavy lifting of objects. Furthermore, a sudden, violent turning of the head in one direction can lead to a sudden slipping out of the intervertebral disc in the neck area (acute herniated disc).
Chronic herniated discs of the cervical spine are much more common, mainly due to constant poor posture. Especially with people who sit for a long time or who stay in one position, the cervical spine may show signs of wear.
Occupational groups such as professional drivers or people in office work are also more often affected by a herniated disc of the cervical spine (Cervical spine).
Factors that can also promote a herniated disc are restricted mobility and the patient's lack of movement. A herniated disc of the cervical spine can also be hereditary. The main reasons are weak connective tissue, which can promote a herniated disc. The reason is that the muscles and the connective tissue that keep the vertebral bodies lying on top of each other are weakened and can thus encourage the vertebral bodies and intervertebral disc to slip. For this reason, people who are in an untrained muscle state are also more at risk of a herniated disc.
Furthermore, anatomical factors can promote a herniated disc in the cervical area. Certain constellations of stability and the anatomical position of the vertebral bodies in relation to one another can also lead to premature prolapse of the intervertebral disc. In addition to the degenerative causes of a herniated disc (leaning forward posture, sedentary work, etc.), trauma can also lead to a herniated disc. A trauma or accident that affects the spine can lead to acute instabilities, which on the one hand can cause the intervertebral disc to slip out between the vertebral bodies, and on the other hand a chronic herniated disc can result from an acute instability.
Appointment with a specialist for a herniated disc?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
A herniated disc is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
Therefore, treating a herniated disc requires a lot of experience.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Symptoms of a herniated disc of the cervical spine
The cervical spine supports the head and supports its ability to move. In the area of the cervical spine, nerves emerge that innervate the arms and hands, as well as the diaphragm.
If there is nerve root irritation or compression of the nerve roots, they can become inflamed, which is perceived as pain. This pain in the neck, shoulders, and arms is usually the first sign that the nerves are inflamed.
In addition, abnormal sensations occur in the relevant dermatomes (areas of skin that the nerve innervates), which increase over the course and are constantly present. These abnormal sensations include numbness or a tingling sensation in the arm or hand that resembles an ant run and can be another sign of a herniated disc. An excessive sensation of pain or burning is also counted as abnormal sensations.
In addition, muscle strength may decrease. As a result, there is weakness in the arm and hand. Furthermore, the patients have symptoms such as headache, dizziness and also ringing in the ears such as tinnitus occur. Sensory disturbances, such as numbness or tingling, can also appear on the face.
Symptoms increase when the head is tilted, either to the side or back. With these movements 5% of the patients feel something that can be compared to an electric lightning bolt and that goes through the whole body (Lhermitt's sign).
You may also be interested in the following article: Numbness in the arm
In addition, the pain increases when lying down, and it can even get so bad that lying down is no longer possible because the pain is too strong. If paralysis or loss of sensation occurs, a doctor should be urgently consulted.
Read more on this topic at: Symptoms of a herniated disc of the cervical spine
Pain from a herniated disc
The pain associated with the herniated disc in the cervical spine is caused by the compressed nerves caused by the displaced disc. Depending on how much the nerve or its root is compressed, the strength and nature of the pain also varies. It may be sharp, burning and can be localized precisely (e.g .: shooting pain / circumscribed knocking pain / Lhermitt's sign) or dull, pulling and difficult to localize. The pain occurs mainly in the neck and shoulder area, radiation to the arms and head is also possible. Worsening of the pain of a herniated disc occurs when the head is tilted backwards or sideways, or when lying down and at night.
At this point you can read which drugs are suitable for a herniated disc: Medication for a herniated disc
diagnosis
The initial consultation with the patient is an important part of the diagnostic process. The complaints expressed, such as back pain, especially in the neck and shoulder area, can indicate a prolapse of the cervical spine. In addition, the doctor asks questions such as "Have you noticed numbness or tingling in your arms or individual fingers?"
With simple physical examinations, the suspicion of a herniated disc of the cervical spine can be reinforced. If symptoms of paralysis, sensory disturbances or a reduction in strength of the arm or finger muscles occur, this indicates a complicated course of a herniated disc of the cervical spine. Such a disease can also occur asymptomatically, i.e. without any real symptoms.
Then only an imaging test can detect a herniated disc of the neck. A decrease in height of the intervertebral disc can indicate an incident on the X-ray. Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) are available for a precise diagnosis.
With an MRI of the cervical spine, sectional images of the cervical spine are made. Here you can see the exact location of the herniated disc of the cervical spine.
Further information on this topic can also be found at:
- MRI of the cervical spine (Cervical spine)
- MRI for a herniated disc
Usually the disc between the sixth and seventh vertebral bodies is affected. The direction of the incident can also be determined using CT or MRI. In rare cases, especially in severe forms, a so-called myelography is performed. A contrast medium is injected into the spinal canal and an X-ray or CT image is then taken. In this way, the nerve root can be accurately assessed.
Read more on the topic:
- Recognize herniated disc
- Diagnosing a herniated disc
In the presence of paralysis or sensory disorders, the muscle and nerve activity can be measured using electromyography (EMG) or electroneurography (ENG). With EMG, the electrical activity of individual muscles is measured using a needle. With ENG, it can be discovered which nerve root is being pressed off the intervertebral disc. Other diseases that can cause numbness or paralysis, such as polyneuropathy, can also be diagnosed using the ENG.
In summary, the MRI examination of the cervical spine is the most valuable diagnostic tool.
Read more on the subject at: MRI of a herniated disc
Treatment of a herniated disc of the cervical spine

Can be treated one disc prolapse the cervical spine conservative or operational. While the conservative treatment of the Therapy of herniated disc of the lumbar spine corresponds to (physical therapy, Pain therapy) there are some differences in the operative procedure. In the so-called Microtherapy, which is part of the pain therapy for a herniated disc, is under CT control a fine needle is inserted between the vertebral bodies and a Local anesthetic injected near the intervertebral disc. Percutaneous nucleotomy is one option for the surgical treatment of a herniated disc of the cervical spine.
Small cannulas are used with increasing Lumens brought close to the herniated disc as part of an endoscopic procedure. Then small microsurgical instruments are inserted, the herniated disc is displayed and removed. In some cases, with a enzyme the intervertebral disc pretreated.
This causes the nucleus of the disc to shrink. Another surgical method is that microsurgical operationwhere small incisions are made over the affected area of the cervical spine. This procedure is carried out using a surgical microscope. The intervertebral disc is approached from the front, probed and then removed. The herniated disc is also removed. If there are also bony constrictions in addition to the herniated disc, these can also be removed in the same session.
A stable implant is used to replace the intervertebral disc, which is also known as Cage referred to as. There is only a single one disc prolapse before or if the incident is only in one segment, the indication can lead to a Intervertebral disc prosthesis be asked. This operation is performed under general anesthesia and takes about 2 hours. The intervention on the Cervical spine is carried out from the front. This is done by means of a skin incision. Front access minimizes the risk of spinal cord injury. The intervertebral disc is removed and a movable plastic core is inserted, which is fixed and anchored between the vertebrae. The advantage of this surgical method is that early and immediate mobilization is possible again after the operation physical therapy the operation can be connected. Thanks to the plastic core between the vertebrae, the spine does not lose its mobility. Patients can be discharged home approx. 2 days after the operation. You will still need to wear a ruff for a few weeks.
The prognoses show a very low complication rate. 85% -90% of all patients are symptom-free after the procedure. Conventional surgical methods such as For this reason, joint stiffening is performed less and less frequently. A follow-up check can be carried out a few weeks after the procedure CT or MRI of the cervical spine be carried out on the patient.
Please also read our topic: Therapy of a herniated disc of the cervical spine
Exercises for a herniated disc
Herniated discs are still operated on too often, although in most cases targeted and professionally guided physiotherapy is just as promising. The therapy exercises must be learned in detail and initially instructed, as the cervical spine is a sensitive and mobile structure that must be protected at the same time. The most important exercise is to learn a healthy head and body posture and to maintain it in everyday life. Often the head is leaned back too much during office work, which puts a strain on all structures of the cervical spine. The upright posture can also be supported muscularly in addition to mindfulness in everyday life. With the help of Tera ligaments, the straightening of the upper thoracic spine can be strengthened, which is often responsible for herniated discs in the cervical spine. During these exercises, the thoracic spine should be fully straightened against the tension of the ligaments and the shoulder blades should be moved backwards.
To stretch and strengthen the neck and neck muscles, you can continue to bend your neck forward and sideways against slight resistance. The resistance can be created by the weight of your own arm or by gravity. The forward bend can be done lying on the back by slowly moving the chin against the force of gravity towards the chest. The cervical spine should not be overstretched for the time being, as it is often involved in the mechanism behind the herniated disc.
Medication for a herniated disc
Many different medications are used to alleviate the discomfort associated with a herniated disc in the cervical spine. Pain relievers and muscle relaxants (drugs that relax the muscles) are particularly important. The range of different pain relievers is wide. For mild to moderate pain, conventional painkillers that do not require a prescription can be used. These include ibuprofen, diclofenac and paracetamol.
If the pain is particularly severe and only under medical supervision, opioids can be prescribed to relieve the pain. The opioids, however, are not suitable for long-term use, as they have serious side effects (constipation, nausea, vomiting) and can lead to habituation and dependence. Another starting point of drug therapy are means for muscle relaxation.These include, for example, sedatives (active ingredients from the group of benzodiazepines), which, in addition to the desired effect, also cause fatigue, drowsiness and gastrointestinal complications. These substances can also be addictive if they are taken for a long time. Medicines that are otherwise used to treat epilepsy and can also cause drowsiness work against nerve pain (neuralgia).
You can find extensive information on this topic at: Medication for a herniated disc
OP of a herniated disc of the cervical spine

An operation is preferred to conservative therapy if it has failed and the symptoms persist after a few weeks, or if it does not Pain also neurological failures (Sensory disturbances, muscle weakness, paralysis) occur. Furthermore, a herniated disc of the cervical spine is operated on if that Spinal cord was harmed (Myelopathy). The operation will inpatient in hospital under general anesthetic carried out.
The intervertebral disc surgery is a minor intervention that has meanwhile become minimally invasive can be performed through a surgical microscope. The purpose of the procedure is to remove the leaked tissue without damaging the spinal cord. From this point on, two different procedures can be selected. One possibility is to stiffen the vertebrae in the cervical spine by using a placeholder (Bone graft or similar) instead of the intervertebral disc and with Metal plates, as well as screws connecting. This is intended to stabilize the spine again, which means that the patient will lose mobility in the stiffened vertebral segment. This method is mainly used because of the loss of flexibility in the elderly used.
If a patient had a herniated disc of the cervical spine at a young age, one would be more likely to do so Intervertebral disc prosthesis implant after the defective disc has been removed. For both operations, the surgeon can distinguish between two access routes for the intervertebral disc operation: either from the Neck side from (front) or starting from the neck (back). The operation lasts regardless of the access route between 60 and 90 minutes. Then the patient still has to 4-6 days in the hospital stay before he is released home, where he should take it easy for the first 4-6 weeks. Following this Rest phase can then under a physiotherapy with the Reconstruction of the neck and neck muscles to be started.
Complications rarely occur during disc surgery on the cervical spine. Depending on the access route, vessels or nerves can be injured Damage to the spinal cord have become very rare due to the minimally invasive approach. However, after a disc operation on the cervical spine, as with all other operations, Wound infections or Wound healing disorders, such as Secondary bleeding occur.
Prevention of a slipped disc
If a few points are observed, a herniated disc of the cervical spine can be prevented:
- Regular gymnastics and sports, such as swimming, hiking, jogging, to strengthen the back muscles and relieve the spine
- compensatory movement for sedentary work
- trained relaxation techniques to loosen tense back muscles and improve posture
- a suitable mattress that is tailored to your body weight; the spine should not kink while sleeping
- if you are overweight, reduce your weight as quickly as possible.
Read more on the topic: How can I best prevent a herniated disc?
Exercise in the case of a herniated disc of the cervical spine
To prevent a herniated disc it is important that To strengthen muscles.
Anyone who has suffered a herniated disc of the cervical spine should contact us directly physical therapy kick off. The Exercises for a herniated disc of the cervical spine serve the Relief of the spine and contribute a lot to that Healing process at. Also important are practices that the Musculature relieve and relax, for example relaxing exercises (stretch) or Movement therapies (for example Aqua gymnastics). To rehabilitation If you have a herniated disc, exercises that also do the Improve posture.
The exercises should be continued at home after rehabilitation. It is important to choose a sport that does not strain the intervertebral discs and the back and should therefore be discussed with the doctor! Are recommended Endurance sports, how Swimming, cycling, walking or hiking, because there is no compression or rotation of the spine and move- and Abdominal muscles is stressed evenly.
Jogging is very popular but not recommended as a prophylaxis after a herniated disc. Nevertheless, despite a herniated disc, jogging is of course not prohibited. However, there are a few things to keep in mind.
We have written a completely separate topic for this: Jogging after / despite a herniated disc
Targeted Strength training the back muscles under instructions can also help strengthen muscles. Because of the excessive compression or twisting of sports such as riding, downhill skiing, tennis, weightlifting without instruction, etc. is not advisable. In order to protect the intervertebral discs in the long term, one should seek advice to find a suitable sport.
- Exercises for a herniated disc of the cervical spine
and - Sport after a herniated disc