Treatment of a bowel obstruction
introduction
Treatment for an intestinal obstruction depends on the cause, the person's age, the time of diagnosis, and the person's current condition. There are basically two directions in treatment. On the one hand, conservative therapy, i.e. waiting and administering medication, can be tried. The other option is surgical treatment of the intestinal obstruction. The possibilities must be planned individually and adapted to the person concerned. Emergency surgery may only be necessary in acute cases.

Conservative therapy
Purely conservative therapy is usually only possible if the intestine is paralyzed. Doctors call this a paralytic ileus. In the acute phase, suctioning off the pent-up intestinal contents is sometimes necessary in order to relieve the gastrointestinal tract. To do this, the person affected is given a nasogastric tube. After that, a number of different drugs can be used. So-called prokinetics can increase bowel movements and thus enable the food pulp to be transported further. Spasmolytics relieve the cramps and have an analgesic effect. Pure pain killers can also be given for this.
In addition, antibiotic therapy is often necessary because a large number of microorganisms live in the intestine. If these get elsewhere in the body, they can cause serious infection and inflammation. Antibiotics attack these bacteria.
In addition to drug therapy, attention must also be paid to balancing the salt and water balance, which is why those affected often receive infusions. A swivel enema can also help those affected. The intestine is flushed through this enema and the stool remains are removed.
nutrition
A balanced diet can partially prevent an intestinal obstruction. However, there is no complete protection. As with healthy people, care should be taken to ensure adequate water intake when eating. However, alcohol and acidic juices should be avoided as they can irritate the intestines.
With the fixed diet, the distribution over the day is particularly important. Those affected should eat many small meals and not overwhelm the body with large amounts. The food should be swallowed slowly and well chewed. Avoiding grains, seeds and nuts as well as fibrous fruits can also have a preventive effect. Fruit and vegetables can also be eaten without their peel.
You should also avoid eating foods that cause gas. A high-fiber diet for prevention, but a low-fiber diet after an intestinal obstruction makes sense. A precise nutrition plan should always be discussed with the attending physician, as other diseases also require a certain diet and all individual aspects must be taken into account.
Medication
A combination of several drugs is used to treat an intestinal obstruction. The first group are prokinetics or antiemetics. These are drugs that increase the forward movement of the bowel muscles and prevent vomiting. Examples are cholinergics such as carbachol and dopamine receptor antagonists such as domperidone.
The second group are the antispasmodics. These are to alleviate intestinal cramps and thus also have a pain-relieving effect. A well-known representative of this group is Buscopan®. In addition to the anticonvulsants, pure pain relievers can also be used. It should be noted, however, that opioids can lead to further constipation. Novaminsulfon, which is known under the name Novalgin, is more suitable here.
Another important group of drugs are antibiotics. Since many bacteria live in the intestine and these can trigger peritonitis and blood poisoning if they penetrate the intestinal wall, these must be stopped by the broadly effective antibiotics. An often underestimated drug is also the sodium chloride infusion, as it is necessary to balance the salt and water balance.
How should one behave?
An acute intestinal obstruction is an absolute emergency situation. If this is suspected, a hospital should be visited immediately. Waiting is not recommended, especially if the affected person has already had intestinal obstruction. Diet and other activities should be discussed with the treating physician during treatment. The correct intake of the medication, especially the antibiotics, is important for the success of the treatment. If side effects occur, this should be discussed with the doctor and in no way lead to an unauthorized discontinuation of the medication.
If there is a tendency to bowel obstruction, adjusting the diet can have a preventative effect. In the same way, even after an intestinal obstruction, a light diet should first be eaten in many small meals. Drinking enough water is also important for the prevention and treatment of intestinal obstruction. In the case of recurring intestinal obstruction, a more detailed examination should take place in order to discover the cause and treat it.
also read: Symptoms of intestinal obstruction
When do you have to operate?
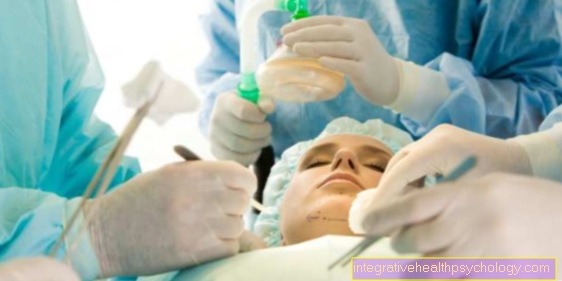
In the case of an acute mechanical bowel obstruction, surgery is often the only way to cure it, as the blockage has to be removed or the bowel has to be turned correctly again. This can also be necessary with paralyzed intestinal muscles if conservative therapy does not work. If there are complications such as a rupture of the intestinal wall, surgery is inevitable. In diseases such as Hirschsprung's disease, the paralysis cannot be resolved with medication. In this case, too, an operation is the only way to provide lasting help to the affected baby.
Procedure of the operation
There are different surgical options for an intestinal obstruction. Usually such an operation is a large and open operation that involves making an incision on the abdomen. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. If the intestine is twisted as the cause, it is brought into the correct position. If there is a blockage due to excrement stones or adhesions, the obstacle must be removed immediately. In many cases it is necessary to remove parts of the intestine. In the case of benign diseases, as small a piece as possible is pinched off and the ends are brought together again.
Sometimes it is also necessary to create an artificial anus. This involves moving part of the intestine outwards and creating a stoma. Those affected wear a bag directly on the skin of the abdomen, which they can empty themselves. After these operations, tubes are placed in the wound so that the wound secretion can drain away. If the contents of the intestine have already entered the abdominal cavity, they must be flushed thoroughly during the operation. In most cases, the abdomen is closed again after the operation, but sometimes it is necessary to apply a vacuum bandage and then the abdomen is only completely closed after a few days. After the operation, the anesthesia is stopped and the affected person is taken to the recovery room.
You might also be interested in this topic: Everything you need to know about the operation of an intestinal obstruction
Treatment after surgery
After an operation, the treatment of the intestinal obstruction is not yet over. First of all, it is necessary to take care of yourself, as the operation on the affected section of the intestine is a serious intervention in the body. If an artificial anus was placed during the operation, the person affected must learn to deal with it. This is followed by further drug therapy with painkillers, anticonvulsants and antibiotics. The antibiotics are necessary to prevent serious infections in the surgical area.
Those affected are closely monitored to ensure that the surgical sutures are holding. Following the operation, the diet must first be built up gradually. Pureed light foods are often necessary at the beginning so as not to overwhelm the intestines. It is also useful to adjust the diet later. The water and salt balance must also be monitored after the operation. In some cases, the artificial anus can be removed later through another operation. Here, the bowel is moved back and those affected can go to the toilet normally again.
Duration of treatment
The duration of treatment varies individually depending on the cause of the intestinal obstruction and the type of treatment. The treatment can take many months, especially when an artificial anus is created, until the artificial anus is removed. In the case of drug therapy, however, it can last only a few days. If the cause is chronic, lifelong therapy may be necessary. An exact period cannot therefore be given in general.