Exercise ECG
What's this?
With a stress ECG, the electrical signals of the heart are recorded and recorded via an EKG device, while the person being treated is physically active and thus stresses the heart and the circulation. The stress ECG is an important diagnostic tool for diagnosing certain diseases of the heart.
In particular, diseases that are associated with a lack of oxygen supply to the heart are usually diagnosed or excluded with an exercise ECG. In principle, the devices used are those for a normal EKG, which are attached to the body with sufficiently long cables.

The person who is to be examined must be on a piece of sports equipment, usually a bicycle ergometer, and a certain performance (measured in watts) provide. If there is an oxygen deficiency in the heart, the electrical activity changes visibly during physical activity and a suspected diagnosis can be made.
If there is no disease of this type, the ECG changes due to the faster heartbeat, but typical changes in oxygen deficiency cannot be found.
Who needs that?
Exercise ECGs are typically created when the attending physician suspects that there may be an insufficient supply of oxygen to the heart. Symptoms that can indicate the presence of such a disease are therefore a reason to perform an exercise ECG. This includes in particular Chest pain. The examination can be useful even if there are no symptoms. If one or more Risk factors for the creation of a coronary heart disease (CHD), it is advisable to check the heart regularly. A stress ECG can be carried out for longtime smoker, Overweight people, increased blood lipids or high blood pressure help prevent serious consequences of heart disease.
The exercise EKG also comes as a control examination many heart diseases after treatment. The long-term therapeutic success can be observed with the help of the stress ECG and, if necessary, follow-up treatment can be initiated in good time.
The exercise ECG is also performed as part of a regular health checks for men (from 45) and women (from 55) of a certain age is recommended to monitor the development of heart diseases apart from risk factors and previous illnesses.
Course of the stress ECG
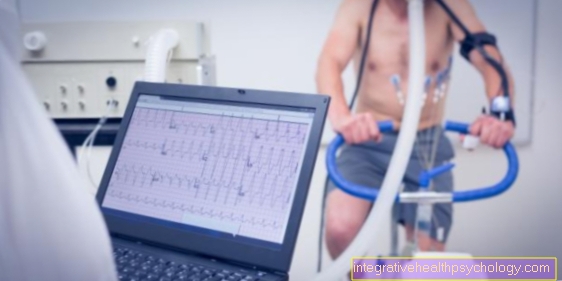
An exercise ECG is usually carried out as part of a routine examination by the family doctor or cardiologist, as well as in the event of a specific suspicion of a heart disease. The examination itself is usually always similar. First, the person to be examined is asked to go to the treatment room, in which the EKG device and either a Exercise bike or a Treadmill stands.
So that the electrodes of the EKG can be connected, the Upper body area cleared become. Now the Electrodes connected as well as a Blood pressure cuff on the upper arm or leg attached and one first measurement at rest carried out.
Now the patient is asked to sit on the ergometer or to stand on the treadmill. As soon as the patient is ready, physical activity is started and the EKG records it Cardiac activity as well as the Blood pressure at regular intervals on. The power that has to be applied can usually be displayed directly on the ergometer in the form of watts.
The performance is in the course of the recording as far as possible increased to provoke possible changes in cardiac activity. Strict attention is paid to how the person examined feels during the entire examination malaise the investigation abort to be able to. The blood pressure and the electrical activity of the heart are also monitored so that the examination can also be interrupted in the event of critical changes.
Overall, an exercise ECG takes about 10-15 minutes. With preparation and introduction to the examination by the attending physician, the entire duration of the examination can be up to 30 minutes take advantage of.
After the examination, the service to be provided is shut down in order to gently reduce the load. The patient can usually go home after discussing the results. If the exercise ECG led to the suspicion of a heart disease, you may further diagnostic examinations and a hospital visit may be necessary.
Watt values for exercise ECG
The power achieved during the exercise ECG is given in watts. Be at the beginning of the investigation 25 to 50 watts set on the ergometer, which is roughly the performance for walking normally or a little faster corresponds.
Thereafter, the load level is increased by 25 watts every two minutes. A performance by 75 to 100 watts you can go with it slow cycling or swimming to compare, 125 to 150 watts correspond fast cycling or jogging. One reaches 150 watts or more is it a extreme athletic performance.
How far the performance is increased depends on the individual values. It is increased until the maximum heart rate is reached, which is determined by the formula 220 heartbeats / minute - age (in years) +/- 12 heartbeats / minute can calculate. At a 40 year old person the maximum frequency would be e.g. With 186-192 beats per minute reached.
At how many watts, i.e. at what power, this frequency is reached, differs from person to person.
Blood pressure during exercise ECG
In addition to cardiac activity, blood pressure also plays an important role in assessing cardiac output. The blood pressure is checked at regular intervals while a stress ECG is being carried out. Blood pressure should be measured before the examination. At a very high blood pressure there is even one Contraindication for performing the stress ECG.
A high blood pressure is one of the most common diseases in Germany. In the long run, high blood pressure can cause great damage to the heart. Long-term high blood pressure can develop Changes also during the exercise ECG demonstrate. In the long run, the vessels supplying the heart are damaged and the heart becomes insufficiently oxygenated, especially when it is exerted. There is also one abnormal enlargement of the left heart.
The diagnosis of a so-called Exertional hypertension can also be performed with the help of a stress ECG. This is a high blood pressure, which occurs only with moderate or heavy stress.
Cost of the exercise ECG
Usually an exercise ECG is performed as part of the diagnostic checkups just like Suspected heart disease carried out. In these cases, insured persons do not have to pay anything as the Health insurance assumes the costs of the examination. As part of the preventive examinations, however, a certain age must be reached so that the examination is covered by the health insurance company without any previous symptoms. This is 45 years for men and 55 years for women.
Performing a stress ECG can also be useful for other reasons. Sports medicine examinations for example, often include performing an exercise EKG. It depends on the individual health insurance company whether the costs of the examination are covered. Sports medical examinations of this kind are often used only partially or not at all, which is why the health insurance company should be contacted beforehand. An exercise ECG, if the health insurance does not cover the costs of the examination, usually costs between 60 and 100 €.
Evaluation of the exercise ECG
The evaluation of the stress ECG usually follows directly after the examination and often takes place already during the investigation instead of. During the examination, care is taken to ensure that the electrodes do not slip during physical activity and thus make the evaluation impossible. Also should sudden changes the heart or blood pressure must be monitored so that the examination can be terminated in good time.
During the actual evaluation of the so-called EKG strip, on Irregular heartbeat as well as recording the electrical activity of a single heartbeat. If no pathological change can be seen here both at rest and during exercise, a serious heart disease is unlikely.
Should be a Oxygen starvation of the heart changes can be seen in the recording, especially under stress. The heart needs a lot of oxygen, especially when it is under stress. Certain heart diseases reduce the oxygen supply to the heart and abnormal activity occurs, which is recorded in the EKG.
Exercise ECG for diagnosing CAD
The suspicion of the presence of a so-called coronary artery disease (CHD) is one of the main reasons for performing an exercise ECG. With this disease it comes to Changes in blood vesselswhich supply the heart with blood and thus with oxygen. Deposits in the vessel walls narrow these extremely important vessels and can even close them - in this case it comes to Heart attack.
A non-invasive method of detecting CAD is to perform an exercise ECG. At rest, the vessels can often still supply the heart with sufficient oxygen. If there is a physical strain and thus a increased oxygen demand of the heart muscle, the cardiac vessels constricted by the CHD are no longer able to supply the heart with sufficient oxygen. This lack of oxygen during exercise can be converted into a changed electrical activity under stress recognize in the EKG.
Please also read our page Diagnosis of coronary artery disease.