Soft tissue injuries

definition
A soft tissue injury is a violent injury. The soft parts include tissues that protect and surround the bones, such as muscles, tendons, ligaments, skin, subcutaneous tissue, fatty tissue, including vascular and nerve tissue. Statistically the most common injuries are Achilles tendon, kneecap tendon or biceps tendon.
In the case of soft tissue injuries, a basic distinction is made between open and closed injuries. If there is still uninjured skin over the injury, it is a closed injury. If, on the other hand, there has already been an injury to the skin, it is an open injury.
Classification according to Tscherne and Oestern
In order to better assess the extent of the injury, one was designed Classification of soft tissue injury, Which open and closed injury differs.
Open soft tissue injury
The open soft tissue injury can be seen in four degrees organize:
- Grade 1: Grade 1 is one Impaling the skin from the inside to the outside.
- Grade 2: Grade 2 is one major soft tissue injury, With Violence from the inside out. This increases the risk of inflammation.
- Grade 3: Grade 3 is one exposed fracture with additional injuries to vessels and annoy.
- Grade 4: Amputation injury
Closed soft tissue injury
The difficulty with closed soft tissue injuries is that you can easily overlooked serious injuries can or that The extent of the injury is initially unclear is.
- Grade 0: simple fracture injury, no or hardly any soft tissue damage through indirect violence
- Grade 1: simple to moderate fracture injury with superficial skin injury or bruising through bone fragments
- Grade 2: moderate to severe fracture injury, it is a deep often contaminated wound with skin abrasion, contusion through direct violence and a feared one Compartment syndrome (In the case of the compartment syndrome there is an increase in pressure in the tissue, for example due to bleeding into the tissue. The increase in pressure leads to a Squeezing of the vessels and nerves and thereby to a circulatory disorder and tissue death.)
- Grade 3: Severe fracture injury with excessive skin bruising and / or muscle damage, Peeling wounds (Decollement: here upper skin layers are separated from deeper soft tissue layers by tangential force), Compartment syndrome (see above) and Vascular injuries
root cause
Soft tissue injuries are often caused by Falls, direct or indirect violence. Soft tissue injuries also often occur with sports injuries. At Traffic accidents or Falling from a great height serious soft tissue injuries can occur.
Diagnosis
In diagnostics, there is one thorough consideration (inspection) the wound is important so that nothing is overlooked. One should pay attention to Redness, swelling, bleeding, bruising, overheating, color, odor and leaking fluid the wound. Redness, swelling, overheating, pain, functional restrictions are so-called Signs of inflammation.
Also one physical examination with orthopedic examination techniques are important in order not to overlook joint injuries, hemorrhages, and other accompanying injuries.
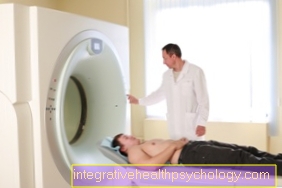
In addition, diagnostic imaging methods are important Severity and localization of fractures and injuries. One should be in front of a direct MRI diagnostics be careful because it is at metallic foreign bodies becomes attracted to the MRI machine, which can lead to further serious injuries and complications. True is one MRI diagnostics very informative for complicated soft tissue injuries, but as I said, metallic foreign bodies should be excluded beforehand. In addition, MRI diagnostics are expensive in contrast to alternative X-ray and CT images. Whereby X-ray and CT the Disadvantage of radiation exposure and a less precise soft tissue assessment in contrast to MRI takes place. So you should look after careful consideration decide on meaningful imaging if necessary.
therapy

Depending on Extent of injury you have to conservative and / or operative steps initiate.
Conservative action
Definitely not should be taken as a first step deep-lying foreign bodies without precise knowledge of the surrounding vessels and nerves remove manually. These foreign bodies become later surgically removed. The initial measures, however, include:
- a temporary first hemostasis by pulling the trigger
- a drug pain relief
- Immobilization the joints by splints
Further measures then include a classic wound care with wound cleaning, rinsing, disinfection, ointments and sterile dressings with gauze bandages. With the ointments one differentiates depending on Ointments for wounds that are too dry or Ointments for wounds that are too moist.
There should also be one corresponding to the injury Dressing change respectively. The first dressing change after an operation takes place at the earliest 48 hours afterwards, if the dressing has not been perfused.
With conservative measures it can also lead to Application of splints and plaster come to rest and pain relief. This can be essential for wound healing. Still, one should go for one possible small step movement value of the joints, otherwise it will lead to Muscle and tendon shrinkage can come.
Conservative therapy also includes Checking the tetanus vaccination status, which should definitely be refreshed, especially in the event of soft tissue damage. The prophylactic vaccination occurs 5-12 hours after the injury. Tetanus prophylaxis is used for large wounds or if the vaccination is boostered a long time ago.
In some cases it can also be used for large wounds prophylactic antibiotics come. This should always be judged based on the severity of the injury and how dirty the wound is. But it can also become a therapeutic antibiotic administration come when there is inflammation of the soft tissue injury. Should be in pain Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs administered. In the case of very severe pain or extremely large wounds, a local anesthesia or the initiation of a anesthesia be helpful.
Operational measures
Depending on the type of injury, you may need one first operative cleaning the wound. After a suitable diagnosis and localization of foreign bodies, Foreign body surgically removed become. In addition, a direct Ligation of vessels be necessary to stop bleeding.
At septic wounds (i.e. wounds that are already inflamed) you have to either have one careful excision of the wound make or a so-called wound toilet, in which after cleaning the wound one thorough removal of dead tissue undertakes.
Depending on the injury, it can be used for the therapy of tendon, muscle and ligament injuries Use of direct seams, Refixations to the bones (here there are different sutures, anchors, drill holes for the anchors or indirect seams) but also for complicated reconstructions come to the removal of tissues from other body region and reinsertion in the affected region. Also Vascular and nerve injuries must be supplied with sutures and reconstructions.
There are various ways of using it for wound closure: Here there is one simple approximation of the wound edges with plaster strips. These are other alternatives Gluing, stapling or sewing in different techniques depending on the soft tissue affected.
forecast
The Soft tissue injury prognosis depends on several factors. For one thing, it matters whether it is a direct or indirect violence The severity of the injury and infection from pollution are important factors in the prognosis.
The forecast is too depending on the injured body region. For injuries to the abdominal, Chest cavity and des Basin profuse internal bleeding may occur.
That is not to be underestimated either other general condition of the patient, if for example still Other diseases exist. Patients with a Immune disease, diabetes and Tumor diseases.