Biceps femoris
Synonyms
German: biceps thigh muscle, Hamstring flexors
- to the thigh muscles overview
- to the musculature overview
introduction

The biceps femoris (two-headed thigh muscle) lies on the back of the thigh and belongs to the flexor group (flexors in the joint). It is clearly visible and palpable on the outer back of the thigh.
You can find more information on the subject here
- Thighbones
- hip
- Hip osteoarthritis
- Hip surgery
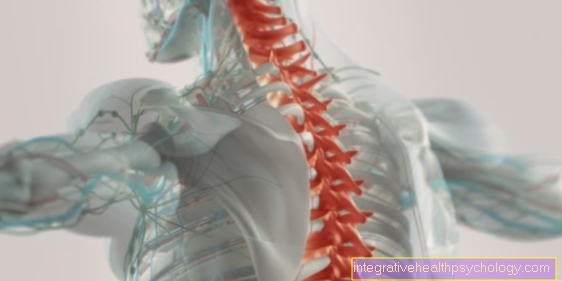
Figure biceps femoris

Biceps femoris muscle
Two-headed hamstrings
(1.+2.)
- Biceps thigh muscle,
long head -
Biceps femoris muscle,
Caput longum - Biceps thigh muscle,
short head -
Biceps femoris muscle,
Caput breve - Fibula - Fibula
- Shin - Tibia
- Femur - Femur
- Ischium - Os ischii
- Pubic bone - Pubis
- Sacrum - Sacrum
- Iliac scoop - Ala ossis ilii
- Rough line - Linea aspera
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Approach, origin, innervation
Approach: Fibula head (Head fibulae)
Origin:
- Long head (caput longum): Ischial tuberosity (Sciatic tuberosity) and sacrum and ischial tuberosity ligament (Lig. Cacrotuberale)
- Short head (Caput brevis): bony groin of the back of the femur (Labium laterale linea asperae)
Innervation: Common peroneal nerve L5, S1
Tendon of the biceps femoris
The biceps femoris muscle consists of two muscle bellieswho agree and work together on the head of the fibula (Head fibulae) have their approach. The tendon runs from the bottom of the thigh to the outside of the knee joint. To protect the tendon from damage, there is one in the attachment area Bursa. However, the biceps femoris muscle, acting as a hip extensor and knee flexor, and its tendon remain particularly vulnerable Cracks or Inflammation.
More information can be found here: Tendon tear, Tendinitis
Pain in the biceps femoris tendon
Pain in the biceps femoris tendon can occur various causes to have. It can be a Tendinitis, one Bursitis, one Muscle tear or one Tendon tear act. The pain is typically located in the hollow of the knee or on the outside of the hollow of the knee and can radiate into the fibula. If the biceps femoris is used (i.e. when bending the knee), the symptoms can worsen. Whether it is an inflammation or a tear, it is in both cases Rest and relief appropriate because a tendon takes time to heal.
Tendon is inflamed
A Inflammation of the tendon (Tendonitis) of the biceps femoris muscle is characterized by pain on the outside of the hollow of the knee, which can radiate into the fibula. A Tendinitis can occur as a result of frequent minor injuries. Can be used to treat inflammation Cryotherapy as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to be used. Bandages, heat and electrotherapy can also be used. Also, are early physical therapy, as well as stretching and light training exercises to prevent a loss of mobility and strength. Differential diagnosis should include the "runner's knee" (Iliotibial tract chafing syndrome) and external meniscus damage can be excluded.
Tendon "jumps"
Pain at the back of the knee and a "snapping" tendon can be caused by a Subluxation the tendon of the biceps femoris arise. Such a phenomenon can occur, for example, when the tendon is not properly attached to the fibula head or the fibula head is enlarged. Both examples are often anatomical variants that only become noticeable under greater stress (competitive sport). In most cases, symptoms appear when the knee is flexed. The recommended therapy is knee surgery, in which the incorrectly fixed biceps tendon is sewn back in the anatomically and physiologically correct position or a fibula head is reduced. Other causes of a snapping tendon can be in the area of the Menisci, the kneecap or the ilio-tibial Ribbons lie.
How is the muscle trained / contracted?
The biceps femoris, like the entire rear thigh muscles, can preferably be trained with the hamstrings. Special, guided equipment in the gym is best for this.
The hamstrings can be performed lying down and sitting.
- Hamstrings
For more information, see Weight Training
Exercises for the biceps femoris
The essential functions of the biceps femoris are that Knee flexion as well as the Hip extension. To train the biceps femoris, for example, knee flexion with (or without) dumbbells is recommended. The knee flexion should be done slowly and the back should be done at the same time as straight as possible stay. A barbell or a multi press can also be used to increase this. One variation is to hold the barbell over your head with your arms straight. Due to the additional pressure on the shoulders, the muscle has to exert more force to straighten the hips and slowly bend the knee.
A second type of exercise for the biceps femoris would be Lunges. Here you have to take a big (lunge) step forward and bring your knee on the opposite side almost to the floor. It is also important that your back is doing this as straight as possible remains. You can also use small dumbbells or barbells for this exercise. Fitness machines such as back straighteners or leg presses are also good for training biceps femoris strength. The muscles can also be trained while lying down, for example by lifting bent knees and feet on the floor, buttocks and lower back. The top of your back, arms and shoulders should stay on the floor.
Exercises for the biceps femoris
The essential functions of the biceps femoris are that Knee flexion as well as the Hip extension. To train the biceps femoris, for example, knee flexion with (or without) dumbbells is recommended. The knee flexion should be done slowly and the back should be done at the same time as straight as possible stay. A barbell or a multi press can also be used to increase this. One variation is to hold the barbell over your head with your arms straight. Due to the additional pressure on the shoulders, the muscle has to exert more force to straighten the hips and slowly bend the knee.
A second type of exercise for the biceps femoris would be Lunges. Here you have to take a big (lunge) step forward and bring your knee on the opposite side almost to the floor. It is also important that your back is doing this as straight as possible remains. You can also use small dumbbells or barbells for this exercise. Fitness machines such as back straighteners or leg presses are also good for training biceps femoris strength. The muscles can also be trained while lying down, for example by lifting bent knees and feet on the floor, buttocks and lower back. The top of your back, arms and shoulders should stay on the floor.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of and work as an orthopedist at .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me live every 6 weeks on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is not enough time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of all treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
How is the muscle stretched?

The stretching exercises for the back of the thigh are found by many to be very uncomfortable and sometimes painful. The athlete stands with his legs closed and straight and tries to touch the tips of his toes with his fingers. The back should be kept as straight as possible.
Notice: Athletes who do not manage to touch the tips of their toes when their legs are stretched usually do not suffer from any shortened muscles, but simply lack mobility. This can be seen very clearly in our illustration.
See Stretching for more information
(Kinesio) taping
Muscle taping is appropriate for various types of injury. For example, if you have a muscle strain in the thigh area, you can tap the biceps femoris muscle. For this, the person affected should stand and bend forward with the upper body in order to tense the biceps femoris muscle. To tap the biceps femoris effectively, the first strip of the back outside of the hollow of the knee to the buttocks appropriate. For this it is recommended to straighten the knee and turn the upper body slightly to the opposite side. This strip is attached without too much tension.
The second strip should be a Double stripes be, that is, two thin strips with a common base. This can be achieved very easily by simply cutting the strip down the center, but leaving one end in common. The base of the double strip is glued to the lower pole of the muscle, so a few inches above the hollow of the knee and the two strips are under middle pull around the muscle belly appropriate. If possible, the two loose ends should be glued together. This taping can improve the function of the muscle and you can thus achieve (pain) relief.
More information can be found here: Taping the knee
function
The function of the biceps femoris (two-headed thigh muscle) consists in flexing and external rotation of the lower leg in the knee joint.
It also causes extension and adduction of the thigh in the hip joint.