Removal of sweat glands
General

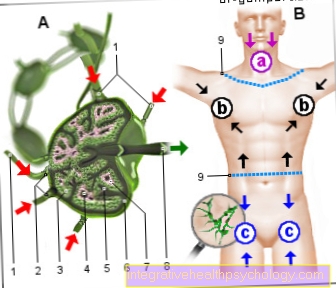
The sweat glands (Glandula suderifera) belong to the so-called skin appendages and are located in the dermis (Technical term: Korium). The sweat is then released to the surface through the pores of the skin and mainly serves to regulate the heat balance.
A distinction is also made between ecrine and apocrine sweat glands.
These differ in terms of their function, appearance and location.
The ecrine sweat glands are not associated with hair, whereas the apocrine sweat glands open into hair follicles.
Ecrine sweat glands are found all over the body, but apocrine glands (also called scent glands) are only found on certain parts of the body.
These include the armpits, nipples, genital and perianal regions.
The heat balance and pH value of the skin are mainly regulated by the ecrine sweat glands.
Apocrine sweat glands fulfill functions of social and sexual behavior through pheromone-like fragrances (pheromones).
Learn more at: Pheromones for men
First and foremost, however, they simply determine the body odor.
However, various diseases can make it necessary to remove the sweat glands.
Cause hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis (hyperhidrosis) can be a cause of the removal of sweat glands.from greek (hypér) „even more, beyond, beyond ... beyond and (hidrós) Sweat) be.
Sweating is an all natural process that occurs for the person Heat balance of the body is essential.
So physiological sweating is for ours Homeostasis conducive and important. It should not be forcibly suppressed through surgery.
But unpleasant hyperhidrosis can make this necessary.
But when do we speak of hyperhidrosis? This is when the sweat production in an armpit exceeds 100 mg per 5 minutes.
However, this is the scientific limit.
Subjectively, those affected perceive even smaller amounts as excessive and unpleasant.
Such a disease is diagnosed using tests that the Amount of sweat per time can determine.
Such tests are e.g. of the Iodine Strength Test or the Gravimetry.
In addition to various medicinal and conservative therapies and procedures, surgical measures are of course available for treatment.
Cause bromhidrosis
A special form of hyperhidrosis is bromhidrosis (Greek (brômos) goat stink of animals; (hidrós) sweat).
The increased sweat formed on the Horny layer the skin with favorable germination conditions for colonization bacteria.
Degradation products of these bacteria such as short-chain Fatty acids and the amino acid Alanine then lead to an unpleasant body odor, especially in the armpits, the groin area and the spaces between the toes.
This unpleasant smell is above all a psychological burden for those affected and can be an indication for the removal of sweat glands. Frequent washing does not improve it. In addition to drug therapies, sweat gland removal is also an option here
Procedure sweat gland excision

The sweat gland excision is a surgical procedure for Removal of the sweat glands.
During this procedure, the affected skin area is virtually cut out. Then the edges are sewn together.
However, there is also the option of only attaching parts of the skin Armpits to remove and then the sweat glands scraping.
This method has both advantages and disadvantages that must be considered. As a radical operation, it removes a large part of the diseased sweat glands and thus greatly reduces hyperhidrosis, unlike it might minimally invasive Process.
In return, however, large visible ones are created scar and very common complications from Wound healing.
The large and deep scars also limit the patient's mobility.
In addition, it is often not possible to cut out all of the affected areas. Because of these disadvantages, this method is used less and less nowadays.
Procedure subcutaneous sweat gland suction curettage
The subcutaneous sweat gland suction curettage is a surgical procedure that involves local anesthesia is carried out.
For local anesthesia a so-called Tumescent solution used.
This type of local anesthesia offers several advantages.
For one, it saves the risks one anesthesiaOn the other hand, the application of large amounts of liquid into the tissue leads to good expansion and loosening there. This makes the procedure easier.
Furthermore, this is Risk of bleeding low, as the so-called tumescent solution Vasoconstrictors contains which vessels constrict.
Last is that antiseptic To name the effect of the solution as an advantage. The sweat gland suction curettage is a minimally invasive procedure in which usually 3 - 4 small skin incisions about 0.5 cm long in the armpit serve as surgical access.
A special surgical instrument is inserted under the skin through these small incisions in the skin. The diseased sweat glands are then cannulated using a cannula scraped off and subsequently sucked off.
The success rate of this procedure is around 70-80%.
Very good results are achieved because the sweat glands that have been sucked off can no longer be renewed. After a year, however, recurrences may be possible if remaining sweat glands start producing sweat again. The procedure is an outpatient procedure and takes between one and two hours.
The patient receives one Compression bandage and is ready to work again after approx. 2 - 3 days.
Endoscopic Transthoracic Sympathectomy (ETS) procedure
This procedure is not a removal of sweat glands in the direct sense.
However, it pursues the same goal as removing the sweat glands.
It is a minimally invasive operation under general anesthetic, which directly on sympathetic trunk takes place.
Of the Sympathetic is part of the autonomic nervous system and thus controls unconscious body functions such as sweating.
Overall, it increases the willingness to perform and behaves contrary to Parasympathetic nervous system.
Operative access takes place endoscopic over the abdominal cavity.
Here, the sympathetic trunk ganglia, which contain the nerve cells that supply the sweat glands, are completely severed, coagulated or clamped with a metal clip.
However, the procedure harbors high risks and is only used for severe and therapy-resistant disease.
There are good results with hand sweating, but not so good with axillary sweating.
However, there is a great risk to developing one compensatory hyperhidrosis.
This is a shift of the hyperhidrosis to other skin areas. Compensatory hyperhidrosis is very difficult to treat and should therefore not be underestimated.
There are other complications Horner syndrome, one Vocal cord paralysis and Pleural effusions.
This has to do with the fact that these areas belong to the supply area of the sympathetic nervous system and are thus injured in the event of damage.
Because of these risks, it is preferable to use metal clips to clamp off the sympathetic ganglia during the procedure. This ensures that the procedure can be reversed, unlike, for example, with coagulation or radical removal.
Above all, this prevents the existence of compensatory hyperhidrosis for life.
Cost of sweat gland removal
The indication for a removal of the sweat glands is always made when there is one in certain parts of the body in the patient excessive sweat production comes and conventional herbal and medicinal measures do not bring relief.
The removal of the sweat glands is usually done by means of a Suction performed (Glandular suction). In 60-80%, the complaints are resolved afterwards.
The costs depend on the Stay in the practice or clinic, and whether it is Complications there that must be treated accordingly. Furthermore, the costs depend on the number of sweat glands to be removed. The larger the area to be treated, the more expensive the procedure will be.
As a rule, depending on the provider, you have to reckon with costs between 600 and 1500 EUR. This then includes treatment and follow-up treatment. An inpatient stay is not planned for the procedure and would be correspondingly more expensive.
Aftercare
Like any surgical procedure, sweat gland removal requires good and careful aftercare to avoid unpleasant Wound healing disorders to prevent.
Good follow-up care for surgical wounds begins with regular dressing changes.
In addition, an adequate one Wound hygiene essential for the healing process.
However, the patient can also influence this positively or negatively through his lifestyle.
A healthy way of life, i.e. protection of the wounds, sufficient Water supply and the waiver of Luxury foods, have a positive effect on the healing process.
The swelling of the wounds is promoted by elevating the affected areas, be it the arm, the feet or the hands.
Ultimately, the attending physician ensures a good recovery with a late appointment.
After about one to two weeks, the stitches are pulled, which usually ends the medical follow-up.
However, if patients notice that they are sweating despite the removal of the sweat glands or the sympathectomy, it is advisable to consult a doctor to discuss how to proceed.
Summary
A sweat gland removal is necessary in patients who suffer from bromhidrosis or hyperhidrosis, i.e. patients with a very unpleasant body odor or one excessive sweat production.
The level of suffering in such patients is usually very high and a sweat gland removal can alleviate this very well and the life quality increase enormously.
The method of choice is that minimally invasive sweat gland suction curettage, as it promises good results and the healing is quick and without major scarring.
However, there are also procedures, such as endoscopic transthoracic sympathectomy, that do not directly remove the sweat glands.
However, by tying off the nerve cells that supply them, this procedure has the same effect.
However, due to the high risks, this is only indicated if the course is resistant to therapy.