Colon
synonym
Colon
Definition of colon
The colon is part of the human digestive tract.
It lies between the appendix (Cecum, not to be confused with the appendiculum known colloquially as “appendix”, which only makes up part of the actual appendix), which joins the small intestine and ends in front of the rectum, also called rectum in German (medical rectum).
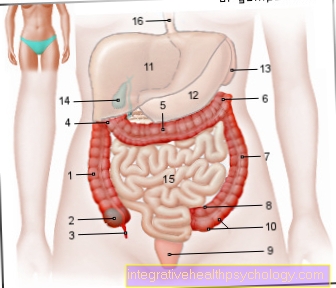
Figure large intestine

- Colon, ascending part -
Ascending colon - Appendix - Caecum
- Appendix -
Appendix vermiformis - Right colon bend -
Flexura coli dextra - Large intestine, transverse part -
Transverse colon - Left colon bend -
Flexura coli sinistra - Large intestine, descending part -
Descending colon - Large intestine, s-shaped part -
Sigmoid colon - Rectum - Rectum
- Bulges of the
Colon Wall -
Haustra coli - Liver - Hepar
- Stomach - Guest
- Spleen - Sink
- Gallbladder -
Vesica biliaris - Small intestine -
Intestine tenue - Esophagus -
Esophagus
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
construction
The whole Large intestine (included Cecum) is about 1.5 meters long, the main part of which is divided into four sections Colon (Colon).
Of the ascending colon (Colon anscendens) lies in the right central abdomen, it is supported by the transverse colon (Transverse colon), followed by the descending one in the left central abdomen Colon (Descending colon) which goes into the sigma (Sigmoid colon) transforms. This ends here Large intestine and flows into the rectum (rectum). The form encloses the Colon the Small intestine like a frame that is open at the bottom.
Of the Colon has some morphological (its shape) peculiarities.
These include the Wrinkles visible from the inside (Plicae semilunares) which, viewed from the outside, is a constriction of the Colon -Wall condition.
This creates Bulges of the colon wall, so-called House doors.
Still typical of that Colon are his three longitudinal outer muscle strips, the so-called Taenien. Each of the three muscle strips has its own name.
How to distinguish:
- Taenia libera
- Taenia mesocolica
and - Taenia omentalis
Fourth characteristic of the Colon are his Fat appendages (Appendices epiploicae).
The inside of the Colons is of mucous membrane (Mucosa) lined with invaginations (crypts), the top layer of the mucosa (epithelium) contains numerous goblet cells, which are responsible for the production of mucus. The predominance of crypts over villi (Mucosal protuberances) and the multitude of goblet cells are microscopically typical for the Colon.
Blood supply
The Colon ascencendens is primarily used by the Arteria colica dextra (right colon artery) supplies that Transverse colon through the Media colic artery (middle colon artery).
Both vessels stem
The Left colic artery (left colon artery), on the other hand, which supplies the blood to the colon descending guaranteed, comes from the Inferior mesenteric artery (lower intestinal artery).
Often there is a connection between the flow areas of the superior mesenteric artery and inferior mesenteric artery, this is called Riolan's anastomosis designated.
In the event of an occlusion of one of the two intestinal arteries, it ensures a supply of the otherwise poorly supplied with blood Colon - share.
If you are even more interested in this topic, you will find more information at: Blood supply intestine
Nerve innervation (nervous supply)
The nervous supply of the Colon happens about that vegetative (involuntary, i.e. not deliberately controllable) Nervous system.
Of the Sympathetic provides - roughly speaking - reduced bowel activity.
He cares for the colon, among other things on the Major and minor splanchnic nerves (large and small visceral nerves).
Of the Parasympathetic nervous system ensures a stimulation of the intestinal activity, it supplies the "front" (orally located) part of the colon via branches of the Vagus nerve, portions further "back" (downward) are shown over the Pelvic nerve (Pelvic nerve) supplied.
The point at which this supply change takes place is called Cannon-Boehm point designated. It lies in the area of the left colonic flexure, i.e. the transition between the transverse colon and the descending colon Colon.
If you are interested in this, you can find more information under our topic:
- Sympathetic
- Parasympathetic nerve
Function of the colon
The main function of the Colon (Colon) consists in a thickening of the food.
So there is strong water absorption. The onward transport of food by peristaltic waves is also one of the tasks of the colon.
Typical diseases
Important diseases that (also) affect the colon are for example
- the inflammatory bowel disease how
- Ulcerative colitis
and - Crohn's disease
- Diverticular disease (numerous protuberances on the intestinal wall = Diverticulosis, if the diverticulum is inflamed, one speaks of a Diverticulitis)
- Colon polyps (Mucosal protrusions, which can occur sporadically or in large numbers, whereby one then Polyposis coli speaks)
and - as one of the most common types of cancer - - of the Colon cancer (colorectal cancer), whereby most of the tumors are not in the colon (colon), but in the adjoining rectum / rectum (rectum) are localized.
















.jpg)