Saddle thumb joint
synonym
Articulatio carpometacarpalis (lat.), carpometacarpal joint
Definition of the thumb saddle joint
The thumb saddle joint is located in the area of the wrist. It is largely responsible for the flexible mobility of the thumb and, as one of the most stressed joints, is often affected by degenerative processes.
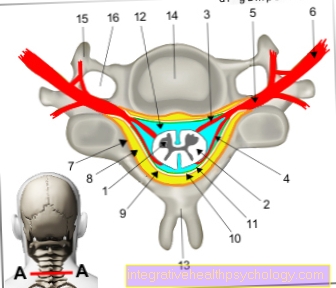
Illustration of the thumb saddle joint

- Thumb saddle joint -
Articulatio carpometacarpalis
pollicis - Distal phalanx -
Phalanx distalis - Phalanx -
Phalanx proximalis - Metacarpal bones
of the thumb -
Os metacarpi - Trapezoidal bone
(= large polygonal leg) -
Trapezium - Spoke - radius
- Cubit -Ulna
- Scaphoid bone of the hand -
Scaphoid bone - Trapezoidal bone
(= small polygonal leg) -
Trapezoid bone - Metacarpal bones -
Ossa metacarpi
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
construction
The thumb saddle joint is formed by the large square leg (Trapezium), which belongs to the carpal bones, and from the base of the first metacarpal bone (Os metacarpal I).
The joint is not where the thumb seems to start when looking from the outside, but further down, namely in the area of the wrist.
The reason for the name is the saddle-like shape of the trapezium in the area of the joint.
The capsule surrounding the thumb saddle joint is relatively slack, while ligaments ensure that movements are safely guided.
Nonetheless, the joint is much less tightly tensioned by ligaments than is the case with the joints between the carpal and metacarpal bones of the other fingers, which results in its large range of motion.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
Function of the thumb saddle joint
The thumb saddle joint is primarily responsible for the pronounced mobility of the human thumb.
This is possible, among other things, through the shape of the joint surfaces. These enable different levels of movement: The Flexion (Diffraction) and Extension (Stretching) that Abduction (Spreading) and Adduction (Introduce) and Rotational movements.
An indispensable movement for humans is that opposition of the thumb. This describes the movement that is performed when one touches the fingertips of the other fingers of the same hand with the thumb.
This movement also takes place in the thumb saddle joint, it is a combination of several of the movements listed above. Opposition is essential for fine motor gripping, for example in the form of the tweezer grip.
Clinical significance
The thumb saddle joint is exposed to a wide variety of stresses and is therefore often the site of degenerative (wear-related) changes.
The arthrosis of the thumb saddle joint, the so-called thumb saddle joint arthrosis (Rhizarthrosis), is a widespread disease that leads to pain, swelling and restricted mobility in the thumb.
Saddle joint pain
Pain in the area of the Saddle thumb joint can very unpleasant be there almost every movement of the hand also with one Move in the thumb saddle joint. As a result, every movement is felt to be painful. The pain can have a different character. You can rather dull and boring or else bright and stabbing be. The pain may go away thumb from down to the forearm. However, you can also sign up as a punctual pain or Tenderness express at joint level. Initially, the pain usually only occurs during movement; if the pain is based on a progressive disease, the thumb saddle joint often hurts as it progresses Idle state. Not infrequently, in addition to the painful restrictions on movement, there are other complaints, such as one swelling, Redness or overheat in the joint area. Everyday movements are often significantly impaired by the complaints, as the thumb plays a major role in all of them Gripping movements the hand plays. The thumb saddle joint allows the thumb to be brought up to the little finger (opposition). This movement is critical to a person's ability to grip. When there is pain in the thumb saddle joint, impairments occur everyday movements on, for example, when screwing a screw cap on or off, holding heavy objects, pressing an object together by hand (typically secateurs) or filigree tasks (manual work, playing the piano, picking up small objects, etc.).
The pain in the area of the thumb saddle joint can have different causes. Is a Thumb saddle joint arthrosis causally, this is how the Pain by the fact that the cartilaginous articular surfaces have worn out. The neighboring bones rub against each other with every movement, causing pain. They can also become smaller over time Cartilage and bone fragments exfoliate and additional discomfort and Inflammation cause in the joint. If the thumb saddle joint is not arthritically changed, the cause of the complaints can also be a previous one trauma (e.g. fall) in which the joint was squashed / compressed or broken.
Surgery of the thumb saddle joint
Surgery on the thumb saddle joint is often necessary with an existing one Thumb saddle joint arthrosis be undertaken if this cannot be treated by conservative measures. This is the case when despite conservative methods of treatment (Plaster splint, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs) there is no improvement in the symptoms, or the pain even worsens. If the function of the affected hand is so limited that everyday work can no longer be performed, an operation is recommended.
Procedure: Surgery on the thumb saddle joint can outpatient or stationary be made. During the operation, the Carpal boneswhere the thumb begins. This carpal bone is that Trapezium (the so-called large polygonal leg). In this way, the pain caused by the friction between the two joint surfaces is eliminated. The missing bone is replaced by an artificially created one Tendon loop, the so-called APL plastic (Abductor Pollicis Longus Plastic). To do this, the Tendon of the muscle, which spreads the thumb (abductor pollicis longus) around the Wrist flexor tendon laid and sewn there. In this way, a new abutment is created for the thumb, which at the same time prevents the thumb from slipping too much towards the wrist. In some cases, the APL plastic is not used at all. However, this only works if the ligament relationships of the affected hand are stable enough to fix the thumb in its normal position.
Follow-up treatment: After the operation, the thumb must be used for approx. two weeks be fixed in a plaster splint or bandage so that the wound surface can heal in peace. Then the threads are removed and the thumb for more two weeks with the help of a Orthosis immobilized. This is a more flexible splint that can be strapped around the wrist with Velcro fasteners. This can also be removed for showering. To four weeks can finally be targeted with physiotherapy exercises normal, pain-free hand function can be restored. The muscles are strengthened and the thumb regains its usual mobility. To three to six months the thumb is usually completely healed and resilient to almost normal levels.
Thumb saddle joint arthrosis
The thumb saddle joint arthrosis, too Rhizarthrosis called, is through a Wear of the articular surfaces caused. Over time, the cartilage is so worn out that the bony joint surfaces rub against each other. this leads to uncomfortable painwhich initially only occur when moving, later also when at rest. Sometimes smaller bone fragments also split off, causing further friction in the joint and making the pain even worse. Initially, the thumb saddle joint arthrosis manifests itself in only one Morning stiffnessthat wears off as the day progresses. Pain later everyday movements, especially opening and closing screw caps, grasping small objects and forcefully squeezing objects such as secateurs. Often there is also one swelling, Redness and overheat in the joint area. In advanced stages, the arthrosis of the thumb saddle joint can be external visible deformation of the joint.
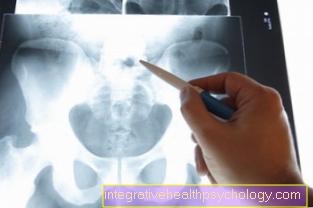
Diagnosis: If the joint is x-rayed because of the symptoms, it will also show in X-ray image typical signs of arthrosis. This includes one Narrowing the joint space, roughened joint surfaces with small fragments of bone (Osteophytes), as well as a compression the bony joint parts (Sclerotherapy).
Therapy: In some cases the saddle joint arthrosis with conservative, that is with non-operational measures be treated. To do this, the thumb is first used Associations immobilized. Optionally can anti-inflammatory or analgesic ointments be applied. Also anti-inflammatory drugs in tablet form like Ibuprofen are used. Heavy strain on the thumb, for example resting on one hand, should be avoided if possible.
If the symptoms do not improve in this way or even get worse, one must operative therapy should be considered. As a rule, the large polygonal bone (os trapezium) is removed and replaced by a Tendon loop replaced. The thumb now slides on this tendon loop and can with adequate physiotherapy training to regain its original functionality. After about three to six months the operating area is usually completely healed and can be loaded normally again.












.jpg)