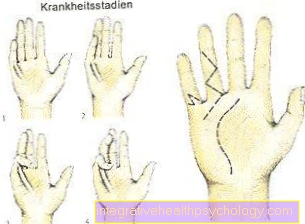
Diverticulitis stages
introduction

The Diverticulitis denotes a Inflammation of small pouches of the Intestinal lining of Colon. she stays often symptomless, however, can also manifest through pain and possibly also life threatening when a diverticulum ruptures and bowel contents empty into the abdomen.
The disease can occur in different stages to be grouped. The classification is based on the one hand clinical symptoms of the patient, on the other hand, according to the findings that occurred in the Colonoscopy (Colonoscopy) results and the Imaging (CT of the abdomen).
Stage 0
The Stage 0 is considered easy Diverticulosis designated. The patient has it with him no symptoms. In the Colonoscopy only show the small bulges (Diverticulum) of the intestinal lining, however unattractive, i.e. not inflamed. Computed tomography of the abdomen shows the diverticulum as Small cavities filled with gas or contrast medium.
Stage I.
The Stage I. is indicated by a uncomplicated acute diverticulitis. The patient mostly feels Pain in the (left) lower abdomen and can fever to have. In the colonoscopy, the diverticula appear as reddened and swollen pouches the intestinal lining. If contrast agent is added, they show up Spicules (thorn-like contrast medium expansions) and one Thickening of the intestinal lining. The thickened intestinal mucosa can also be seen on CT.
Stage II
The Stage II In contrast to stage I, diverticulitis denotes the complicated acute diverticulitis. This stage is divided into three sub-forms.
Stage IIa
If stage IIa is present, it is a so-called phlegmonous diverticulitis or one Peridiverticulitis. The patient feels one severe pressure pain in the abdomen, on physical examination there is one Defense tension of the abdomen in front. In the lower abdomen, a roller-like resistance Keys.
Usually the patient also has a fever. The colonoscopy shows up significant redness around the diverticular necks. Using contrast media, as in stage I Spicules and a thickened intestinal lining to be watched. The CT shows the thickened intestinal mucosa and thickening in the Adipose tissue around the colon.
Stage IIb
Stage IIb is awarded if a abscessing diverticulitis, a covered perforation or a fistula exist. Abscessive diverticulitis has already developed local accumulation of pus formed in the intestinal mucosa (abscess).
In the covered perforation a diverticulum is torn, but still not completely breached into the abdomen. A fistula is present when a Connecting passage has arisen between the diverticulum and the abdomen.
The patient usually has a fever, one local peritonism (Pain from irritation of the peritoneum). The colonoscopy shows that same finding as in stage IIausing a contrast medium to see whether there is a tear in the intestinal mucosa or intestinal wall. In this case it can Contrast media emerge from the intestinal lumen. An abscess becomes visible on computed tomography.
Stage IIc
Are at this stage one or more diverticula finally completely ruptured, so broken through into the free abdominal cavity. So there is a direct connection between the intestine and the abdominal cavity.
Patients have a Acute abdomen, which is through very severe abdominal pain, possibly one Shock symptoms and Vomit expresses. A colonoscopy is not performed with such a clinical picture. In the Computed Tomography shows free air in the abdomen that comes from the intestines as well free liquid and, if necessary, abscesses.
Stage III
The Stage III is at chronically recurring (recurring) diverticulitis forgive. The patients complain in certain time intervals repeatedly about pain in the lower abdomen. Sometimes they also have a fever, constipation or air leakage with the urine (so-called champagne urine). This can happen if through repeated inflammatory processes a Connection between the bowel and the bladder originated. The air from the intestines can then enter the bladder and exit with the urine. During the colonoscopy, there may be a local narrowing of the intestine (Stenosis) or a fistula (connecting duct). The same is then also in the Computed Tomography visible. The intestinal wall is usually thickened.
The Diverticulitis staging is important because the Therapy of the disease significantly oriented.
While in the early stages the disease one conservative therapy is mostly successful, must be in stages IIb and IIc surgical intervention should be considered. Therapy in stage III must be individual depending on the patient's condition to get voted. A general indication for surgical therapy is no longer given for chronic recurrent diverticulitis. However, the disease already has to serious bottlenecks in the large intestine, for example the affected person Section of the intestine completely removed become (sigma resection).


.jpg)










.jpg)