Ovaries
Synonyms in a broader sense
Ovary, ovaries (pl.), Ovary, ovary, oophoron
English: ovary
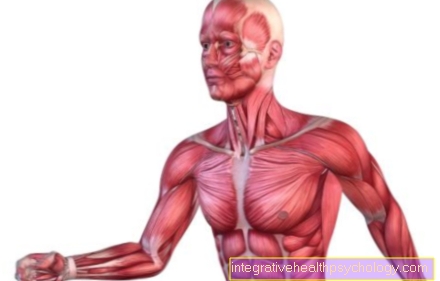
Illustration ovaries

- Ovary -
Ovary - Basic tissue of the ovary -
Stroma ovarii - Mature vesicle follicles -
Folliculus ovaricus tertiarius - Corpus luteum -
Corpus luteum - Uterine cavity -
Cavitas uteri - Cervix -
Ostium uteri - Ovarian ligament -
Ligamentum ovarii proprium - Fallopian tube fringed funnel -
Infundibulum tubae uterinae - Fallopian tubes -
Tuba uterina - Ovarian artery -
Ovarian artery
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Ovarian diseases
As the function of the ovaries depends on the Hormones the pituitary gland (gonadotropins), disorders of the function of the result in special diseases that change the amount of gonadotropins released into the blood Ovaries and thus also the rhythm of menstrual bleeding. Pain in the lower abdomen caused by the ovary can e.g. by turning the handle, Adnexitis or ovarian venous hormones develop.
Menstrual disorders (menorrhea)
A usual bleeding rhythm is between 25 and 31 days (eumenorrhea). If you have arrhythmia, your menstrual bleeding may be longer (Oligomenorhroe) or to smaller ones (Polymenorrhea) come.
A previously existing Menstrual period initially absent altogether. There is then no more bleeding for more than three months (secondary Amenorrhea). As a result of the disorders of the hormonal system and the resulting disruption of the ovaries, women can suffer from a infertility (Sterility) suffer.
Other reasons for amenorrhea (lack of menstrual bleeding) include, for example Malnutrition or anorexia. In the context of anorexia, malnutrition and disorders in the hormonal balance lead to a lack of Menstrual period (Period).
Malfunction of the ovaries can also result from ascending infections vagina (Colpitis), from the Cervix (cervicitis), the body of the uterus (Endometritis / myometritis / endomyometritis) or the Fallopian tubes (Salpingitis) result in the one Inflammation of the ovaries cause (oophoritis). An inflammation of the ovaries and at the same time the fallopian tubes are referred to as Adenexitis.
Such inflammations can result in abscesses and adhesions of the internal female genital organs, which can lead to infertility of the woman.
The function of the ovaries can also be affected by cysts (Ovarian cyst) or tumors (ovarian tumor = Ovarian tumor) be irritated.
Ovarian cancer
In which Ovarian cancer (ovarian cancer) it is a malignant tumor of the ovaries that can appear on one or both sides.
One differentiates the type of ovarian cancer on the basis of its fine tissue (histological) picture. The tumors are thus divided into epihelial tumors, germ cell tumors as well as germ cord and stromal tumors.
Epithelial tumors are tumors that originate from cells on the surface of the ovaries. They make up about 60% of all malignant ovarian tumors. Those emanating from the germ cells of embryonic development (development of the fruit of the body) Germ cell tumors account for around 20% of all malignant ovarian tumors. Stromal tumors are tumors that develop from the ovarian tissue and make up around 5% of all malignant ovarian tumors. In addition, around 20% of malignant ovarian tumors are deposits of cells from a tumor that originally developed elsewhere (metastases). The metastases usually occur on both sides and about 30% originate from one Uterine cancer (uterine cancer) and about 20% of one Breast cancer (Breast cancer) or cancer from the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal carcinoma).
Further information on the subject can be found at: Ovarian cancer
Cyst on the ovaries
Cysts on the ovaries are benign masses that appear as fluid-filled cavities. They can arise in the ovary for a variety of reasons and are very common. Most of the time, cysts are incidental findings with no further disease value. As a rule, a check-up takes place after a few weeks, after which the cyst has usually disappeared again.
- On the one hand, there are functional cysts, such as the follicular cysts. These are the most common cysts and represent a non-cracked egg cell / a so-called Graaf's follicle. Since such follicles constantly develop and mature in the ovary before the end of the menopause, such cysts are common in young women.
- Yellow body cysts can occur during the menstrual cycle or in pregnant women and produce progesterone (pregnancy-maintaining hormone).
- Thekalutein cysts can arise, for example, during fertility treatment through the administration of hormones. They usually go away after stopping hormone therapy.
- Endometriosis cysts develop when dislocated uterine tissue settles in the ovaries. They are filled with blood because the scattered mucous membrane takes part in the cycle and, like in the uterus, is shed during menstruation. Because of the accumulation of blood (coagulated brownish) they are also called chocolate cysts.
- Retention cysts are caused by an accumulation of glandular secretions. They are rare in the fallopian tube.
Cysts can be diagnosed very well on ultrasound. You can see them as black, round, smoothly delimited structures, as the liquid in them is shown dark. If there are multiple cysts in the ovary, polycystic ovarian syndrome may be present, which is also associated with masculinization. This can lead to hair growth, acne and menstrual cycle disorders.
Most cysts resolve on their own by rupturing and the fluid is broken down. Sometimes, however, a large cyst can lead to severe pain, in which case such a cyst can also be surgically removed after weighing up. Usually a laparoscopic operation is performed. In this so-called "laparoscopy", a camera and instruments are introduced into the abdominal cavity by means of small incisions and the operation is performed under view. This is a procedure that is gentle on the tissue.
The cyst rupture can be very painful and rarely lead to significant fluid or blood loss. Often the pain then subsides again after the burst. Another complication can be a twisting of the ovary stalk, which cuts off the blood supply. This can be promoted by large cysts with a high dead weight. Often there is a twist of the stem (torsion) after an awkward movement or during sports. An immediate operation is necessary here, otherwise the organ will die and infertility will ensue, at least in this ovary on this side.
Read more on the topic: Cyst on the ovaries, ultrasound of the abdomen
Twisting of the ovaries
A Twisting of the fallopian tubes and ovaries can be extremely painful. The pain spreads above the Groin area and can easily be with a Appendicitis be confused. Vomit and nausea can be another reference to this so-called Adnexal torsion be. This twist represents one gynecological emergency represents - if not the most common gynecological emergency.
In most cases, the twist is caused by Ovarian cysts or Tumors. Women who have a child because they want to have children are at increased risk Hormone therapy do. Adnexal torsion also occurs particularly frequently in the pregnancy on.
In contrast to the previous approach, surgical removal of the adnexa is not performed today because of the high risk of bleeding. Rather, as part of a surgerywhere the cyst or tumor is removed that Ovary returned to its normal position.
Incidentally, women who have had a history of adnexal torsion have a lower risk of developing adnexal torsion Endometriosis have gone through or had an abdominal infection. It is assumed here that adhesions on the adnexa provide more stability.
Ovaries stuck together
The Ovaries usually do not stick, but when the Fallopian tubes glued, this can be too infertility to lead.
The function of the fallopian tube is that cracked egg first with his so-called Fimbria funnel (which work like little feelers) and secondly along the fallopian tube to be transported to the uterus.
Therefore, the fimbriae or the fallopian tube can be glued together delicate hairs (Ciliated epithelium), which move the egg towards the uterus in a few days, lead to a loss of function. When the egg can no longer find its way into the uterus, there is one Pregnancy is no longer possible naturally. In addition, the fallopian tube is the Place of fertilization, because here usually the Sperm hit the egg cell.
Often one arises Adhesion after inflammation. The pathogens are mostly Intestinal bacteria (for example Escherichia Coli, Enterococci) that have the Scabbard ascended to the fallopian tube are. Since the fallopian tube is open to the abdomen, the pathogens can practically spread throughout the abdomen and affect all abdominal organs. Gluing can also be carried out in the opposite direction by a open abdominal inflammation arise, as they do with Organs burst open (ruptured purulent cyst, perforated Intestines/ appendix, Gallbladder etc.) occurs. Also through the scattered uterine lining in the fallopian tube (Endometriosis) sticking can occur.
Therapeutic can be used in the event of an infection Antibiotics give to a The germs rise or one Scarring / sticking to prevent. There is also the option of a glued fallopian tube to reopen operationally. The chances of success depend on the Severity of the sticking.
In addition, with a Desire to have children different methods use, an egg cell can also be punctured from the ovary and in vitro (in a glass) with a sperm to be fertilized. The fertilized egg can then implanted in the uterus and the embryo will mature naturally from then on.
Inflammation of the ovaries

Inflammation of the ovaries is called in medical terminology Oophoritis or Ovarian disease. This inflammation is usually caused by bacteria. There are several causes of bacterial infection of the ovaries. This can be due to birth, abortion or menstruation. The cause can also iatrogenic in nature be. This means that there is a cause underlying the ovarianitis which is determined by the doctor. This can be, for example, the use of a contraceptive coil and does not mean that it is due to a medical malpractice. The causative pathogens include Staphylococci, gonococci, streptococci and chlamydia.
Other causes of inflammation of the ovaries are spread of the inflammation in the context of other infectious diseases such as tuberculosis. This dispersion takes place via the bloodstream. In addition, an infection of the neighboring organs (e.g. appendicitis) can spread to the ovaries via the lymph. Also an inflammation of the peritoneum, a so-called Peritonitis, can affect the ovaries. Ultimately, in rare cases, there may be an autoimmune cause behind a Oophoritis stuck. Oophoritis is usually accompanied by inflammation of the fallopian tubes. This is called Salpingitis or Adnexitis.
Acute inflammation of the ovaries manifests itself in fever, severe pelvic pain, nausea and vomiting. In addition, there is a Defense tension to observe. A defensive tension is understood as a strong tension of the abdominal muscles when touching the abdomen.
At a Oophoritis there is a risk of getting one Ovarian abscess or that the pathogens spread into the abdomen and so ultimately one Peritonitis cause. Hence a Oophoritis in any case in need of treatment.
The inflammation is treated with broad spectrum antibiotics. Broad spectrum antibiotics are antibiotics whose effects cover a wide range of pathogens. In addition, you can also still non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs used to treat inflammation. If conservative drug therapy is unsuccessful, surgery can be considered. This operation is a Oophorectomywho have favourited surgical removal of the ovaries. The diagnosis of oophoritis is made with the help of various diagnostic measures. Inflammation parameters, which include special proteins, can be determined using laboratory diagnostics. Vaginal swabs can provide information about the type of pathogen. By means of a sonographic examination the ovaries can be visualized and assessed with regard to their size and condition (e.g. abscesses).
Read more on the topic: Inflammation of the ovaries and symptoms of fallopian tube inflammation
Pain in the ovaries
Pain in the ovaries can affect women in the right or left abdomen project and have various causes.
Pain in the ovaries occurs especially during pregnancy. You can find out more about this at Ovarian pain in pregnancy to inform.
Most common is one Pulling in the lower abdomen at the physiological ovulation. Some women can ovulate feel rightwhen the mature egg cell pops / bursts from the ovary and pain occurs. Ovulation takes place about halfway through the cycle, 14 days after the start of the last Menstrual period instead of and thus lies between the Bleeding (Menstruation).
At the time of the bleeding, many women have it Lower abdominal painthat are often convulsive and by the Uterine contractions arise. These are uncomfortable, but not bad. Provide relief warmth, tightened legsto relax the abdominal wall and Antispasmodics such as drugs with the active ingredient "butylscopolamine" (Buscopan).
Also for Timing of menstruation can have pain in the Endometriosis framework occur when there is bleeding in the body because here is Uterine lining (Endometrium) originated or got there in the wrong places in the body. Possible locations are, for example Ovaries, but also the bladder or the Intestines. These scattered uterine lining is subject to the normal cycle, builds up and grows and is also repelled again.
As part of a normal pregnancy it can occasionally too Abdominal pain come, mostly through the Pressure of the baby on the organs are explainable. One is also rare Pregnancy in the fallopian tube possible, which is called an ectopic pregnancy in the fallopian tube instead of in the uterus Ectopic pregnancy (Pregnancy outside the womb (= uterus)) come in the ovary (ovary) itself. It is one of them Fertilization and implantation of the egg come in a place other than the uterus.
This can be found in Ultrasonic and by means of the Determination of pregnancy hormones as with a pregnancy test. There is an extrauterine pregnancy not deductible and can be very dangerous there major bleeding possible are.
Cysts in the ovary (Ovary) there relatively often. They too can lead to pain but often burst by themselves and are usually not in need of treatment.
A Ovarian inflammation (Adnexitis) can be caused by Rise of pathogens, mostly bacteria, arise. In doing so, often get through improper hygiene, Bacteria from the intestines via the vagina into the uterus and from there can get into the fallopian tubes and the ovary, but also into the abdomen in general, as a open connection from the fallopian tube to the abdomen. A Infection of the genital organs may show up as a burning sensation and discharge (purulent). Likewise can Painful intercourse and also with the Evacuation of the bladder and bowel occur. It can too fever and Vomit come and in the worst case to one Bonding the structures. This allows a infertility arise because the fallopian tubes can no longer transport the cracked egg cell when an adhesion has developed.
Inflammation of the ovaries will mostly treated with antibiotics. When a as hard as a board and severe pain Immediate admission to a clinic is necessary. A hard stomach can be for you Breakthrough of an inflamed structure talk (ovary / fallopian tubes / appendix) and make one Involvement of the peritoneum probably. Immediate clarification should also be given in the event of severe pain suddenly completely painless as this description is typical of the Rupture of the inflamed structure is (perforation).
A one-sided pain that sets in absolutely acute can through a Rotation of the stalk of the ovary (Ovars) arise. Typically this happens during sport / exercise. The ovary rotates around its suspension and pushes off the supplying vessels. It's about one emergency, the quickly to an operation should lead, since without blood supply there is a risk of organ death and loss of function.
A important differential diagnosis at right side lower abdominal pain is appendicitis (correct appendix inflammation appendicitis).
Ovarian cancer (Ovarian cancer) almost shows up never through pain in the abdomen, usually it is noticeable by other symptoms. Possible pain due to a tumor arises very late through repression phenomena.
Pulling and squeezing the ovaries
Pulling or pushing the ovaries is quite unspecific. So you can't tell exactly what the cause of the abdominal pain is based on this. However, there are various options, which are explained in more detail below. First of all, ovarian pulling may indicate a tumor. However, inflammation of the ovaries can just as easily cause severe abdominal pain. There is also the theory of the so-called Middle pain. Some women experience pulling or stinging of the ovaries close to ovulation, which occurs monthly. However, it has not been proven whether this pulling is actually a sign of ovarian activity or whether there are other causes of what is known as "middle pain". The middle pain can vary from month to month and, according to the statements of the patients, also changes sides. It is believed that the mature follicle is causing this sharp pain when it bursts open during ovulation. However, no more precise statements can be made. The middle pain is therefore not a sure indicator of ovulation and should therefore not be used as a means for family planning. He cannot be treated. Affected women can, however, relieve their symptoms with a gentle posture or a hot water bottle. However, if the pain is very severe and persistent, a doctor should always be consulted in order to rule out other pathological causes for the pain.
Learn more about: Middle pain
Removal of the ovaries
A surgical removal of the ovaries is called Oophorectomy or Oohorectomy. Removal of the ovaries can be particularly beneficial in the case of malignant changes such as Ovarian cancer (Ovarian cancer) or with Ovarian cysts to be required. Also, removing the ovaries lowers the Hormone production, which is why an oophorectomy is required if one is present Breast cancer (Breast tumor) may be indicated.
There are three ways to remove the ovaries.
- Laparatomy: In a laparatomy, the abdominal wall is opened to remove the ovaries.
- Colpotomy: The intervention takes place here via an access through the vagina the woman.
- laparoscopy: Laparoscopy is one of the minimally invasive surgical interventions. This means that the smallest possible incisions are made, resulting in only small wounds. The ovaries are removed through a small incision in the abdominal wall. This procedure is the most common because it involves the fewest complications and does not prevent a good healing.
Consequences of an oophorectomy
The Removal of the ovaries causes the Loss of fertility. Important hormones like estrogen, progesterone and Androgen are made in the ovaries. The loss of this source of hormones has an impact physically as well as mentally out on the woman concerned. It can nausea, dizziness and migraine as well as mental illness, in the worst case even depressions, occur. The Entry of the menopause (Menopause) occurs with additional Removal of the uterus, so that Sweats, Mood swings and sleep disorders can arise. By means of a Hormone replacement therapy these side effects can be counteracted somewhat.
Anatomy uterus

- Uterine cavity
- Cervix / cervix
- Scabbard
- Tube / fallopian tube
- Ovary / ovary
- Corpus / body
- Portio / cervix
















-buschmcke.jpg)