Symptoms of hypoglycaemia
Medical: Hypoglycemia
English: hypoglycemia

Symptoms of hypoglycaemia
Individual differences in the symptom picture from person to person Hypoglycaemia are typical. The symptoms associated with hypoglycaemia are generally divided into autonomic and central nervous symptoms, whereby the autonomic symptoms are caused by a disturbance of the autonomic (autonomic) nervous system, the central nervous system by changes in the central nervous system (brain, Spinal cord) arise.

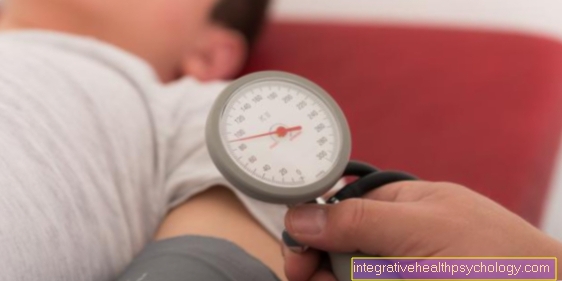
The autonomic symptoms of hypoglycaemia include food cravings, weakness, nausea and vomiting. Sweating, restlessness, increased pulse rate (tachycardia), rising blood pressure (hypertension) and tremors (tremor) are also included. Central nervous symptoms of hypoglycaemia mainly affect the brain, as it reacts very sensitively to hypoglycaemia because only glucose is available in the brain for energy production. Symptoms take the form of headache (cephalgia), irritability, bad mood, lack of concentration, or confusion. Furthermore, disorders of the coordination, the respiratory and circulatory center, epileptic seizures, paralysis, visual disturbances and abnormal drowsiness (somnolence) can appear accompanying hypoglycaemia. In the worst case, hypoglycemic shock occurs.
The hypoglycemic shock as a result of low blood sugar is characterized by a sudden loss of consciousness, which is triggered by the falling blood sugar level. In addition, sweating with damp and pale skin, increased reflexes and cramps may occur as a sign of hypoglycaemia.
more information on this topic
- Hypoglycaemia
- Hypoglycemia symptoms
- Hypoglycaemia cause
further interesting information from this area:
- nutrition
- Iron deficiency
- Nutritional therapy
- Diabetes mellitus
- Dizziness and blurred vision
You can find an overview of all published topics in this area at Internal medicine A-Z