Inflammation of the small intestine
introduction
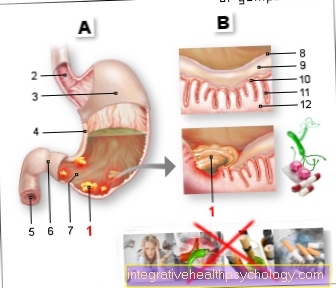
Of the Small intestine connects with its 5-6 meters length stomach with the Large intestine. The small intestine is divided into 3 parts. At the beginning there is the approximately 30 cm long directly after the stomach gatekeeper Duodenum (= Doudenum), whose main task is the neutralization of gastric hydrochloric acid and the decomposition of food components with the help of the secretion of the Pancreas, as well as the bile is. This is followed by the Jejunum and the Ileum, whose main task is the absorption of the food components into the body. In addition, 80% of the water is withdrawn from the food here. The remaining 20% is absorbed in the large intestine, which adjoins the small intestine.

causes
Inflammation in the small intestine can occur in the duodenum due to circulatory disorders, drugs that damage the mucous membrane, autoimmune diseases or the colonization with Helicobacter pylori.
There are a few other important causes of inflammation in the other sections of the small intestine that lead to permanent inflammation of the small intestine. For example, celiac disease, which is also called Sprue designated intolerance of the cereal protein gluten, a permanent inflammation is the basis. Here the immune system reacts to gluten, a very common grain protein, and fights the cells of the intestinal mucosa that are in direct contact with gluten. The cells react to this attack by the immune system with inflammation. Gradually, the cells can no longer withstand the immune system and the intestinal mucosa becomes increasingly thinner due to progressive cell death (= Atrophy).
Also to be mentioned is Crohn's disease, a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that leads to episodes of chronic inflammation of the intestinal mucosa. This inflammation can in principle occur in any part of the intestine, but often affects the small intestine. Like celiac disease, the inflammation arises as an autoimmune disease, which means that the body no longer recognizes the intestinal mucosa as belonging to itself and fights it through the immune system, which, as with celiac disease, manifests itself in an inflammation. In Crohn's disease, the entire mucous membrane is not evenly affected and only changing parts of the intestinal mucosa show signs of inflammation. This creates a patchy picture in the intestine of inflamed and non-inflamed parts of the intestine. The first signs of this disease often appear between the ages of 20 and 40.
You might also be interested in this topic: Leaky Gut Syndrome
An acute (that is suddenly occurring and limited time) Inflammation usually occurs as part of an infection with viruses, bacteria or other undesirable pathogens that have a typical "Intestinal flu" trigger. The germs lodge in the intestinal mucous membrane and lead to inflammation there after a varying length of time. In medicine, this infection is called enteritis.
Among the viruses are Rota-, Adeno or also the Noroviruses the most famous representatives. Several of these pathogens, such as this Norovirus fall under the so-called statutory reporting obligation and must be reported to the local health department if they are found.
Other rare causes are inflammation caused by radiation exposure to a tumor or inflammation caused by reduced blood flow to the small intestine.
Symptoms

The symptoms of small bowel inflammation differ depending on the cause. Enteritis, i.e. inflammation caused by infection with bacteria, viruses or other pathogens, is often associated with diarrhea and abdominal pain, accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
When listening to the stomach, increased movement of the bowel (= Peristalsis) as "Cluck“Perceive. Possibly a fever can be added, which then speaks more for a bacterial cause of the enteritis.
Crohn's disease, the permanent or intermittent inflammation of the lining of the small intestine, typically manifests itself during an episode with pain in the lower right part of the abdomen similar to appendicitis, mild diarrhea and loss of appetite.
Celiac disease, also characterized by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the small intestine, manifests itself in childhood after eating foods containing gluten. Due to the death of the cells, the affected person can no longer absorb the nutrients ingested with food and symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue, failure to thrive but also unspecific symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite occur. The doctor often only goes to the doctor because of the increasing weight loss of the children. The symptoms increase due to the increasing and progressive destruction of the intestinal mucous membrane cells in the course of the disease if the person concerned does not switch to a gluten-free diet.
Find out more about the topic here: Burning in the intestines
therapy

Enteritis usually ends by itself within a few days to a maximum of 2 weeks. In most cases, drug therapy is not necessary. Since the most common inflammation is caused by viruses, there is also a antibiotic only rarely necessary and should only be used if the bacterial cause is proven. The main representatives of the antibiotics used are Metronidazole, Ciprofloxacin or Trimetoprim in combination with Sulfmethoxazole.
All of these preparations are ideal for a wide variety of germs in the intestine, so that an exact determination of the bacterium is not always necessary.
The important thing in all cases is Compensation for fluid loss through diarrhea and the loss of important salts in the body. This loss can lead to total dehydration of the body and in extreme cases can be life threatening. Above all, they are threatened with dehydration fairly quickly Infants or the elderly and for this group, enteritis often ends with a hospital stay in order to compensate for the loss of fluid and salt by administering fluids directly into the body's vasculature.
If the diarrhea persists or if it has to be stopped on certain occasions, the drug can be used in exceptional cases Loperamide used, which can stop the diarrhea by stopping the bowel movements.
Celiac disease can only be solved by one gluten free diet Get a grip, but not cure. Are gluten free cereals Corn, rice or millet. Are forbidden Wheat, barley, rye, green spelled and spelled.
Crohn's disease as an autoimmune cause of inflammation is just like celiac disease not curable and accompanies those affected throughout their lives. With optimal treatment, however, the affected person can live almost normally. The therapy consists on the one hand of cortisone- as well as other drugs that downregulate the immune system so that it does not fight the body's own structures. Antibiotics can also be used during acute attacks.
Important Natural remedies with inflammation of the small intestine garlic, basil, Savory, ginger, mint, clove, cinnamon, lemon, juniper, Propolis, Swedish herbs, thyme or lavender.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of intestinal flu is usually quite simple based on the symptoms. Which pathogen is underlying the inflammation usually does not matter, since in the vast majority of cases they all heal within a few days. Only when the diarrhea and the symptoms persist do you get the special pathogen out of one Stool sample filter out and determine in order to then be able to initiate a special therapy.
Celiac disease can often from the history of those affected guess. The parents report the onset of the complaints since the child consumed the first cereal products. Final clarity then usually brings one Blood test. Often found in the blood of affected people antibodywhich, as part of our immune system, cause inflammation in the intestines. These special antibodies are against the so-called Endomysium, the Gliadin and the so-called Tissue transglutaminase directed. Also taking a sample as part of a Colonoscopy can bring clarity.
The diagnosis of Crohn's disease is based on various tests. Above all they play here Colonoscopy, roentgen, Ultrasonic, Blood and stool tests a crucial role. In the colonoscopy, the extensive, "map-like“Inflammation, since entire sections of the intestine are almost never affected.
In order to diagnose inflammation of the small intestine, the last one too MRI according to Sellink established. After the administration of contrast medium, an MRI examination of the small intestine is made, which shows changes in the mucous membrane very clearly.
forecast
The course of Crohn's disease is very variable and differs from patient to patient. With adequate adherence to therapy, the prognosis for people with Crohn's disease is good and around 50% of those affected can live symptom-free. Life expectancy is not restricted by the disease.
Celiac disease also exists lifelong and can only be alleviated, not cured. Untreated celiac disease increases the risk of tumors developing within the digestive tract. However, a gluten-free diet can almost reduce the risk of long-term damage lower it to a minimum and keep the damage in the intestine low.
prophylaxis
The best prevention against diseases of the bowel in general is one healthy, balanced diet and adequate hydration of at least 1.5 liters a day. In terms of nutrition, should Fiber, fruit and vegetables are on the daily menu.
Enteritis can get through adequate hygiene often prevent. Many of the pathogens cannot survive outside the body for long. Therefore, above all, applies regular hand washing and at best regular hand disinfection one of the most effective means to prevent enteritis.
A prophylaxis of celiac disease or Crohn's disease is not possible according to current knowledge and a familial accumulation suggests a hereditary cause of celiac disease.