Hair loss from the thyroid gland
introduction
Hair loss, in which more than 100 hairs fall out per day, is called Effluvium. Suffering from this is an enormous psychological burden, especially for women. Often the cause is found in a malfunction of the thyroid gland! For example, if your hair is overactive, it will grow a lot faster, but it will become thinner and thinner and fall out more and more. An underactive thyroid can also be the cause. The thyroid produces the hormones T3 (L-triiodothyronine) and T4 (L-tetraiodothyronine), which play an essential role in many growth processes and metabolic processes in the body.

root cause
The thyroid controls many organs in the body, including the skin, the largest organ in the human body. It is responsible for controlling growth and for many metabolic pathways. Everything is controlled by the hormones T3 and T4. If there is a malfunction, both a subfunction (Hypothyroidism), as well as an overfunction (Hyperthyroidism) ,, the thyroid gland can no longer work properly and so it happens that the hair structure changes. A similar thing can be observed in the toenails and the fingernails. Diffuse hair loss is mainly observed when the thyroid is overactive. This hyperfunction can have various causes, such as an autoimmune disease (Graves' disease) or the use of iodine-containing medication. Typically, other symptoms such as a fast heartbeat (tachycardia), diarrhea, increased sweating and heat intolerance occur.
You might also be interested in: Hair loss in women
Hair loss after thyroid surgery
Thyroid surgery may be necessary for various diseases. Either parts of the thyroid gland or the entire thyroid gland are removed. A total removal of the thyroid means that the body can no longer produce its own thyroid hormones. The result is an iatrogenic hypothyroidism caused by a medical intervention. Therefore, thyroid hormones are medicated for life after removal of the thyroid gland, usually with L-thyroxine. If the dosage is not high enough, this also results in hypothyroidism. Brittle and brittle hair is typical. However, hair loss is unlikely. Since the hair breaks off more often, the impression of hair loss can arise. In the case of such hypofunction, the dose of thyroid hormone must be increased. Too high a dose of drug-substituted thyroid hormones can lead to an overactive thyroid. This can lead to real hair loss. In this case, it is necessary to reduce the drug dose. The hair loss is then reversible and the hair grows back.
Further information on the subject of hair loss in the case of thyroid dysfunction can be found here: Hair loss from a thyroid disorder
Concomitant symptom: tiredness
Hair loss is a typical symptom of the widespread hyperthyroidism. The high concentration of thyroid hormones also leads to a number of other symptoms. This also includes fatigue and, above all, rapid fatigue. This is mainly due to sleep disorders from which those affected often suffer. At the same time, there is also a feeling of inner restlessness and tension.
Symptoms
With the symptoms one has to distinguish between an overactive thyroid (Hyperthyroidism) and an underactive thyroid (Hypothyroidism) differ. At a Subfunction are usually not just the hair on the head, but also the rest of the Body hair affected. The hair is also brittle due to the restricted function of the thyroid gland and it is no longer formed properly. In addition, hair diameter and hair density decrease and the hair looks dull and dull.
At a Hyperthyroidism on the other hand, hair grows too quickly and so easily breaks off and becomes thinner and thinner. They grow very quickly and only reach a short length due to the fragility and because they enter the resting phase much earlier. But the hair loss and the decreased or increased hormone release do not always have to correlate with each other. Sometimes there is severe thyroid malfunction and yet it does not manifest itself in hair loss. In addition to hair loss, there are numerous other symptoms such as Sensitivity to cold, Lack of drive, Skin dryness and constipation With an underactive on the one hand and with an overactive on the other hand, the following symptoms occur: Restlessness, Palpitations, Weight loss, frequent bowel movements, warm skin and Heat intolerance.
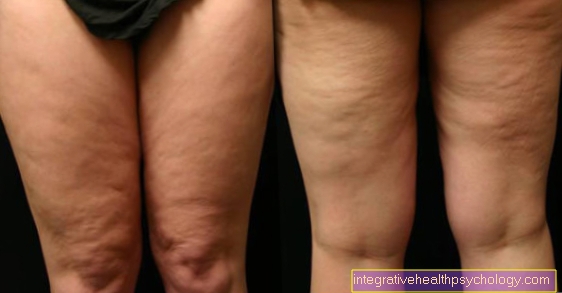
Thyroid-related hair loss on the legs
An overactive thyroid can cause hair loss. Typically, the hair loss is noticeable through increased hair loss and overall light hair. However, especially people who tend to have increased body hair, for example on the legs and arms, can also notice thinning hair in these areas.
treatment
Usually the Thyroid malfunction treated. If the formation of the hormones or the Hormone content has regenerated in the body, the structure of the hair can normalize again. If you have an underactive thyroid (Hypothyroidism) are mostly the missing ones Hormones T3 and T4 in Tablet form because it is often not possible to determine the underlying disease that is preventing the thyroid from working properly. Usually the drug levothyroxine is administered. It works in the organism like T4, which is normally formed in the body.
It is usually not a problem for the body to convert T4 to T3, so this form of therapy is usually sufficient. In some cases there is one Combination therapy necessary with T3 and T4. It is recommended to take the tablets on an empty stomach take and then wait about 40 minutes with breakfast. The hormone control usually takes place relatively late, after about six weeks, because only then can you reliably say whether there has been an improvement. It takes a relatively long time because the pituitary gland needs a certain amount of time to adjust to the changed hormone concentrations.
An overactive thyroid (Hyperthyroidism) is treated as follows: Since too many hormones are produced here, you have to administer drugs that reduce the production of hormones. In addition, there are drugs that are generally called Anti-thyroid drugs designated. Before the thyroid hormones T3 and T4 can be formed, iodine must be built into the body. The drugs mentioned can stop or minimize this incorporation.
diagnosis
To be able to determine if the cause of the hair loss (Effluvium) is a thyroid malfunction, a laboratory test must be carried out. The content of the hormone TSH (Thyroid gland (Thyroid) stimulating hormone) in the body. If the TSH is below 0.1 uIU / ml, then there is an overactive thyroid and if the TSH is over 20 uIU / ml then an underactive thyroid is present.
Will my hair grow back?
The hair loss caused by an overactive thyroid is reversible. This means that with proper treatment of the underlying disease, hair loss will stop and the hair will become stronger again. It is not what is known as scarring alopecia. In such a case, the hair would not grow back.
forecast
A thyroid dysfunction is often not completely cured, but with medication all in one maintained tolerable level. If the malfunction is not cured sufficiently, it is possible that the hair structure does not regenerate completely. Nevertheless, one can see significant improvements compared to untreated thyroid dysfunction.
prophylaxis
To prevent an underactive thyroid, an examination is carried out very early after birth to identify congenital hypothyroidism and thus counteract it before symptoms appear. Iodine deficiency is rarely a cause of one HypothyroidismHowever, it is important to always consume sufficient amounts of the trace element. This works through, for example iodized salt very good. Pregnant and breastfeeding women have an increased need for iodine and must pay particular attention to proper nutrition. Sea fish have a very high iodine content, which is why they should be eaten several times a week.
It is difficult to prevent an overactive thyroid because it is usually caused by another disease that you cannot influence yourself. Still, there are a few reasons for one Hyperthyroidismthat you can prevent yourself. An overdose of thyroid hormones can lead to hyperthyroidism. In addition, one should prevent overdosing of other substances containing iodine, such as medication or contrast media containing iodine.
Hormones T3 and T4
T3 is in the body for the most part bound to protein. Only a very small amount is freely available in the organism. This free T3 is that for the Body usable hormone. It depends on the time of day how big the salary of T3 is. One finds lower values during the day than at night. Outside the thyroid gland that will most of T3 out of T4 educated. The T4 is formed by the thyroid gland and serves as a precursor to T3. The formation of the hormones is originally stimulated by the hypothalamus. This is a center of the brain that is stimulated, for example, by physical stress or heat. Of the Hypothalamus stimulates the distribution of TRH on. TRH in turn stimulates the distribution of TSH from the pituitary gland (Pituitary gland) on. TSH causes an increased formation of T3 and T4 in the thyroid gland and a release into the blood. T3 and T4 increase energy expenditure of the body and adapt it to cold and movement. At the same time, however, they also inhibit the release of TRH. This is called negative feedback.











.jpg)