Healing a fractured vertebra
cure

The healing of a vertebral fracture depends first of all on the severity of the vertebral fracture, the number of fractured vertebrae, the time until a suitable therapy, the type of therapy and the Pre-existing illness dependent on the patient.
First of all, of course, it is best to recognize the break as quickly as possible and initiate appropriate therapy.
The earlier the break is recognized, the better the chances of recovery.
It should be a complete one bony injury the vertebral fracture usually heals quickly.
On the other hand, complications can occur with simultaneous injury Ribbons and Band washers give.
It is also relevant which Nerve tract and spinal cord damage due to the vertebral fracture. Nerve tract injuries and spinal cord damage can be partially irreversible, especially if complete Paraplegia present.
For osteoporosis
In the further course after a vertebral fracture, prophylaxis against osteoporotic vertebral fractures is also important or whether one osteoporosis already exists.
The presence of osteoporosis is another factor that makes healing difficult.
Therefore, therapy should be started immediately Calcium and Vitamin D initiate in the presence of osteoporosis, on the one hand, not to hinder the healing process and to prevent further vertebral fractures.
A distinction must also be made with regard to the healing, whether it is stable or unstable Fractions acts.
In stable vertebral fractures, the leading edge of the vertebra is usually compressed, but the trailing edge is still intact, creating a stable structure. In addition, the spinal cord and nerve tracts are usually not constricted.
Stable vertebral fractures include fractures caused by osteoporosis, in which minor trauma causes the fractures.
In the long term, body weight in osteoporosis can cause a wedge-like Changes in the vertebrae occur, resulting in multiple vertebrae becoming one Hunchback or humpback leads.
This usually results in chronic pain.
In the case of unstable vertebral fractures, the rear edge of the vertebra is usually also injured. Here, vertebral fragments press on the spinal cord or surrounding structures.
Vertebral fractures due to accidents with a high level of damage mostly fall into this category Violence. Depending on the severity, this can result in paraplegia. However, paralysis that has already occurred is usually not reversible.
There are also other underlying diseases such as Tumor diseasesthat may play a role in healing.
Constitutional previous damage also affect the healing process, such as Scoliosis, Kyphosis, Transition vortex, Spondylolisthesis.
Appointment with a back specialist?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The spine is difficult to treat. On the one hand it is exposed to high mechanical loads, on the other hand it has great mobility.
The treatment of the spine (e.g. herniated disc, facet syndrome, foramen stenosis, etc.) therefore requires a lot of experience.
I focus on a wide variety of diseases of the spine.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Treatment methods
In addition, despite therapy, the spine can no longer be restored to its original shape and misalignments arise.
From this you can Incorrect loads result, which can lead to chronic pain or damage other surrounding vertebrae in the long term due to the disproportionate load.
Another aspect of vertebral fracture healing is the type of therapy.
In the conservative therapy patients usually visit one Back school.
They visit them in the first 2-4 weeks, after which they will be outpatient further treated.
Further healing also depends on the location of the vertebral fracture.
In the case of fractures between the thoracic and lumbar spine, there is usually further outpatient treatment through a corset for 6-8 weeks.
On the other hand, patients with fractures must at the Cervical spine another 6-12 weeks for healing Cervical brace wear.
With the surgical treatment methods, the healing process is a little different.
For minimally invasive interventions like the Vertebroplasty, Kyphoplasty and Endoscopy healing takes place the fastest and relieves the patient immediately.
Because after the operation, the spine can be directly stressed.
In addition, the patient only has to stay in the clinic for a few days, no special rehabilitation is required, and pain and blood loss are very low.
In the case of invasive surgical methods, however, a short-term one Bed rest for a few days and mostly wearing one Corsets necessary, plus a period of several weeks rehabilitation.
With invasive procedures, healing takes approx. 6-9 months. In addition, there is also whether the operation went without complications or whether additional structures were injured.
Another factor is the severity of the injury.
The classification of the degrees of severity plays a role here and the result Degrees of disability.
The following table gives a brief overview, the abbreviation GdB refers to the degree of disability. From the age of 20 one speaks of a degree of disability, which goes up to a maximum of 100. The higher the percentage, the more serious the impairment. From 50 GdB it is a severe disability.
From this one can conclude the most likely outcome of the healing process.
Severity: (GdB)
- Compression fractures with spinous process fractures (<10)
- Vertebral fracture with an axis deviation below (10-20)
- Vertebral fracture with an axis deviation of more than 15 degrees (20-30)
- Unstable movement segment after trauma together with radicular symptoms (30-50)
- incomplete paraplegia (30-100)
- complete paraplegia (100)
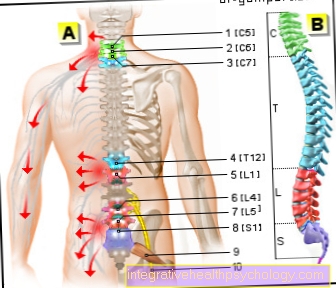
Figure vertebral fracture

Vertebral fracture (vertebral fracture)
- Transverse process -
Transverse process - Spinous process -
Spinous process - Upper articular process -
Superior articular process - Lower articular process -
Inferior articular process - Spinal nerve -
Spinal nerve - Spinal cord -
Medula spinalis - Gelatinous core - Nucleus pulposus
- Vertebral arch - Arcus vertebrae
- Fiber ring - Annulus fibrosus
- Vertebral bodies - Corpus vertebrae
- First thoracic vertebra -
Vertebra thoracica I - Twelfth thoracic vertebra -
Vertebra thoracica XII - First lumbar vertebra -
Vertebra lumbalis I - Fifth lumbar vertebra -
Vertebra lumbalis V
a - cervical spine (cervical spine)
b - thoracic spine (BWS)
c - lumbar spine (lumbar spine)
A - vertebral fracture (spinous process,
Vertebral bodies) from above
B - vertebral fracture (spinous process,
Vertebral body) from the right
C - Most common area of the
Vertebral fracture
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations

-buschmcke.jpg)