Ectopic pregnancy
Synonyms
Tubular pregnancy, tubal pregnancy, tubal pregnancy, graviditas tubaria
English: tubal pregnancy
definition
Ectopic pregnancy is the most common form of pregnancy outside the uterus, accounting for 98% (uterus). This form of pregnancy is abbreviated as EUG (Extrauterine pregnancy).

Usually there is a disorder in the patency of the fallopian tubes (Bonding) or the fallopian tube peristalsis is disturbed. This allows the egg to be in that Fallopian tubes implant before it reaches the uterus. Regardless of where the fertilized egg is located, it will implant itself as soon as it has reached a certain stage of development.
The egg can
- in the initial part of the fallopian tube (ampullary ectopic pregnancy)
- in the middle section of the fallopian tube (isthmic ectopic pregnancy) or
- in the part of the uterus of the fallopian tube (interstitial ectopic pregnancy) nest.
The risk of an ectopic pregnancy is around 1-2%. Patients with ectopic pregnancy usually lose their child and it is also more difficult for them to become pregnant in the future. After a previous ectopic pregnancy, the risk of a new ectopic pregnancy is increased by 15-20%.
Epidemiology
From 100 Pregnancies is about one outside of the uterus. Out of 100 pregnancies outside the uterus (extrauterine pregnancies) 99 are located in the fallopian tubes.
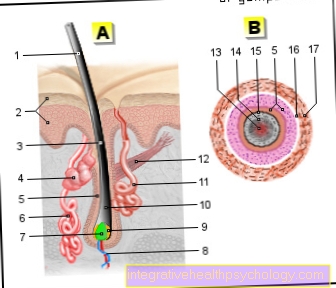
Figure fallopian tube

- Fallopian tubes -
Tuba uterina - Fallopian tubes -
Isthmus tubae uterinae - Large part of the fallopian tube -
Ampulla tubae uterinae - Folds of the fallopian tube lining -
Plicae tubariae - Fringed funnel of the fallopian tube -
Infundibulum tubae uterinae - Uterine cavity -
Cavitas uteri - Cervix - Ostium uteri
- Ovary - Ovary
- Uterine tip -
Fundus uteri - Mucous membrane -
Tunica mucosa tubae - Muscle wall
(inside ring layer) -
Tunica muscularis - Muscle wall
(outside longitudinal layer) -
Tunica muscularis - Peritoneum cover -
Tunica serosa - Vein of the muscle wall
- Artery of the muscle wall
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
causes
Below are some of the causes that can lead to an ectopic pregnancy:
- Disturbance of the absorption capacity of the enlargement (ampoule) of the fallopian tube
- Previously performed operations in the area of the fallopian tube with scarring as the tissue heals as a result can cause adhesions or kinks in the fallopian tubes.
- Inflammation or scarring that has arisen as a result of inflammation. This inflammation is triggered by genital infections, in which pathogens and bacteria get into the fallopian tubes.
- In addition, there is inflammation of the abdominal cavity (such as appendicitis), which can lead to adhesions and thus contribute to the impermeability of the fallopian tubes.
- Local damage to the fallopian tubes, for example from foci of atypically localized uterine lining (endometriosis)
- Contraception using an IUD (intra-uterine pessary). This cause depends on the type of IUD.
- Use of mini pills
- Artificial fertilization
- Incomplete sterilization treatment (tube sterilization)
- Hormonal fluctuations and illnesses can lead to an ectopic pregnancy. Hormonal fluctuations increase especially with age.
- Another cause can be tumors of the fallopian tubes, but also benign tumors such as myomas of the uterus. The fibroids press on the fallopian tubes from the outside and narrow them.
Read more on the topic: Diseases of the fallopian tubes
Symptoms and course

The clinical course is very variable and depends on the location of the ectopic pregnancy. Most of them Ectopic pregnancies but perish prematurely and thus remain clinically silent. Due to the lack of nutrients and insufficient supply of the newly developed organism from the fertilized egg cell (Embryoyo) through the fallopian tube mucosa, which is not intended for this purpose, in many cases a natural Termination of pregnancy in the fallopian tube (Tubal abortion). A natural termination can also take place later, in the advanced stage. The egg cell is resorbed (taken up) and broken down by the surrounding tissue.
Pain sensationsthat are uncharacteristic occur from around the 5th S.pregnantschaftswoche (SSW) after the last rule (post menstruation; p.m.). Often bleeding occurs because of the Plaster cake (placenta) goes down prematurely, causing a drop in hormone levels that normally prevent bleeding.
The growth of the fruit increasingly leads to space occupation and later to perforation (Penetrate) with severe, unilateral breakthrough pain (rupture pain) in the abdomen and bleeding into the abdominal cavity (intra-abdominal bleeding).
This situation is life-threatening for the mother. As a result it can lead to circulatory failure and shock come. The rupture often occurs between the 5th and 8th week of pregnancy.
The symptoms depend on the implantation site (Implantation site) of the egg cell. The ampullary Ectopic pregnancy usually leads to tubal abortion, whereas isthmian and interstitial Ectopic pregnancy rather the fallopian tube wall (Tube wall) penetrate and lead to the rupture.
- To the Fallopian tube abortion it usually occurs in an ectopic pregnancy ampoule the fallopian tube. The ectopic pregnancy usually gets into the cavity of the ampoule and so gets into the abdomen. About half is now absorbed. The other part creates complications in the abdomen. It is the most common course of an ectopic pregnancy. The symptoms of a fallopian tube abortion are similar to those of a fallopian tube inflammation, mostly there is pain in the lower abdomen.
- In the Fallopian tube rupture the ectopic pregnancy was previously in isthmus of the fallopian tube. The pregnancy continues to grow until the fallopian tubes rupture. This can lead to extremely heavy bleeding with life threatening! It is the second most common course of an ectopic pregnancy!
- Gestation: This course is by far the rarest!
Location of ectopic pregnancy:
Most often, an ectopic pregnancy occurs with 65% in the ampoule, followed by the isthmus with 25% and 10% in other locations.
diagnosis

When examining the Scabbard (vaginal exam) can be the size of the uterus (uterus) can be determined.
At a Ectopic pregnancy the uterus is smaller than it would be in a normal pregnancy.
During the examination it may also be possible to feel the painful area where the egg has lodged in the fallopian tube. With the help of a Ultrasound examinationStarting from the vagina, it can be determined whether the embryo is actually in the uterus or not. If this is not the case, it either indicates that the pregnancy is less advanced than initially thought and that the embryo is therefore too small for the ultrasound to detect.
Alternatively, it indicates a Miscarriage (Abortion). In this case, however, it can also indicate a pregnancy outside the uterus.
The pregnancy hormone can also be found in the blood hCG (Humanes C.horionGonadotropin) can be measured. The concentration of this hormone in the blood doubles every two days during a normal pregnancy. The concentration of the hCG does not display as normal and the patient also shows the corresponding symptoms, it can be assumed that this is a pregnancy outside the uterus.
therapy
If the ectopic pregnancy is discovered at an early stage, treatment with the chemotherapy drug is usually sufficient Methotrexate out. In cases of late discovery, surgery usually has to be carried out after all. Emergency operations have become very rare due to the good diagnosis.
Urgent bondings
Fallopian tube adhesions cause infertility in around 20% of women in Germany. Most of the fallopian tube adhesions are caused by inflammation. The upper open end of the fallopian tube, where the fimbriae ("fringes" of the fallopian tube) of the fallopian tubes are also located, often stuck together. These are usually ascending infections from the vaginal tract. Often there is also damage to the ciliated epithelium of the fallopian tube, even with inflammation. The inflammation may even form a pus-filled cavity here.
The inflammation is mostly caused by bacterial infections, adhesions can be caused by chlamydial bacteria, anaerobes, gram-negative bacteria, Neisseria gonorrhoeae (also called gonorrhea) and in very rare cases by tuberculosis. Often there is an ascending fallopian tube infection through the vagina. The intestinal bacteria of the enterococci and E. coli are most frequently responsible for the inflammation. But chlamydia is also involved in 40% of the cases. The infections are often without symptoms, only small bleeding suggests it. Only later do other typical symptoms such as pain and fever appear.
In patients with IUDs, the risk of ascending infections is further increased. In addition, the probability increases with frequent sexual intercourse.
Read more about the topics at: Fallopian tubes sticky and symptoms of fallopian tube inflammation