Adrenal hormones
introduction
The adrenal cortex has three layers, with each layer producing certain hormones. From the outside in you can find:
- Zona glomerulosa ("clumpy zone“) Manufacture of mineral corticoids
- Zona fasciculata ("bundled zone“) Manufacture of glucocorticoids
- Zona reticulosa ("reticulated zone“) Production of androgens
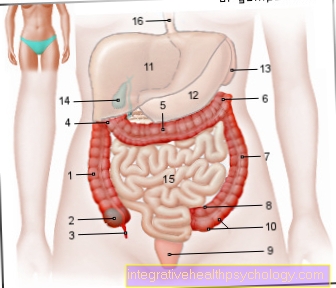
Figure adrenal gland

- Adrenal gland -
Suprarenal gland - Adrenal arteries -
Suprarenal artery - Adrenal vein -
Suprarenal vein - Fat capsule -
Capsula adiposa
(5th-7th adrenal cortex
C.ortex) - Ball zone -
Zona glomerulosa - Bundle zone - Zona fasciculata
- Grid zone - Zona reticularis
- Adrenal medulla - Medulla
- Central vein - Central vein
- Right kidney - Ren dexter
- Renal vein - Renal vein
- Renal artery - Renal artery
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
function
These hormones include Glucocorticoids, Mineral corticoids and Androgens. The former have a variety of effects. On the one hand, as a “stress hormone”, they influence the body's carbohydrate and protein metabolism by increasing blood sugar, breaking down body protein (catabolic function) and thus providing energy.
Second, these hormones have an impact on that Cardiovascular systembecause they have a vasoconstriction (Vasoconstriction) as well as strengthening the heart's strength.
Furthermore, glucocorticoids work against inflammation as well Allergies against (anti-inflammatory = anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic). To the Kidneys The hormones lower the urine output, on the lining of the Stomach they put their "protective layer" with the risk of the formation of Stomach ulcer (Gastric ulcer) down.
















.jpg)