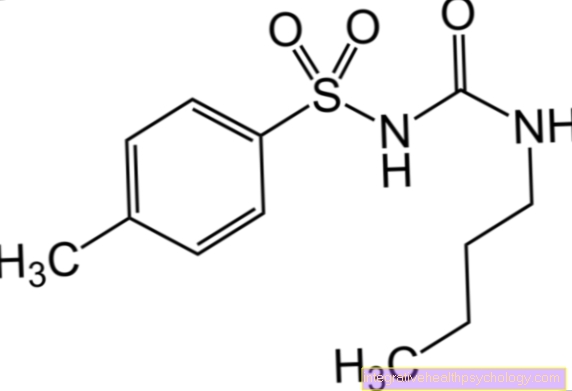
Potassium iodide
General
Potassium iodide is also known as potassium iodine or potassium iodatum and is mainly used to treat and prevent iodine deficiency. It is also used to prevent goiter due to iodine deficiency (enlarged thyroid).
Mode of action
Potassium iodide is an elementary trace element, but in higher doses it acts like a thyrostatic agent. The iodide is absorbed and stored by the thyroid gland so that it can then be used to make thyroid hormones.
If there is too little iodide in the body, the thyroid gland cannot produce a sufficient amount of thyroid hormones, so that the response is often an enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter).
An underactive thyroid due to iodine deficiency can be prevented by external intake of iodine (iodine-containing foods, iodized table salt, iodine in tablet form).
If the body produces too many thyroid hormones, one speaks of an overactive thyroid, a so-called hyperthyroidism. If potassium iodide is taken in very high doses of more than 5 milligrams per day, the release of thyroid hormones is prevented. However, this form of application is no longer in use today.
More information on this topic: Thyroid medication
Side effects
Side effects are very rare when taking potassium iodide, but hypersensitivity to the active ingredient is possible. This hypersensitivity may then manifest itself in fever, Burning eyes, skin rash, diarrhea and a headache.
application areas
Potassium iodide is mainly administered to treat or prevent iodine deficiency or an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) caused by iodine deficiency.
Potassium iodide is used in large concentrations to shrink an enlarged thyroid gland before surgery and to decrease blood flow to the thyroid gland.
In the past, potassium iodide was also used for therapy Overactive thyroid known, but this use of potassium iodide is now obsolete and other anti-thyroid drugs, such as thiamazole, are used instead.
Taking potassium iodide can prevent the absorption of radioactive iodine in the organism, so that it is often given as a preventative measure after an accident in a nuclear power plant.
Interactions
If therapy with anti-thyroid drugs is carried out at the same time as taking potassium iodide, their effect can be weakened.
Used simultaneously with potassium iodide the drug lithium ingested so it can become a Hypothyroidism or an organ enlargement.
If dehydrating agents are taken, there may be an increased potassium concentration in the blood, which can lead to serious circulatory complications.
Contraindications
Potassium iodide should not be used if you have any of the following conditions:
- Hyperthyroidism
- Thyroid tumor
- Iodine allergy
- Dermatitis herpetiformis Duhring
pregnancy and breast feeding period
The need for iodine is increased, especially during pregnancy and breastfeeding, and sufficient intake must be ensured. The recommended daily dose during this time is 200 micrograms, higher amounts should be avoided because of possible effects on the child.