Cartilage build-up
introduction
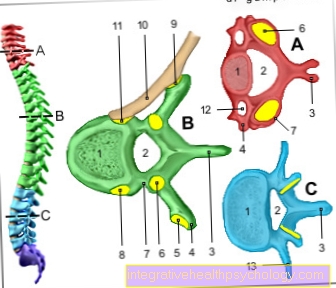
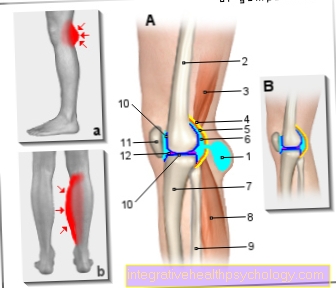
Cartilage is a firm but pressure-elastic tissue and consists of a connective tissue network of fibers. The so-called hyaline cartilage lines joint surfaces and ensures that the bones of the joint partners do not rub against each other.
If the joints wear out (osteoarthritis), the joint cartilage loses substance. With initial wear and tear, this leads to pain at the start of movement or after long or strenuous movement. Later there is also pain at rest.
In order to delay a surgical joint replacement, there are approaches to rebuild the lost cartilage and thus reduce the symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Find out more general information on the topic: cartilage

Can you rebuild cartilage?
Rebuilding lost cartilage is difficult. Especially when a lot of cartilage is already worn out, the cartilage structure is difficult or often impossible.
However, in order to prevent further cartilage degradation and to activate a possible cartilage build-up, especially if the cartilage damage is not yet too extensive, there are different approaches: These include, in particular, nutritional and exercise therapy.
In terms of diet, for example, various foods that minimize cartilage breakdown, such as potatoes or rice, should be consumed more and foods that accelerate cartilage breakdown, such as eggs, dairy products or alcohol, should be avoided.
Since the cartilage tissue is not supplied with blood directly, it is important to stimulate the fluid exchange and metabolism in the cartilage through movement so that defective cartilage can regenerate. In order to positively influence the cartilage structure through movement, joint-friendly sports such as swimming, rowing or cycling should be chosen.
Cartilage protection and regeneration products such as glucosamine, which is supposed to stimulate the formation of new cartilage, can also be taken.
The injection of hyaluronic acid or polynucleotide gel, which activates the cartilage cells, is said to minimize the discomfort of cartilage breakdown.
Another approach, particularly helpful for young osteoarthritis patients in whom the cartilage has not yet been severely damaged, benefits from new research in which the body's own stem cells are injected into the damaged joint, which can then be converted into cartilage cells.
Another possibility is the transplantation of the body's own cartilage (autologous chondrocyte transplantation). Intact cartilage is removed from the knee, for example, grown in the laboratory and then reinserted on the defective area. However, this method was only successful with minor cartilage damage.
Also read: Osteoarthritis therapy
ACT
In ACT, i.e. the autologous chondrocyte transplantation or autologous cartilage cell transplantation, cartilage cells (chondrocytes) are removed from the joint. During the removal, a point in the joint is chosen that is not heavily stressed when moving. The removed cells are then grown in the laboratory.
The cartilage that has grown is then reinserted onto the defective area in the joint. The success of this procedure depends on various factors. On the one hand, the size of the defect is decisive.
The smaller the defect, the greater the chance that the cartilage defect can be repaired. On the other hand, this method works particularly well with younger patients. In addition, the healing success depends on the location of the cartilage damage.
Furthermore, the success of the treatment depends on adherence to the postoperative follow-up care with gradually increasing stress and physiotherapy exercises. This means that too early and too much stress on the joint should be avoided so that the inserted cartilage can grow in.
Read more about this: Cartilage transplant
Can you build cartilage with hyaluronic acid?
Hyaluronic acid is injected directly into the joint when the cartilage is damaged. When it is in the joint, it does not have the effect of building up cartilage, but is intended to improve the gliding ability of the joint partners as a so-called lubricant and protect the defective areas of the cartilage. This can alleviate discomfort.
A direct cartilage build-up is therefore not possible.
The effectiveness of the treatment with hyaluronic acid injections is controversial. It is said that there is a fifty-fifty chance of treatment success. The success should be particularly great if the osteoarthritis is not yet very advanced, i.e. the cartilage defects are not yet great.
The beginning of symptom relief also varies greatly between those affected. Some patients feel pain relief after the first or second injection, others only after the fifth. In addition, the hyaluronic acid injections are a so-called IGeL service, so they are not paid for by health insurance companies. Whether treatment for osteoarthritis makes sense should therefore be discussed individually with the attending physician.
More on this: Chondroprotectives
What are the benefits of supplements?
Supplements (food supplements) such as chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine are said to be another way of promoting cartilage build-up.
Chondroitin sulfate is naturally formed by cartilage cells and makes the cartilage more resistant.
Glucosamine, on the other hand, is a part of cartilage tissue. If these are taken as food supplements, they should work on the joint where they are needed.
However, studies have shown that taking these supplements has no effect. The symptoms did not improve, nor could any cartilage build-up be detected in X-rays. Therefore, taking supplements should be viewed critically.
What are the benefits of vitamin E?
The breakdown of cartilage is often caused by inflammation in the joints. During an inflammation process, so-called free radicals are formed, which damage the cartilage. In addition to vitamin C, vitamin E traps these radicals. In order to reduce a deficiency and thus further cartilage damage due to a higher consumption of this vitamin, vitamin E can be taken daily.
More on this topic: Vitamin E.
What does Devil's Claw bring?
Devil's claw (Harpagophytum procumbens) is a medicinal plant that has anti-inflammatory effects. It cannot therefore promote the development of cartilage. The effect on cartilage damage is particularly to dampen the inflammation in the joint and thus prevent further cartilage degradation.
In addition, due to the anti-inflammatory effect, the pain in the joint can be reduced.
Read this article: Devil's claw
Can diet have a positive effect on the structure of cartilage?
A balanced and healthy diet is generally important to keep the body healthy and prevent diseases. Various foods can help to positively influence the structure of cartilage:
These include foods that contain vitamins A, C, and D. Lysine-containing foods such as legumes or red meat can also promote the development of cartilage. Omega-3 fatty acids, which are found in tuna, seafood, but also in Swiss chard, chia seeds or pumpkin seeds and have an anti-inflammatory effect and thus protect the cartilage from degradation, are also considered suitable foods against cartilage degradation.
In addition, harmful substances such as alcohol and nicotine should be avoided.
What does gelatin do?
Gelatin contains the protein collagen. Collagen is not only an important component of cartilage tissue, it is also contained in tendons and bones. 10 grams of gelatine a day is said to promote the regeneration of the cartilage. The gelatin should not be consumed in desserts, however, as sugar can damage the cartilage and prevent the positive effects of gelatin on the cartilage.
homeopathy
Homeopathic remedies can help build cartilage. Potencies D6 or D12 are suitable here, which should be taken three times a day so that an effect can be achieved. African devil's claw is said to promote the development of cartilage. Arnica, rosemary or juniper can also have a positive influence on the structure of cartilage and reduce the breakdown of cartilage.