Wheat allergy
introduction
A wheat allergy is an allergic reaction of the body to foods that contain wheat. When wheat products are ingested, an immune reaction occurs in the body in which antibodies (in this case IgE (Immunoglobin E.)) which react to protein components of wheat. This affects different parts of the body. These include, for example, rashes on the skin, itching and swelling, shortness of breath or nausea, vomiting and flatulence.
The allergy mainly occurs in childhood.

Symptoms
A wheat allergy can manifest itself in various symptoms. In general, there is an allergic reaction in the body, which can manifest itself differently in different parts of the body.
If the skin is affected, rashes that can vary in size occur, for example. These are often associated with itching and hives, and local swelling can also occur. These symptoms can also affect the mucous membranes. Those affected often feel a tingling sensation in the mouth that can last for up to several hours. If it develops in the digestive tract, nausea and vomiting can occur. Bowel habits are often affected and diarrhea, constipation, and flatulence occur. Many sufferers experience abdominal cramps, especially a few hours after consuming wheat products. In some cases, symptoms can also originate in the lungs and you may experience difficulty breathing. In such a situation it is important to keep calm, breathing exercises can have a supportive effect.
If there is already another form of allergy or, for example, neurodermatitis, the corresponding symptoms of a wheat allergy can be aggravated by the consumption of wheat products.
constipation
Wheat allergies can cause various symptoms in the digestive tract. Their expression a few hours after the consumption of wheat products is characteristic. The allergic irritation leads to digestive disorders and changes in bowel movements. There are often alternating phases of diarrhea and constipation. The latter manifests itself in less frequent bowel movements and a particularly hard stool consistency. This means that you have to press hard when defecating and those affected often have the feeling that they are not completely emptied after using the toilet.
You may also be interested in this topic: Home remedies for constipation
Joint pain
A wheat allergy has a wide variety of symptoms. The substances contained in foods containing wheat activate certain cells of the immune system in those affected, which causes the body to react in different ways. This can include joint pain, which can occur in any joint and is often associated with headaches. These are often intensified with additional physical activity and may last for several hours.
skin rash
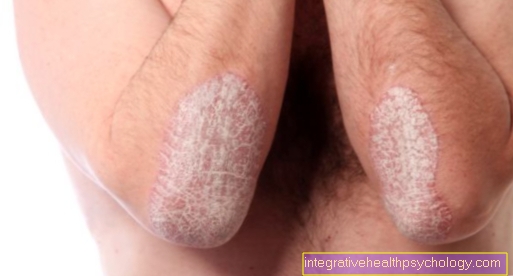
The skin is a frequently affected organ in a wheat allergy. Rashes can occur as a result of the consumption of products containing wheat. This is characterized by severe itching and particularly dry skin. The rashes can appear all over the body, with characteristic spots depending on age, and they are often accompanied by local swelling.
The severity and appearance of the rashes are very variable. Red blisters often form, which can vary in size and are often very itchy. If thickened nodules appear, which are sharply delimited and are noticeably itchy, this is also referred to as prurigo. In adults, these rashes are often found on the flexors of the arms and legs. It can also lead to crust formation and hives. The latter is also very itchy and the rashes are rather flat, pronounced reddish raised areas on the skin.
therapy
Since the symptoms of a wheat allergy arise when consuming products containing wheat, the therapy consists in avoiding all foods that contain wheat. There are no tablets that can be taken in addition to eating foods containing wheat.
It is therefore important to adhere to a wheat-free diet. It must be noted that gluten-free foods can also contain wheat proteins. It is best to make a list of the types of grain that contain wheat proteins and then pay attention to this in your diet, especially if you eat out. Grains containing wheat include wheat germ, wheat germ oil, wheat flour and wheat flakes, as well as couscous, starch, malt, bulgur and whole grain bran. Instead, barley, oats, millet, quinoa, potato flour and rice flour are allowed.
Anaphylactic shock can rarely occur. In such a case, those affected should always be equipped with some emergency medication, such as cortisone.
Read more about this at: Food allergy therapy
causes
The exact causes of the development of a wheat allergy are not yet finally understood. Genetic components have already been demonstrated in many studies. This means that this form of allergy can, but does not have to be, hereditary. In addition, this form of allergy also occurs more frequently in children whose parents suffer from one or more forms of allergy.
The components to which the body reacts in wheat products are primarily proteins. These include wheat albumin, gluten, and globulin. This leads to an immune reaction in the body, which causes more antibodies to be formed. These now attack said components when they are absorbed into the circulation via the intestinal cells and thus lead to various symptoms. These include rashes on the skin, often with itching and swelling. Flatulence occurs in the intestine itself, and nausea and vomiting can also occur. Constipation and diarrhea are also common.
You may also be interested in this topic: Gluten allergy
diagnosis
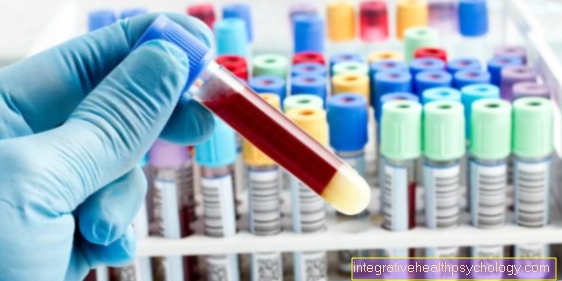
In order to secure the diagnosis of a wheat allergy, the anamnesis, i.e. the doctor-patient discussion, is in the foreground. With the help of a food diary, with good guidance, a connection between certain foods and the symptoms that arise can be recognized. Furthermore, if an allergy is suspected, but there is uncertainty about the corresponding allergen, i.e. the allergy-triggering substance, a skin test can be carried out. In order to secure a targeted suspicion, however, the focus is on blood tests and provocation tests, in which the allergen is given after an allergen-free phase.
More on this: Allergy diagnostics
Tests for a wheat allergy
Various tests can be used to diagnose a wheat allergy. If there is only suspicion of an allergy without knowing the exact allergy-triggering substance, i.e. the allergen, a skin test is carried out. This tests the body's susceptibility to allergies to various substances. If the suspicion is specifically directed towards an allergen, this can be given in a provocation test after a certain allergen-free time and the body's reaction measured. Furthermore, antibodies against the said allergen can be measured in a targeted manner in a blood test.
forecast
If a wheat allergy is diagnosed, it must be expected that it will last for a lifetime, as the cells of the immune system that react to the allergen (i.e. the allergy-causing substance) wheat are permanently in the body. With a corresponding change in diet, however, a relatively symptom-free normal life can be led. It is important to act quickly with the symptoms, especially if there is shortness of breath.
Can I drink beer if I have a wheat allergy?
If there is a wheat allergy, the body reacts to all products that contain certain wheat proteins. In addition to wheat itself, this also includes malt. This is why most people with a wheat allergy cannot tolerate normally brewed beer.
However, there is now gluten-free beer, for example. Instead of the usual ingredients such as barley or wheat, this is made with other types of grain such as buckwheat, millet, soy or rice. Therefore, gluten-free beer is an alternative option for people allergic to wheat. However, it must be noted that many people suffering from wheat allergies also react to gluten-free products with allergic symptoms. Therefore, the gluten-free beer should only be tried in a very small amount and with great caution.
also read: Flatulence after beer
Which cross allergies are there?
With a wheat allergy, as with most other allergies, there can be a wide variety of cross-allergies. These include above all allergies to other types of grain, such as barley or oats, but also rye. Therefore, these foods should also be avoided or at least eaten with great caution. In some cases there are also cross-allergies to pollen allergies, such as an allergy to grass (e.g. ryegrass). Rare cases also report a cross allergy to kiwi fruit.
Read more about this at: Cross allergy