Food poisoning
Synonyms
Food intoxication, food poisoning, food intoxication
English: food intoxication, food poisoning
Also read:
- Symptoms of food poisoning
- Duration of food poisoning
- Nickel allergy
definition
The term Food poisoning denotes a Gastrointestinal diseasegoing through with the food / nutrition ingested toxins. These toxins are toxins that are produced by bacteria, Mushrooms, Plants, metals or their compounds or marine animals.
Epidemiology / frequency distribution
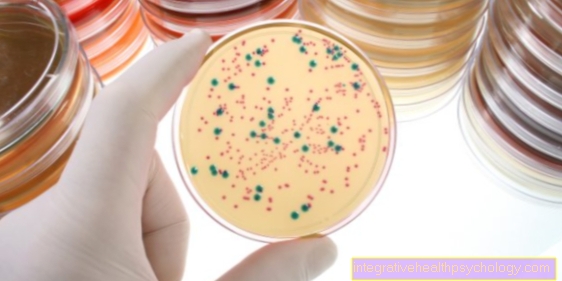
Food poisoning by bacteria how Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus and Clostridium perfringens (Enterotoxin generator) are relatively common, but have an even higher number of unreported cases.
From food poisoning Clostridium botulinum now only get sick in Germany thanks to appropriate food hygiene 10 to 30 People per year.
In general, it is difficult to collect figures on the frequency of food poisoning because, on the one hand, many cases are not reported and, on the other hand, there are already suspicions Intoxication / Food poisoning is reported.
causes

Food poisoning results from ingestion of toxins (Toxins). These can have the following origins:
- bacteria
- Mushrooms
- plants
- Metals/ Metal connections
- fish/ Shellfish
To the toxin-producing bacteria count for example Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Clostridium perfringens such as Clostridium botulinum. Their poisons are often contained in milk or egg products, meat, fish or mayonnaise (potato salad).
Examples of food poisoning are fungal toxins Amatoxin (including green cap mushroom), muscarin (fly agaric) or orellanin (including orange-foxed rocket). Toxins contained in plants include atropine, scopolamine or solanine, for example from nightshade plants. Food poisoning metals include arsenic and lead.
Tetrodotoxin of the puffer fish (among others), saxitoxin of some mussels and ciguatoxin of certain unicellular organisms (Dinoflagellates) belong to poisons of marine animals, which can cause food poisoning.
diagnosis
The doctor makes the diagnosis of food poisoning primarily on the basis of the anamnesis and the clinical picture. Anamnestic on one Food poisoning It is indicative if several people complain of the same complaints who have eaten together within the last 16 hours.
Proof of the relevant Toxins succeed in the ingested food. At botulism In addition, vomit, stool, serum and gastric juice can be examined for the existence of the toxin in order to diagnose food poisoning.
therapy

Food poisoning is treated by replacing water and electrolytes. With some bacterial pathogens you can Antibiotics administered. The administration of antidotes against certain toxins is also a therapeutic option, for example the administration of Chelating agents with lead poisoning.
Treatment for botulism includes gastrointestinal evacuation to remove the toxin from the intestines. In addition, an antitoxin is given in order to bind the free botulinum toxin and render it harmless.
If respiratory paralysis has already occurred, the patient is also ventilated.
Reporting requirement
All in all have to all cases of poisoning are reported to the Federal Institute for Risk Assessment.
In addition, according to the Infection Protection Act, the bacterially caused Food poisoning Notifiable for persons working in the food sector. Even in the event of an epidemic, i.e. at least 2 sick people, the treating doctor must report to the health department.
The reporting requirement at botulism includes suspicion, illness, and death in all patients.
prophylaxis

To trigger a Food poisoning should prevent food hygiene (Expiration dates, adequate heating, cooling) be respected. In addition, food should be freshly prepared and consumed immediately afterwards without long waiting times. The content of bombed canned food (Domed lid) should not be consumed as this Botulinum toxin may contain.
Summary
Food poisoning occurs as a result of the ingestion of certain toxins (Toxins) with food and can have various causes (Bacteria, fungi, plants, metals, marine animals). The poisoning picture includes besides gastrointestinal Complaints (Complaints in the gastrointestinal tract) like nausea, Vomit, diarrhea and stomach pain symptoms characteristic of each toxin.
Food poisoning is diagnosed on the basis of the anamnesis and the clinical picture; The main aim of the therapy is to compensate for the poisoning water- and Electrolyte loss from. In addition, in some cases an antidote (Antidote) or further measures depending on the toxin are initiated.