The conjunctival cyst
What is a conjunctival cyst?
By definition, a cyst is a benign swelling (= tumor) that is filled with fluid. The conjunctival cyst is a cyst that occurs on the conjunctiva of the eye.
The conjunctival cyst arises from the same tissue that the conjunctiva itself is made of. This is what is known as the conjunctival epithelium. From this cell material, a transparent and clear cavity is formed in the conjunctiva, which is filled with fluid.

The reasons
A conjunctival cyst usually develops after an injury to the conjunctiva. This can result from an operation on the eye and primarily affects older people, who are comparatively more frequently operated on the eye than younger people. Injury from a foreign body, such as splinters in an accident, can also be the cause of a conjunctival cyst.
After injuring the conjunctiva, the body begins to form new cell material in the affected area. So new conjunctival cells are created. However, this can lead to malformations, so that the conjunctiva is built up differently than before. This can result in scars and conjunctival cysts on the conjunctiva. Instead of a simple conjunctival layer, the body forms several layers between which a cavity is created. Since the conjunctiva is involved in the formation of tear fluid, fluid can quickly become trapped in this cavity, creating a cyst.
By definition, conjunctival cysts are always benign - so they do not pose a risk of degeneration. As a rule, a conjunctival cyst does not change after its formation, so it does not continue to grow.
Also read the article: The injuries to the eyes.
The symptoms
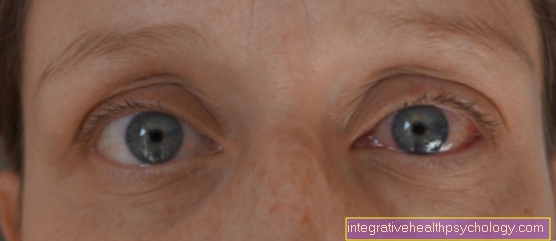
In most cases, a conjunctival cyst is noticed by a foreign body sensation in the eye. The conjunctival tcyst is caused by an injury to the conjunctiva. This area does not heal properly and swells due to the buildup of fluid. This accumulation of fluid is seen as foreign and leads to these symptoms.
The foreign body sensation can be particularly noticeable when moving the eyes. Even when you close your eyes, the eyelid can feel the swelling on the eye and give the body the feedback that something strange is on the eye.
Further symptoms of a conjunctival cyst usually only arise if the cyst is in an unfavorable location. For example, a cyst located on the edge of the eye can be moved under the lid when the eye is moved. This can lead to an increased feeling of foreign objects. In rare cases, the cyst can also cause restricted mobility. If the cyst is immediately in front of the pupil, visual disturbances can be triggered. As a rule, the conjunctival cyst is a clear structure, so that light rays can also fall through the cyst into the eye. However, the conjunctival cyst changes the superficial structure of the eye, which means that the incoming light rays are refracted differently. There is a distorted perception of the light and thus blurred vision.
The diagnosis
The diagnosis of a conjunctival cyst can be made through what is known as a visual diagnosis. When examining the eye, the ophthalmologist can easily see the swelling on the conjunctiva from the outside. Due to its clear structure, this examination is often sufficient to make the diagnosis of a conjunctival cyst.
However, if further clarification is necessary, the cyst can be punctured, i.e. pierced. The liquid material obtained can then be examined more closely. If it is tear fluid, it can be assumed to be a conjunctival cyst. If there are still doubts about the diagnosis, the tissue forming the cyst can also be examined if necessary. A microscopic examination of the cells reveals a conjunctival structure.
The treatment
Since the conjunctival cyst is a benign mass, no therapy is usually necessary. Treatment of the conjunctival cyst only takes place if the cyst is very troublesome. A frequent reason for the treatment is a strong feeling of a foreign body. Restrictions in movement of the eye, which subsequently lead to restrictions in the field of vision, can also be an indication for therapy. Usually, the cyst is only treated if it is in the path of the incident light. This is the case when the cyst is just in front of the pupil.
The therapy of the conjunctival cyst consists initially of a puncture. The cyst is punctured so that the fluid can drain off. The individual wall layers of the different types of conjunctiva are preserved, as they often come together and form an inconspicuous conjunctiva. If the cyst develops again as a result, further intervention may be necessary. The new cyst can be removed with the help of a laser or a minimally invasive procedure, for example. However, operative procedures can also be used. Furthermore, the excess connective tissue material can be removed with cold. In particular, if the conjunctival cyst is in front of the pupil, a gentle procedure must be chosen so that there is no other damage in the area of vision.
Lasers as a therapy option
In ophthalmology, the laser principle is used for various diseases. Different sections of the eye can be reached using laser methods. In the case of the conjunctival cyst, the laser must treat the anterior segment of the eye.
Nowadays, lasers can be set to their target with micrometer precision, so that they treat areas of the eye previously determined on the computer and the rest of the organ is spared. Excess conjunctival material is removed from the cyst by means of the laser beams, so that a smooth conjunctival layer is then again on the surface. The fluid can be emptied from the conjunctival cyst in advance by means of a puncture; occasionally the fluid is only emptied from the cyst during the laser.
This article might also interest you: Laser eyes.
The duration
The conjunctival cyst can - depending on how annoying it is in the eye of the person concerned - remain there for different lengths of time. If there is no relevant impairment of vision or eye movement, the cyst can be left as it is. Sometimes it regresses on its own, occasionally it stays there for life.
If the cyst is perceived as bothersome, the first thing to do is puncture and drain the cyst. The structure can then completely recede. Often, however, it will recur after a few weeks. In such cases, permanent removal can usually be achieved by surgical or laser procedures.
When do you need an operation?
An operation on the conjunctival cyst is usually sought if the cyst is in an unfavorable place on the eye. This is usually the case if it prevents eye movements or is in the area of the pupil and thus leads to impaired vision.
If an initial therapy by draining the fluid is unsuccessful, surgical procedures can be used. The cyst or the excess conjunctival tissue can be removed by laser, cold or with the smallest of instruments.