Liver fibrosis
definition
A fibrosis is generally understood to mean one increasing connective tissue content in a particular organ. In the case of the liver, the healthy, functional liver tissue becomes diverse in sequence Pre-existing illness by collagen connective tissue replaced. This process is usually irreversible, which means that liver tissue that has been lost can result in fibrosis not regenerated again become.
In the case of high-grade liver fibrosis, one also speaks of one Cirrhosis of the liver.
classification
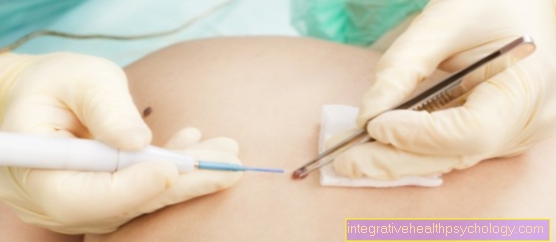
In order to be able to determine the degree of liver fibrosis, a biopsy be made. This is done under Local anesthesia a thin needle is inserted into the liver and removed a tissue punch.
This is then treated pathologically and examined.
Depending on the extent of the fibrosis, the disease turns into different Stages assigned. A common method is Classification according to Desmet. Here will be 5 levels differentiated from F0 to F4. F0 means that no connective tissue fiber has increased. At F4 one speaks of a far advanced liver fibrosis or even of cirrhosis. The higher the score, the worse the prognosis of the patient.
root cause

Liver fibrosis is not an independent clinical picture. It is more a symptom that is caused by various previous illnesses. The most common causes of liver fibrosis are to be considered in more detail below.
Liver fibrosis is most common in developed countries as a result of excessive alcohol consumption. Alcohol is broken down in the liver and then excreted in another form in the urine. If the liver is permanently exposed to drinking alcohol, the phenomenon of fatty liver occurs due to biochemical processes.
In general, one speaks of fatty liver if more than 50% of the liver cells have fat deposits in the histological section. In the early stages, fatty liver can still be reversible, for example through an adapted diet for fatty liver. In the late stage, cells that produce connective tissue increase (Fibroblasts), which ultimately cause liver fibrosis. This process is then irreversible.
In addition to alcohol, high doses of medication can also lead to fatty liver disease. An example would be excessive consumption of steroid hormones.Fatty liver can also be caused by metabolic diseases (e.g. diabetes mellitus) or severe obesity (Obesity) be conditional.
After fatty liver, viral hepatitis is the second most common cause of liver fibrosis in industrialized countries and the most common in developing countries. Most of this comes from the viruses that cause chronic hepatitis. These include forms B and C. Hepatitis means that the liver tissue is inflamed, i.e. an immune reaction takes place in the organ. This is harmful to healthy tissue, but it is a measure taken by our body to protect itself from unwanted intruders.
With chronic hepatitis, i.e. liver inflammation that lasts longer than 6 months, the tissue is exposed to enormous stress over a long period of time. In response, the normal liver cells are replaced by fibroblasts, which form connective tissue and thus lead to liver fibrosis. With long-term inflammation and fibrosis, viral hepatitis can also lead to cirrhosis of the liver.
Another cause of liver fibrosis is so-called congestive hepatitis. With her, blood congestion in the vessels of the liver leads to an inflammatory reaction. Right heart failure can be the cause of such blood congestion. This means that the right heart is no longer able to properly pump normal amounts of blood. The blood thus backs up in upstream organs, such as the liver, and leads to damage. The congestion means stress for the liver cells and inflammation, i.e. inflammation, occurs. As described for viral hepatitis, this means an increased formation of fibroblasts which ultimately lead to liver fibrosis.
Learn more at: Congested liver
Not only blood congestion, but also an obstruction to the drainage of the bile can trigger liver fibrosis. This clinical picture is generally referred to as a so-called cholestasis. Cholestasis can be caused by gallstones or inflammation. A prominent example of this would be primary sclerosing cholangitis. This clinical picture also means stress for liver cells, which respond with fibrosis.
The so-called autoimmune hepatitis is often congenital. The body itself produces antibodies against liver cells. As a result of an immune reaction, the liver becomes inflamed, which often takes a chronic course. Autoimmune hepatitis is in many cases associated with other autoimmune diseases, but it can also occur alone.
These were just a selection of the diseases that cause liver fibrosis. In general, it can be said that fibrosis is always a response to stress for the liver cells, be it from a toxin such as alcohol, or from hepatitis, as is the case with a hepatitis virus infection.
Symptoms
Basically it can be said that there are no symptoms that are characteristic of liver fibrosis. Often it is asymptomatic because the liver fibrosis is not far advanced. Symptoms that suggest a liver disease only appear after cirrhosis.
The initial, atypical symptoms of liver disease include fatigue and tiredness, loss of appetite and weight loss, indigestion and intolerance to alcohol, coagulation disorders, for example in the form of frequent bleeding gums, etc.
In the case of the symptoms mentioned so far, the doctor does not directly think of liver fibrosis. This is because they are very non-specific and can speak for a ton of other diseases as well. Only in the advanced stages of fatty liver or liver fibrosis do symptoms become clearer.
Probably the most striking feature of liver disease is jaundice (Jaundice). The skin and eyes of patients with jaundice become yellow in color. This occurs because a breakdown product of the red blood pigment hemoglobin, bilirubin, can no longer be properly excreted. The bilirubin thus accumulates in the blood and turns the skin yellow. At the same time, the patient's stool becomes lighter or even whitish, as the brown pigment bilirubin does not leave the body with the feces. In healthy patients, bilirubin is responsible for the brown color of the stool.
In a few patients, advanced liver fibrosis manifests itself as itching all over the body. This symptom is also called pruritus. The exact cause of the pruritus is not clear. It is just as unclear why it does not occur in some cirrhosis of the liver, but it does occur in low-grade liver fibrosis.
In the advanced stage of liver fibrosis or liver cirrhosis, characteristic skin markings can be observed in patients. The vessel drawings include so-called spider naevi, the caput medusae and sometimes also petechiae. In addition, male patients can develop gynecomastia and baldness.
diagnosis
Ultrasound is the means of choice for diagnosis. It offers a non-invasive and painless method of examining liver status. Unfortunately, the fibrosis of the liver is often recognized late, as symptoms usually appear late that prompt the patient to see a doctor.
Read more on the topic: Ultrasound of the abdomen
Another diagnostic method is blood analysis. Elevated liver enzymes and IV collagen can be an indication of liver fibrosis. However, the blood test only makes sense at a more advanced stage. The definitive diagnosis of liver fibrosis is usually made today through a puncture. Liver tissue is removed and examined under a microscope. With a special dye for connective tissue fibers, the degree of fibrosis can be determined.
You can find more information about this on our website Liver function tests, bilirubin
A somewhat newer method is the so-called Fibroscan. A transducer emits certain waves that interact with the connective tissue of the liver. This can now be measured in order to determine whether the liver is fibrous.
If in doubt, an MRI of the liver can be used to obtain further information.
You can find out more under our topic: MRI of the liver
therapy
The process of fibrosing the liver is irreversible and therefore not directly treatable. Once the liver tissue is penetrated by connective tissue, its full function can no longer be achieved for a lifetime. That is why it is especially important the diseases to be recognized earlyin order to be able to intervene early. The focus of the therapy is on Treatment of the causative disease. As is well known, liver fibrosis can be preceded by numerous diseases that must be treated differently. It is therefore up to the doctor to diagnose and treat the problem quickly in order to prevent fibrosis of the liver.
In the case of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis, patients are usually only treated symptomatically. For example, a Transfer of the bile ducts to a papillotomy cause an improvement. A Diet change and sufficient Move are a must to keep the body fit. In selected cases, a transplant can be performed for therapy.