Chondrocalcinosis
introduction

Chondrocalcinosis (gr. chondro- = cartilage, lat. calcinose = calcification) is a degenerative disease of cartilage, ligaments and tendons, which is particularly noticeable with discomfort in joints. As the term chondrocalcinosis describes, it is a calcification caused by calcium crystal deposits, especially in the cartilage of joints.
This results in symptoms similar to those of gout, which is why chondrocalcinosis is also called pseudogout. However, there is another mechanism behind this disease, one should not confuse the two diseases.
Most often the knee, hip, and hands are affected, with the knee showing symptoms most often. Usually, however, chondrocalcinosis runs without symptoms.
causes
The causes of chondrocalcinosis are not yet fully understood. It is known that certain calcium crystals are deposited in the cartilage or ligaments and tendons, which are calcium pyrophosphate crystals. Here again the difference to gout can be seen, where urate crystal deposits are the cause of the symptoms.
The calcium pyrophosphate is deposited in the cartilage substance and leads to structural changes there. The cartilage is no longer so elastic, it degrades over time, and inflammatory reactions occur in the joint. Only then do you notice symptoms.
However, the exact causes why the deposits occur is unknown. In chondrocalcinosis, one differentiates between a primary and a secondary form. Primary chondrocalcinosis occurs for no apparent cause and usually affects the elderly. It is insidious but chronic. Hereditary causes are also discussed.
In contrast, the causes of secondary chondrocalcinosis are to be found in other diseases that favor the development of calcification.
Be like that
- an overactive parathyroid gland
- an underactive thyroid
- as well as disorders in iron, magnesium or phosphate metabolism
Associated with the occurrence of chondrocalcinosis and discussed as causes. Genuine gout also increases the risk; deformities or previous inflammations of the joints are also associated with chondrocalcinosis.
Symptoms
Chondrocalcinosis usually runs quietwithout symptoms appearing. If these come up anyway, they are Symptoms typical and are used in a similar manner at the gout observed. This is by far the most commonly affected knee, followed by Finger joints and hip.
But also shoulder, Elbow or Spine can be affected by chondrocalcinosis. In rare cases, not only are joints, but also Tapes, Tendons or Band washers affected by a crystal deposit.
There are several patterns of symptoms. In the acute form, the Pseudogout attack, it comes to a rapidly evolving inflammation of a joint, usually in the knee. You notice one swelling and Redness above that joint, there is pain. These symptoms occur in peace on and worsen with movement, however, are overall less distressing than gout.
Symptoms appear quickly and regress after a few days.
In contrast, the chronic intermittent form to longer flare-ups that can last for weeks, but do not show as severe symptoms. In chronic chondrocalcinosis it comes to degenerative destruction of cartilage and structures involved, the picture resembles that of an active one arthrosis.
Affected joints hurt and are swollen, which comes in severe cases fever with added. The rarest form of chondrocalcinosis is characterized by involvement outside the joints and corresponding symptoms, e.g. the Achilles tendon or Band washers affected.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
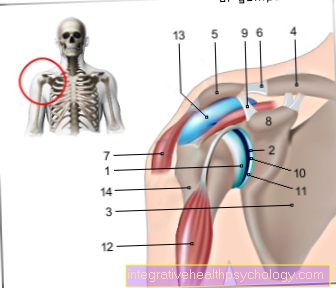
Chondrocalcinosis of the knee
In most cases, chondrocalcinosis shows up on the knee first. In the primary form, the knee is also affected in 99% of cases, and in the secondary forms it occurs in min. 90% of cases result in knee complaints. In half of the cases, the knee is the first structure affected. It shows the typical symptoms.
Pain at rest that worsens with movement results in limited mobility in the knee. In addition, there is usually swelling and redness, which is also reflected in overheating of the skin. These are signs of the inflammatory processes taking place in the knee. The picture of chondrocalcinosis on the knee then resembles a gout attack, which however usually begins on the big toe, or osteoarthritis. Further joints can be affected as the disease progresses.
Diagnosis

Three main methods are used in the diagnosis of chondrocalcinosis. On the one hand, the deposits can be visible in the X-ray; on the other hand, it makes sense to examine blood samples in the laboratory and include them in the diagnosis. In addition to x-rays and a laboratory, a joint puncture is sometimes necessary as part of the diagnosis in order to remove synovial fluid and examine it microscopically. However, this is mainly used in cases of doubt, when the diagnosis based on x-rays and the laboratory was not sufficient.
It is also important not to be too sure of having to treat gout when the symptoms start. This requires a different therapy. In contrast to chondrocalcinosis, gout does not start on the knee, but usually on the big toe. Gout also has other causes. In gout, uric acid crystals, not calcium pyrophosphate, are responsible for the symptoms.
roentgen
The X-ray is one of the main investigations in the diagnosis of chondrocalcinosis. Even if the suspicion of this disease is not obvious, if the symptoms persist, usually an X-ray is requested to diagnose the painful joints. The deposits of the crystals in the cartilage become visible here, as these are radiopaque structures that clearly stand out next to the cartilage.
In the X-ray you can see the Joint space from knee, hip or shoulder fine, strip-like structures, mostly parallel to the bone run away. Depending on the stage of the disease, the X-ray image shows more or less pronounced lines. The deposits can almost always be seen in painful courses, and the diagnosis of chondrocalcinosis is often an X-ray Incidental finding when diagnosing other diseases. In healthy people, the cartilage is on the X-ray not to see.
X-rays are the top priority in diagnostics, especially on the knees, hips and other large joints, but also on the hands.
As an alternative, there is also an X-ray of the affected areas Ultrasound examination in which you can also see the calcification.
Laboratory / blood test
In addition to the X-ray, there is also one Blood test in the laboratory further information on the disease and its course. In the primary diagnosis the laboratory is negligible, but it plays for that Assess the extent and a not unimportant role for follow-up checks.
In the laboratory, chondrocalcinosis shows increased signs of inflammation (leukocytes, CRP value), which are correlated with inflammation in the joint. These should decrease with successful therapy.
Other values that are important for the diagnosis of secondary chondrocalcinosis can also be determined in the laboratory. So the laboratory should absolutelyNext-) Thyroid levels, iron, magnesium and phosphate because deviations in these parameters may indicate secondary chondrocalcinosis caused by an underlying disease. Here the therapy of these diseases is paramount.
therapy

Chondrocalcinosis only rarely requires therapy. The disease is then relatively advanced. The therapy is similar to that of rheumatism or osteoarthritis. Anti-inflammatory agents such as ASA or naproxen are used, which also have an analgesic effect. They can relieve symptoms, especially in the acute phase. Cold applications also relieve symptoms.
Alternatively, colchicine is given in the burst. Pain and inflammation are usually well controlled with these measures.
In the case of chronic progression, it is not cold but especially heat applications that help to maintain mobility and to be pain-free.
In a few cases, chondrocalcinosis requires invasive therapy. If a joint effusion is in the foreground, a joint puncture for relief must be considered. Here the doctor penetrates the joint with a needle under sterile conditions and drains the fluid.
The indication for a joint puncture should, however, be made strictly, as there is always the risk of spreading bacteria into the joint, which can lead to an infection.
The last resort in therapy is surgery if e.g. the menisci in the knee have already been destroyed too far. These are then removed.
In addition, naturally predisposing diseases such as metabolic diseases should be adequately treated in order to treat the chondrocalcinosis causally.
homeopathy
There is also in the homeopathy various remedies, often against rheumatic diseases can also be used against chondrocalcinosis. A well known remedy of homeopathy in this area is Solanum malacoxylon. It will relieve the pain in the joint as well as the inflammation set in.
At initially slight discomfort one can think about therapy with homeopathy, but one should also conventional medical clarification respectively. In addition, homeopathy can be given as an accompaniment to chondrocalcinosis to aid healing. However, an actual effect has not yet been proven.
forecast
Chondrocalcinosis usually proceeds symptom-free. If it comes to inflammation and pain, these can be treated well medicinal treat so that symptoms go away quickly. In the chronic form, the therapy is somewhat more complicated, in rare cases it comes to arthrosis in the joint.
This can in the worst case too permanent damage guide and restrict movement in the joint. Surgery to remove damaged tissue may be necessary. As a rule, however, chondrocalcinosis is not a condition that should be a cause for concern.
prophylaxis
There is no causal prophylaxis against chondrocalcinosis, but it can Reduce risk factors. So it always makes sense to identify diseases associated with chondrocalcinosis, e.g. of the thyroid and des Mineral metabolism to be treated consistently. This can at least minimize the likelihood of secondary chondrocalcinosis occurring.