Mastoiditis therapy
Operational procedures
The therapy of inflammation of the air-filled (pneumatized) Bone cells of the mastoid process (a bone that is located behind the ear), which can be imagined as a sponge or Swiss cheese, is always done surgically, i.e. with the help of an operation. The aim here is that the pus can be removed through drainage tubes.
As part of the surgical therapy, a so-called mastoidectomy is performed, a (partial) removal of the mastoid process (Mastoid process), as one can also use the ending "ectomy“Can be found. There are two different surgical procedures to choose from, both of which are associated with an estimated one-week inpatient admission to a hospital. Regardless of the surgical procedure, additional calculated antibiotic therapy is appropriate. An antibiotic is given in an untargeted manner and without knowledge of the causative agent of mastoiditis, but it is chosen in such a way that it has an effect against the most frequently expected bacteria. The combination of surgery and antibiotic therapy is the best method of treating mastoiditis.
Only in this way can mastoiditis be adequately treated and serious consequences can be avoided. An operation without complications as a therapy for mastoiditis is not a difficult procedure and leads to an improvement within a short time. A full recovery can be expected within a few weeks.
Mastoidectomy
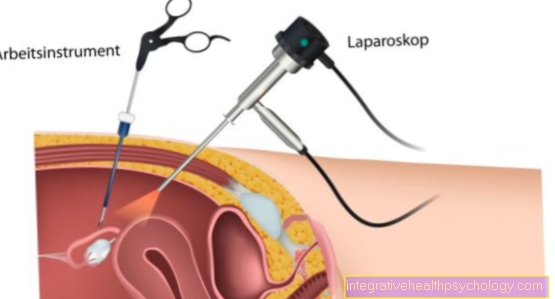
During a Mastoidectomy the air-filled bone cells of the mastoid process are in general anesthetic cleared out. There will also be an opening of the Mastoid antrum, a cavity inside the mastoid process. A so-called retroauricular access, i.e. an incision behind the ear, provides access to the structures. This will be sutured again after the operation is complete. With a mastoidectomy, the back wall of the ear canal is preserved.
Radical mastoidectomy (radical surgery)
Used instead of a Mastoidectomy If a radical mastoidectomy is performed as therapy, significantly more structures are eliminated. These include the back wall of the ear canal and the side wall of the Timpani dome (Epitympanone), i.e. the upper part of the tympanic cavity in the middle ear. In the course of the radical operation, a large cave (Radical cave) between the ear canal and the mastoid cavity, which simplifies maintenance and control. This type of operation is indicated for extensive bone augmentation.
Complications of the operative procedure
Like any surgical procedure, a mastoidectomy is dangerous and in rare cases can lead to complications. The Facial nerve (Facial nerve).
It is true that the operation is carried out with a microscope and the facial nerve is visited during the operation in order to prevent accidental injury.
Irrespective of this, however, damage cannot be completely ruled out. If the facial nerve is injured despite being spared, this can be a so-called peripheral facial palsy, i.e. a functional disorder of the facial nerve, with a one-sided result Facial paralysis condition. The symptoms that then show up include, for example, a one-sided loss of function of the mimic muscles (Facial muscles) and an inability to frown on the affected side. Also the Mouth closure may be impaired and a drooping corner of the mouth can be seen on one side. If an operation is chosen as therapy for mastoiditis, it can in extremely rare cases also lead to a subsequent impairment of hearing. In exceptional cases dizziness and deafness can be observed as complications.
Post-operative behavior
The inflammation usually heals within a few weeks. During this time, the ear must be protected from water as much as possible. Thanks to bathing caps or so-called Floating earmoldsthat can be purchased in a hearing aid store, do not have to do without bathing or swimming fun. Also conditions where pressure fluctuations are to be expected, such as Travel by planeshould be avoided at first.
Operations on the ear inevitably reduce the sensitivity of the Inner ear increases. Some substances that are not beneficial for the human inner ear even under normal conditions are particularly harmful after an operation. These substances include, for example nicotine. Hence that should Smoke be avoided after a mastoidectomy.
Alternative therapies for mastoiditis
Only at the beginning of a Mastoiditis If the symptoms are still mild, a high dose of antibiotic can be given into a vein (intravenous antibiotic therapy) and additionally a Eardrum incision (Paracentesis) be performed.